This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Dinh Thanh Ha - Obstetrician and Gynecologist - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Vinmec Nha Trang International HospitalThe vagina is a tube-shaped organ that extends from the vulva to the opening of the uterus. In terms of location, the vagina is located in the small labia majora, located below the urethral opening and above the anus. The vaginal opening is protected by the hymen and labia. The function of the vagina is very diverse, playing an important role in the reproductive and physiological activities of women.
If not properly cared for and protected, the vagina may experience the following diseases:
1. Vaginitis
Vaginitis is one of the most common gynecological diseases in women, although not life-threatening, it is a cause of infertility and many other troubles. There are many different causes with different vaginitis symptoms. If the symptoms are confused, it will lead to an irreversible condition or cause complications. There are certain conditions that are particularly favorable for vaginitis:Long-term antibiotic use Uncontrolled diabetes Immunodeficiency, immune disorders Vaginal douching or vaginal suppositories Prolonged use of hormonal drugs (birth control pills, thyroid disease, corticosteroids) Pregnancy Contraceptive device, contraceptive implant 1.1 Bacterial vaginosis Vaginal dysbacteriosis is a mild bacterial infection that causes caused by the overgrowth of anaerobic groups compared to beneficial bacteria, leading to an imbalance of the resident flora in the vagina. This is the most common cause of vaginitis.
Common symptoms are discharge that is white or gray and thin, has a foul smell like rotten fish and becomes heavier after sex. However, many women with the disease have no symptoms and are only discovered during routine gynecological examinations.
Bacterial vaginosis is completely curable, is not considered a sexually transmitted disease, and usually does not affect sexual partners. During pregnancy, bacterial vaginosis can cause infection of the amniotic cavity, miscarriage or premature birth, so it should be detected early during pregnancy for early treatment.
1.2 Vaginitis caused by Trichomonas vaginalis Disease caused by Trichomonas vaginalis parasites living in the genitals. Viral vaginitis is mainly transmitted through sexual intercourse. In addition, a pregnant mother with trichiasis can pass it on to her baby at birth through the natural route. The incidence of female disease is higher than that of male.
Common symptoms are green or yellow discharge, often with a bad smell, itching and pain in the vagina and vulva, pain and burning when urinating, possibly accompanied by a UTI. Some women also experience discomfort in the lower abdomen and pain in the vagina during intercourse – these symptoms may increase after the period.
However, many women have no symptoms at all. The disease can be transmitted through sexual contact. For treatment to be effective, both sexual partners need to be treated at the same time. In this case, oral medications are often more effective than topical medications.
1.3 Chlamydia vaginitis Chlamydia vaginitis is usually asymptomatic. Some of you will find yourself with symptoms such as unusual discharge, a strange smell, or inflammation of the urinary tract causing pain, pus, and frequent urination. If you see these symptoms, you should go to medical facilities for examination and treatment to avoid the risk of infection of the fallopian tubes, causing infertility and infertility. The disease is sexually transmitted, so it is important to treat your sexual partner at the same time.
1.4 Vaginitis Fungal Vaginitis is the second most common cause after bacteria, causing vaginitis. According to statistics, up to 75% of women have been infected at least once in their life and 45% of them are re-infected.
It is mainly caused by a fungus of the Candida family that may be present in the vagina. Under normal conditions, this fungus does not cause disease. But if the balanced environment of the vagina is disrupted, the fungus has favorable conditions to grow profusely, crowding out the beneficial bacteria and causing vaginitis.
Common symptoms of the disease are itching in the intimate area, thick, cloudy vaginal discharge, with a slight or no odor, slightly vulvovaginitis. Some people even feel pain after urinating or during and after sex.
2. Leukemia
White discharge, also known as vaginal discharge, is mostly mucus secreted by the glands of the cervix. Normal blood white is milky white, like egg white, with a slightly fishy or odorless odor. Physiological white blood has many beneficial effects such as keeping the vaginal environment with a certain moisture. White blood also helps prevent harmful agents that cause disease and facilitates easy sperm movement to the uterus during conception. There are many reasons why white blood has a pathological nature, at this time it is medically called vaginal discharge.Currently there are 3 common types of infections related to vaginal discharge:
Bacterial vaginosis Trichomoniasis Candida candidiasis. Where trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted disease or another physiological and pathological condition: cervicitis, aerobic vaginitis, atrophic vaginitis, and mucinous cervicitis.
2.1 Candida albicans infection Candida albicans infection is one of the most common gynecological diseases among women. Symptoms include: discharge is milky white, sticky patches like cheese or lumps, usually without a bad smell, accompanied by itching in the vulva. The disease is often caused by prolonged antibiotic use, pregnancy or immunosuppression.
2.2 Due to impurities The discharge will turn yellow or gray, dilute, with a fishy odor. The disease usually appears after sex or by douching deep inside the vagina, pushing the bacteria from the outside into... imbalance of vaginal flora, causing leukorrhea.
2.3 Due to Trichomonas infection Trichomonas is one of the common pathogens causing leukaemia. Common manifestations of Trichomonas infection include: vaginal discharge more than usual, yellow, green, often dilute and foamy, accompanied by vaginal itching.
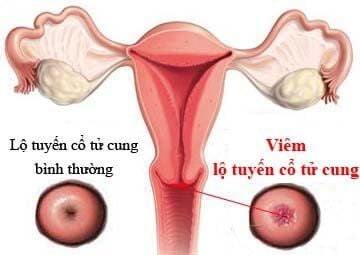
2.4 Due to diseases related to the uterus Some gynecological diseases are the cause of leukorrhea, such as cervical ectropion or uterine fibroids. When you have cervical ectropion, a lot of vaginal discharge will have a milky color, stick in patches and have a bad smell, an uncomfortable itchy feeling.
The more severe the inflammation, the more the discharge and the stronger the smell. In addition, bleeding during sex is also a characteristic sign of cervical ectropion. For uterine fibroids, besides typical symptoms such as menstrual disorders, abnormal vaginal bleeding, women will see more discharge and if there is an infection, the discharge will be mixed with blood. or pus.

Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.