This is an automatically translated article.
The article is expertly consulted by Master, Doctor Le Nhat Nguyen - Obstetrician-Gynecology Specialist - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.The uterus is an upside-down pear-shaped structure in the pelvis located behind the bladder and in front of the rectum. Together, the uterus, vagina, ovaries, and fallopian tubes make up a woman's reproductive system.
1. Uterine prolapse
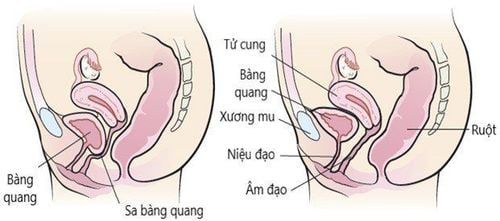
Uterine prolapse occurs when the muscles and ligaments that hold the uterus in place become weak, causing the uterus to descend near the bladder. Many women experience mild to moderate prolapse as they age. The most common symptoms are urinary retention and leakage, but severe cases can also cause pain, especially during or after sex.Uterine prolapse can be seen in any woman, but this disease is common in the following subjects:
Postpartum women, especially those who give birth vaginally, large fetuses or too much labor. After giving birth without abstinence, women have to exercise a lot, causing the bottom of the abdomen to contract too much, causing damage and leading to uterine prolapse. Pre-menopausal women, older women. In general, uterine prolapse progresses slowly. Over time, if not treated, the prolapse becomes more and more frequent, the degree of prolapse is fast or slow depending on age and how heavy or light the work is. Uterine prolapse does not affect the patient's life, but there may be some accompanying complications such as:
Vaginal ulcers: Occurs when the patient has the disease at its highest level. At this time, the prolapsed uterus pulls a part of the vaginal lining that protrudes outside the vagina and causes friction with the pants. This can cause vaginal sores and lead to an infection. Prolapse of other pelvic organs: When the disease becomes severe, the person may experience prolapse of other pelvic organs, including the rectum and bladder. Prolapse of the pelvic organs can cause difficulty in excreting and, worse, increase the risk of urinary tract infections. Surgery is the mainstay of treatment for uterine prolapse. Medical treatment only applies to uterine prolapse grade I or prolapse II, III but the patient is too old, too young, or has systemic disease contraindicated for surgery.

2. Cervical ectropion
This is a benign disease but also the source of some dangerous gynecological diseases, affecting fertility. The disease is quite common in women of childbearing age, strong ovarian period or congenital.Cervical ectropion is usually caused mainly by inflammation or trauma such as cervical tear, repeated curettage, which destroys the inner layers of the cervix, causing the gland to become exposed. When you have uterine ectropion, you will see the most obvious symptoms such as vaginal discharge, pain in the vulva and increased when walking.
3. Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a condition in which tissues that normally develop in the uterus also grow outside the uterus. The tissue inside the uterus is called "endometrium", and the tissue outside the uterus is called "endometriosis". Endometriosis most commonly occurs in the ovaries, fallopian tubes, intestines, or anterior, posterior, and lateral areas of the uterus.There are cases of endometriosis with almost no symptoms, but there are also cases of pain, cysts or difficulty getting pregnant. The main symptom of endometriosis is pelvic pain, often related to the menstrual cycle. Although many people experience menstrual cramps, those with endometriosis often describe menstrual pain that is worse than usual. Pain may also increase over time.
The main complication of endometriosis is impaired fertility. About one-third to one-half of women with endometriosis have trouble getting pregnant. Despite this, many people with mild to moderate endometriosis are still able to conceive and become pregnant. Doctors may advise people with endometriosis not to delay having children because the condition may worsen over time.

4. Cervical polyp disease
Cervical polyps are benign tumors that develop from the cervical stroma and are covered by epithelium, arising from the cervical canal, with or without legs, the size can vary from a few millimeters to a few millimeters. few centimeters, common in women who have given birth many times. Patients with cervical polyps often have no symptoms, but they can also have a lot of vaginal discharge, bleeding, and bleeding after intercourse. Uterine polyps are usually benign, but about 1% of cases have a malignant transformation. The cause of cervical polyps is unknown, but an excessive increase in estrogen is considered a leading risk factor for cervical polyps.Cervical polyps cause many negative effects on female reproductive health: If the polyp is small, it will prevent sperm from reaching the egg, and if the polyp grows larger, it can cause cervical obstruction, sealing the cervix. endanger the patient's health. With cervical polyps, a woman's ability to conceive will be significantly reduced. To a certain extent, when a woman has uterine polyps, the quality of her sex life is affected: the symptoms of cervical polyps such as excessive discharge, vaginal bleeding, etc. cause anxiety during intercourse, which will also reduce arousal.
Depending on the condition of each patient, the specialist will appoint a specific treatment method: Medical treatment or surgical treatment (polypectomy, electric polyp burning).
5. Uterine fibroids
Uterine fibroids are a common gynecological disease of all ages, especially women in the period of childbearing, pregnancy or menopause. Uterine fibroids are benign tumors of uterine smooth muscle cells. Depending on the location of the fibroids, they can be divided into: subserosal, intrauterine, submucosal, cervical or broad ligament.Uterine fibroids are not associated with an increased risk of uterine cancer and almost never develop into cancer.
Many women have uterine fibroids sometimes during their lifetime. But most women don't know they have fibroids because the disease often causes no symptoms. Your doctor may discover fibroids during a pelvic exam or prenatal ultrasound. In symptomatic women, the most common signs and symptoms of uterine fibroids include: Heavy menstrual bleeding, menstrual cycles lasting more than a week, pelvic pain, frequent urination, constipation, back pain, leg pain,..

Treatment of uterine fibroids can be by means of monitoring, medical treatment or surgery. Treatment goals are to relieve symptoms (abnormal uterine bleeding, pain, symptoms due to compression, ...), reduce the size of fibroids. The choice of intervention method depends on many factors such as: size, tumor location, accompanying symptoms, patient's wishes (cost, desire to preserve the uterus,...).
6. Cervical cancer
Cervical cancer is a malignant tumor in the tissues of the cervix. The two main types of cervical cancer are: squamous cell cancer, which is the most common, and adenocarcinoma. The causes of cervical cancer are still unknown. However, certain factors increase a woman's risk, such as infection with HPV (the name for a group of viruses that cause warts) and smoking, which produces chemicals that damage cells. of the cervix and makes it easier for cancer to develop.If early cell changes develop into cervical cancer, the most common signs include vaginal bleeding between periods; bleeding after sex; pain during sex; abnormal vaginal discharge; vaginal bleeding after menopause; excessive fatigue; leg pain or swelling; lower back pain.
All of these symptoms are present in many conditions and may not mean you have cervical cancer, but, if you have these symptoms, you should see your doctor. Most of the most unusual changes in cervical cells are detected by the Pap test. A woman should have a smear test every two years.
Surgery is common for small tumors found only in the cervix. The extent of the cancer in the cervix determines the type of surgery needed. This could be a colectomy to preserve fertility, a cone biopsy, or a hysterectomy.

Currently, at the Vinmec International General Hospital system, the basic gynecological examination and screening package is being applied.
With a team of medical - doctors who are leading experts, highly qualified, dedicated and wholeheartedly for the benefit of patients Comprehensive and professional medical examination, consultation and treatment service Equipment system Modern equipment, effective diagnosis and treatment, modern, civilized, luxurious and sterile medical space Fully guaranteeing the safety and privacy of customers. Modern, efficient and effective model for managing, sharing and connecting information online. Doctor Le Nhat Nguyen has more than 20 years of experience in the field of Obstetrics and Gynecology. Formerly a doctor of obstetrics and gynecology at Gia Dinh People's Hospital in Ho Chi Minh City. BS has high expertise and strength in the diagnosis and treatment of Obstetrics and Gynecology diseases. Currently a Doctor of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec International Hospital Da Nang.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.