This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with resident Doctor Le Thanh Tuan - Gastroenterologist - General Surgery Department - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.Surgical closure of the tracheoesophageal fistula is an indicated solution to treat cases of congenital or recurrent tracheoesophageal fistula and esophageal stricture. This is a very dangerous condition that can cause sudden death. Therefore, early detection and closure of esophageal fistula is very important and should be taken with caution.
1. Overview of congenital and recurrent esophageal fistula
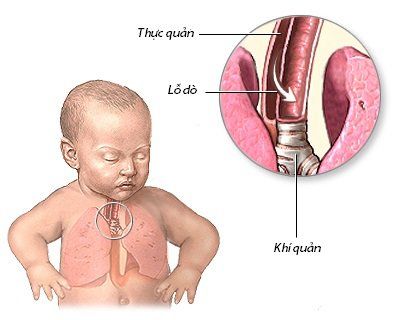
Esophageal fistula is an abnormal esophageal fistula, so it is also called a congenital tracheoesophageal fistula. This condition makes it difficult to carry out daily activities. Because it will cause food from the esophagus to leak into the trachea and lead to many dangerous complications such as pneumonia, aspiration of food into the respiratory tract and even death.If the disease is not treated, food or digestive juices will pass through the esophageal fistula into the respiratory tract and cause a recurring inflammatory reaction. This leads to prolonged lower respiratory tract inflammation, so this is also known as recurrent tracheoesophageal fistula.
There are many causes of congenital tracheoesophageal fistula such as:
Abnormalities from birth: Right from the time in the womb, the child has had congenital malformations of tracheoesophageal fistula or esophageal stricture . This rate accounts for 1/2,500 - 4,500 live births Due to intubation, tracheostomy Due to trauma. Common signs and symptoms seen in children with esophageal fistula include coughing, choking or choking when eating; the appearance of foam or bubbles in the child's mouth; With the dangerous complications that can occur, even leading to death, the intervention in the esophagus by surgery to close the esophageal fistula is very necessary. However, care must be taken when performing this technique.
2. Closure of congenital tracheoesophageal fistula by endoscopic respirator TRICHLOROACETIC ACID 50%
After using endoscopic diagnostic methods to detect recurrent or congenital tracheoesophageal fistula, doctors will carefully review the patient's condition to surgically close the esophageal fistula. Care should be taken when performing it to avoid complications. Usually, recurrent tracheoesophageal fistula will account for 5 - 14% after the first surgery to close the esophageal fistula and 10-20% after the second surgery.The repair of recurrent esophageal fistula closure by Thoracic surgery can cause complications. Therefore, this is also a challenge for the surgeon. Closed esophageal fistula through respiratory endoscopy with rigid bronchoscope has been successfully applied in many developed countries and in a few hospitals in Vietnam. It can be used as an alternative to thoracotomy in patients with recurrent tracheoesophageal fistula and congenital tracheoesophageal fistula but without esophageal stricture.
Although the method is widely used and applied, in surgery to close the tracheoesophageal fistula, there are still questions to be asked:
Respiratory endoscopy with a rigid bronchoscope to surgically close the air fistula Is esophagitis a safe method for the patient and a guarantee of success for the surgery? Currently, there are many methods to repair tracheoesophageal fistula. So which method is the best choice? Many clinical studies have shown that endoscopic resection of recurrent tracheoesophageal fistula is less invasive and has a lower mortality rate than thoracotomy. In 2014, a comparison result of surgery for congenital, acquired tracheoesophageal fistula of 57 patients through gastrointestinal endoscopy and respiratory endoscopy with 108 patients through thoracotomy concluded: Treatment of recurrent tracheoesophageal fistula through thoracotomy is a technique with a much lower rate of complications, mortality and recurrence.
Endoscopic repair of tracheoesophageal fistula is an alternative technique to treat recurrent tracheoesophageal fistula in large experienced hospitals and selected patients. Further clinical trials are needed to help ensure the success of laparoscopic surgery.
Previously, in 2008 according to reports of recurrent esophageal fistula closure surgery was successful endoscopically with ACID TRICHLOROACETIC (TCA) 50% in 3 patients with 3 endoscopic visits. , TCA esophageal fistula closure can be safe and effective for patients with recurrent tracheoesophageal fistula.

Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.