This is an automatically translated article.
Thyroid nodule is a disease that can be detected early based on clinical symptoms and laboratory tests. In particular, people with a family history of thyroid disease need to pay attention to changes in the neck area and have regular health checkups.
1. Thyroid goiter is a disease like?
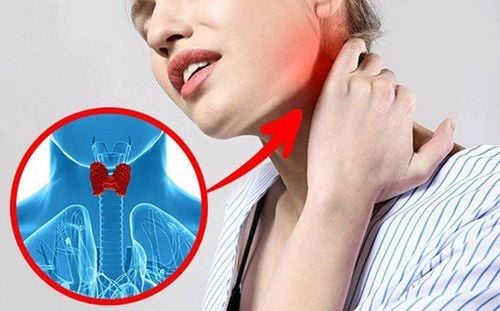
The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped organ, located in the neck region, responsible for the production of hormones including Thyroxine (T4), Tri-iodo-thyronine (T3), which play a role in regulating vital activities. in the body. A thyroid nodule is a thyroid disease that results from abnormal cells that cause changes in the structure and endocrine function of the thyroid gland. The disease can be benign or malignant, but most are benign (non-cancerous). Accordingly, if the disease is detected as early as possible, the higher the possibility of treatment, therefore, the patient should be examined early when the symptoms related to thyroid goiter are suspected.2. Clinical symptoms of thyroid nodules
Most patients with thyroid nodules have no specific symptoms, only discovered when they happen to have a medical examination or perform thyroid ultrasound. However, if you notice the following symptoms, you should see a doctor and get advice from a doctor:
Feeling of neck enlargement or palpation of a lump in the neck area Neck pain, difficulty swallowing, difficulty breathing , hoarseness Manifestations of thyroid dysfunction : Hand tremors, palpitations, insomnia, anxiety, thinness, weight loss Family history of thyroid-related diseases People who have been irradiated in the neck region
Nên đi siêu âm tuyến giáp khi thấy những triệu chứng bất thường ở vùng cổ
3. Subclinical tests for thyroid nodules
3.1 Thyroid ultrasound Thyroid ultrasound is a commonly used test in the diagnosis and treatment of thyroid nodules. The test helps to observe the features of the thyroid gland that cannot be recognized by physical examination by evaluating the characteristics of the size, number, location, and nature of the thyroid nodules.
Thyroid ultrasound is also used to support a number of procedures such as fine needle aspiration thyroid cytology, aspiration therapy, alcohol injection, laser treatment, and treatment effectiveness monitoring.
Ultrasonography has high value in determining the characteristics of thyroid nodules but is not really reliable in the differential diagnosis of benign or malignant lesions.
3.2 Blood Biochemistry The biochemical test used is to measure the levels of thyroid hormones (FT3, FT4 and TSH). The test is of an initial nature, helping the doctor to classify the disease and orient the correct cause of the disease. In thyroid nodules, thyroid hormone levels are usually normal. If levels of these hormones go up or down, your risk of developing hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism is higher.
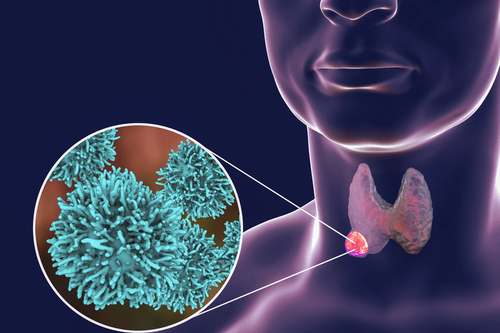
3.3 Fine Needle Thyroid Aspiration Thyroid aspiration cytology is highly valuable in the differential diagnosis of benign or malignant thyroid nodules, with a confidence level of up to 95%. The test is indicated when there is a thyroid nodule ≥ 5mm and the results of cytology of the thyroid nodule.
The success rate of thyroid cytology is higher with the combination of ultrasound. Under the ultrasound image, the thyroid gland is clearly shown to help the doctor determine the exact location of the thyroid nodule for aspiration, thereby increasing the reliability of the test results.
The results of aspiration cytology are read as follows:
Malignancy: The cancer rate ranges from 4-5%, mainly in 4 types (papillary cancer, follicular cancer, medullary cancer and medullary cancer) undifferentiated cancer). Benign: 69-74%, mainly in colloid goiter, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, subacute thyroiditis, thyroid cyst. Suspicion: Cystic hyperplasia, Hurthle cell hyperplasia and some results suggest cancer but not yet confirmed. Unspecified: An unspecified condition caused by aspiration at the wrong site, resulting in only foam cells or cystic fluid, or too few cells or too many red blood cells.

Chọc hút tế bào giúp chẩn đoán chính xác bệnh bướu nhân tuyến giáp
3.4 Thyroid scintigraphy Thyroid scintigraphy helps to identify mononodular or multinodular goiter but does not determine the size of the nodule. In addition, the test is also valuable in diagnosing retrosternal tumors.
Test results are read as follows:
Hot nucleus: Increased radioactivity, seen in 10% of solid nodules Cold nucleus: Decreased radioactivity, high risk of malignancy (5 - 15%) due to Cancer cells capture iodine worse than normal cells Warm nucleus: Equivalent to surrounding tissue 3.5 CT scan and magnetic resonance (MRI) CT and MRI are not valuable to differentiate benign thyroid nodules or malignant, but is valuable in accurately assessing the extent of spread as well as the degree of tracheal compression of the retrosternal nodule.
Thyroid goiter is a disease that, if detected at an early stage, is much more treatable than other diseases. Therefore, when you see symptoms of the disease, you should go to the medical center to examine and diagnose thyroid-related diseases.
The screening and screening package for thyroid diseases of Vinmec International General Hospital helps: Check thyroid function, and Screen & detect common thyroid diseases early such as: goiter simply, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, thyroiditis, thyroid nodules, thyroid cancer, ... so that appropriate and timely treatment measures can be taken.
For advice and registration to book an appointment, customers can contact Vinmec hospitals and clinics nationwide HERE.