This is an automatically translated article.
Article written by Doctor Han Thu Huong - Vinmec Hi-Tech Center
The results of the chromosomal test will be consulted by genetic experts and depending on the type of mutation, the person with the chromosomal mutation and their family will be consulted and have a specific prognosis about possible causes and possibilities. for them as well as for future generations.
1. Concept of chromosomal formula
The karyotype formula is used to describe the set of chromosomes (chromosomes) in a vegetative cell of a eukaryotic species. Chromosomes are depicted (by microscopic arrangement) in a standard format known as a karyogram or idiogram: in pairs, arranged according to size and position of the centromere with respect to chromosomes of the same size.
Normal human chromosome set includes 22 pairs of autosomes and 1 pair of sex chromosomes with karyotype written as: 46,XX in female or 46,XY in male. The 46 human chromosomes are grouped into seven groups, designated A, B, C, D, E, F and G, according to the position of the center.
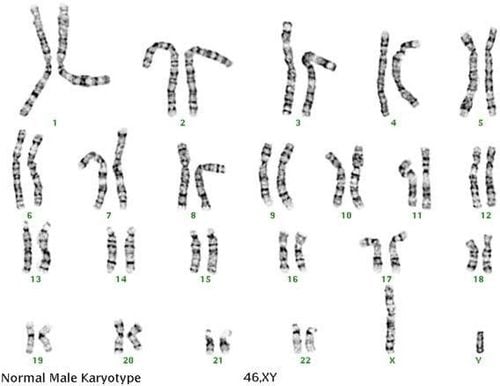
Karyotype bình thường ở nam giới (Genetic Testing Techniques, 2018)
Group A has 3 pairs of chromosomes with the largest size. Pair number 1: center center, pair number 2: eccentric center, pair number 3: center center. Group B has 2 pairs of chromosomes 4 and 5. The chromosomes in this group are large and indistinguishable in length. They are all eccentric. Group C has 7 pairs of chromosomes, including from 6 to 12 are the chromosomes of average length. The X chromosome is also included in this group. All C chromosomes are eccentrically located, making it difficult to distinguish between them. Group D has 3 pairs of chromosomes 13, 14 and 15. All chromosomes in this group are of medium size and are all central chromosomes, with satellites attached to the short arm. Difficult to distinguish between them. Group E has 3 pairs of chromosomes 16, 17 and 18, these chromosomes are relatively short. Chromosome 16 has a central center, while pairs 17 and 18 have an eccentricity. Group F has 2 pairs of chromosomes 19 and 20. Both of these chromosomes are short in size and have a central center. Group G has 2 pairs of chromosomes number 21 and number 22. The chromosomes are short in size, have head centers and satellites. The Y chromosome is also included in this group. The two chromatids of the Y chromosome are more parallel than those of the G group. The Y chromosome has no satellites.
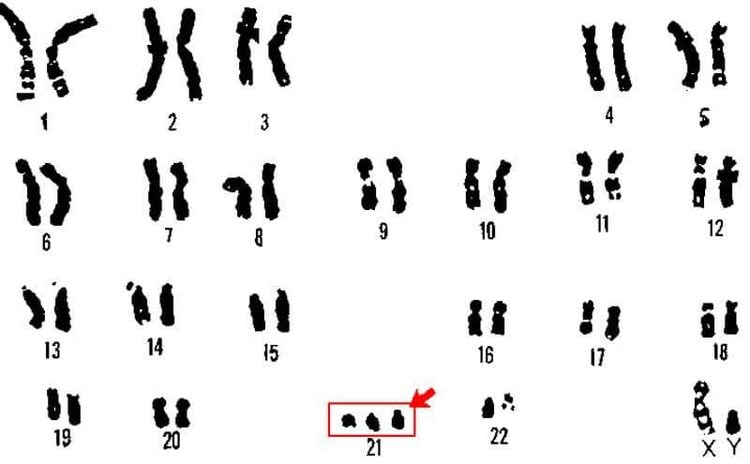
NST số 21
2. Chromosome formula test
The chromosomal formula test is a technique that allows the human chromosome set to be examined. The commonly used technique for karyotyping is the G-band staining technique, which is now used in most cytogenetics laboratories. This technique allows only large structural anomalies to be detected. Cases of chromosomal abnormalities with small size, tissue mosaicism, low mosaic ratio will not be detected.
Any change in chromosome number or structure can be a sign of genetic disease. The chromosomal formula test is used to detect genetic disorders in prenatal and postnatal diagnosis.
In prenatal diagnosis, pregnant women are prescribed amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling for fetal chromosomal testing in some cases: Pregnant women have a history of spontaneous abortion, consecutive stillbirths women with a history of birth defects. Pregnant couples have been identified in which one of them has a heritable chromosomal mutation. Older pregnant women, pregnant women with abnormal fetal ultrasound results. Pregnant women with serological screening results (Double test, Triple test) have a high risk of having a baby with birth defects.

Những thai phụ lớn tuổi cần làm xét nghiệm công thức nhiễm sắc thể
In the postpartum diagnosis: chromosomal testing from peripheral blood or bone marrow is indicated in some cases: Newborn with birth defects. Children with psychomotor retardation of unknown cause. Ambiguous about gender, genitals are not clear whether male or female. Family history of chromosomal mutation. Couples with primary or secondary infertility. Female primary amenorrhea or secondary amenorrhea. Couples have miscarriages or miscarriages in a row. Patients with acute myeloid leukemia or lymphoma, neuroblastoma...
3. Implementation process
3.1. Sampling Peripheral Blood: 2ml of sterile peripheral blood in a heparin anticoagulant tube. Bone marrow: 2 ml of sterile marrow blood (biopsy) in a heparin anticoagulation tube. Amniotic fluid: 15-20 ml of sterile amniotic fluid (amniocentesis). Spinach: 15-20 mg of vegetable spike (biopsy). Immediately transfer the sample to the laboratory for culture. In case it cannot be transferred immediately, it should be stored at 4-8oC for 24 hours.
Lấy máu ngoại vi xét nghiệm
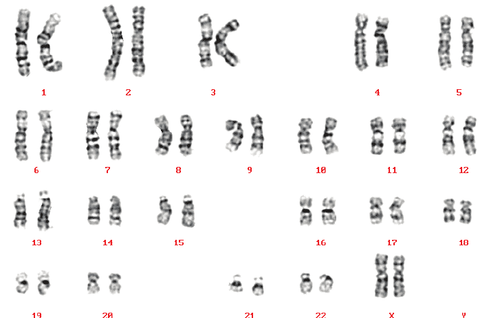
Karyotype bình thường ở nữ giới (Reproduced courtesy of Human Genome Centre, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Malaysia)
Abnormal numbers and structure of chromosomes Quantitative disorder: more or less 46 chromosomes. Some common diseases are Down syndrome (Trisomy 21), Edwards syndrome (Trisomy 18), Turner syndrome (45,X)...
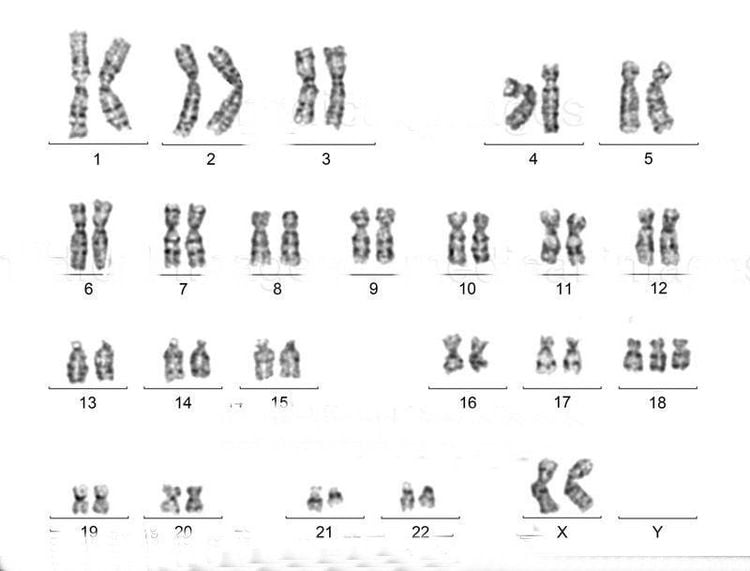
Karyotype bất thường của nữ giới mắc hội chứng Edwards (Trisomy 18) (https://www.medicalimages.com/)
Structural disorders: chromosomal structural changes such as deletions, duplications, inversions, translocations.
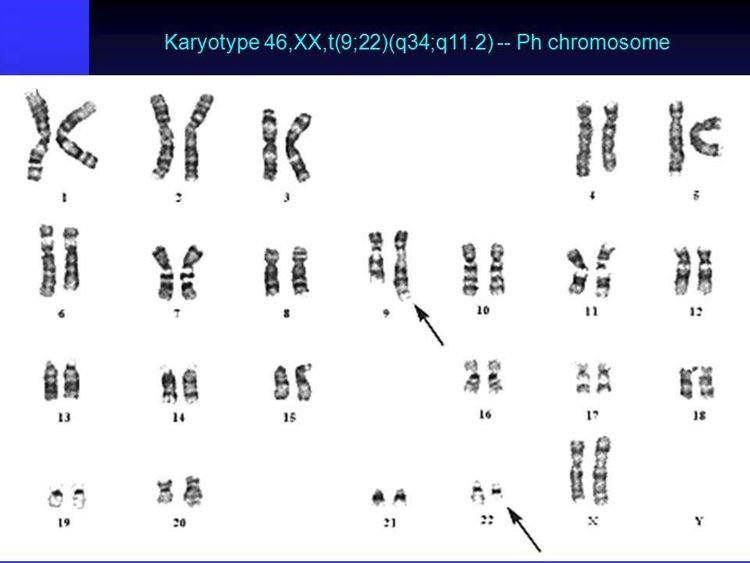
Karyotype bất thường ở nữ giới có chuyển đoạn (9;22) (Leukemia AML ALL FAB classification WHO classification- https://slideplayer.com/)
Structural disorders: chromosomal structural changes such as deletions, duplications, inversions, translocations.
The results of the chromosomal test will be consulted by genetic experts and depending on the type of mutation, the person with the chromosomal mutation and their family will be consulted and have a specific prognosis about possible causes and possibilities. for them as well as future generations.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.
References
J. McGowan-Jordan, A. Simons, M. Schmid. ISCN 2016: An International System for Human Cytogenomic Nomenclature . Marilyn S. Arsham, Margaret J. Barch, Helen J. Lawce. The AGT Cytogenetics Laboratory Manual . Fourth Edition, 2017. Suresh Kandagal Veerabhadrappa, Pramod Redder Chandrappa, Seema Yadav Roodmal, Sharan J Shetty, Gunjiganur S Madhu Shankari, Kumbar P Mohan Kumar. Karyotyping: Current perspectives in diagnosis of chromosomal disorders. Sifa Medical Journal, 2016. MORE:
Diseases caused by chromosome abnormalities