This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Phan Ngoc Hai - Pediatrician - Neonatologist - Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec International General Hospital Da Nang and resident doctor Duong Van Sy - Department of Pediatrics - Newborns - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.Abdominal pain is a common condition in children and is one of the leading reasons children are brought to medical facilities (hospitals, clinics or doctors' offices). Sometimes, it's a sign of a serious medical condition that, if not diagnosed correctly and treated early, can be life-threatening. Children with fever, abdominal pain, nausea can also be among the symptoms of appendicitis.
1. Expression of abdominal pain when the child has a fever
In fact, young children often experience minor abdominal pain and fever. Signs of abdominal pain in children with fever can originate from many different causes, can be acute abdominal pain but can also be long-term abdominal pain.Acute abdominal pain in children accompanied by fever makes the child writhe, cry, pale face, sweat a lot, lose temper. Therefore, family members during the doctor's examination of the baby need to be calm to provide complete and accurate medical information so that the doctor can examine the baby in the most convenient way. In children with fever, abdominal pain and vomiting, one of the most common causes is appendicitis.
With children over 2 years old, appendicitis will have the same signs as in adults, such as: Pain in the right iliac fossa, only mild pain at first, then the pain increases, pain associated persistent, often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, low-grade fever (about 37 - 38 degrees Celsius). When examining, children often complain of pain and push the doctor's hand not to touch the right iliac fossa or abdomen.
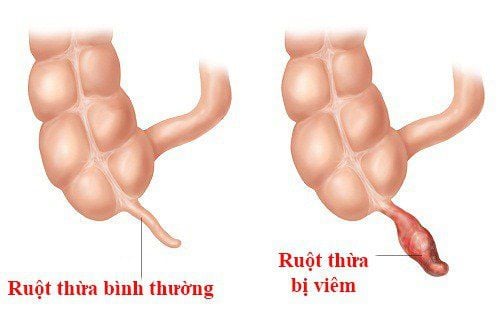
For children under 2 years old, the diagnosis of appendicitis is often more difficult, so detection of the disease will also be slower, because the symptoms at this time are not typical of older children or adults. Therefore, the disease is easy to cause dangerous complications such as appendicitis perforation, peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum), leading to very serious consequences. Common symptoms in children under 2 years of age with appendicitis are: The child has a fever, complains of abdominal pain, vomits, is fussy, looks lethargic, pale. In addition, the child may have gas, bloating, when the doctor examines the abdomen, the child cries. Abdominal pain due to appendicitis in children may initially be pain in the epigastrium, around the navel, then spread and localize in the right iliac fossa.
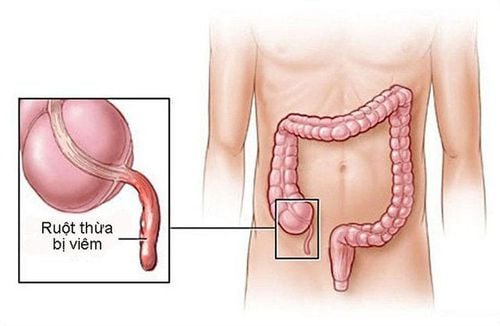
Ruột thừa bị viêm gây ra đau bụng, sốt, nôn ói
2. Children with appendicitis are easily misdiagnosed
Parents often think that it is due to digestive disorders when children have fever and abdominal pain, so they should self-medicate at home, sometimes parents think that abdominal pain is due to menstruation until puberty, but they do not think it is due to inflammatory disease. in the appendix. In fact, cases of such misdiagnosed children with appendicitis are not uncommon.The appendix is a small organ about the size of a thumb, located in the lower right of the abdomen, with one end sealed, the other end connected to the cecum (the first part of the large intestine). If for some reason the lumen of the appendix is obstructed (possibly due to fecal stones, hyperplasia of the lymphoid tissue in the wall of the appendix, foreign bodies appear) it will lead to inflammation, swelling, and swelling of the appendix. infection. If appendicitis is left untreated, the appendix can become necrotic, rupture, cause complications such as peritonitis, sepsis, and eventually death.
However, children with appendicitis are often difficult to diagnose because children are hardly able to clearly express their pain and are not easily distinguishable from other diseases that also have symptoms of fever and pain. stomachache. The point of abdominal pain is difficult to determine because young children most often see the doctor because they are afraid, cry, cause many difficulties in the process of locating the pain, even, when examining the abdomen, every place will complain of pain. On the other hand, imaging tests such as ultrasonography do not always detect appendicitis lesions. Therefore, the diagnosis of appendicitis must be based largely on the symptoms of the disease detected by the family members and the results of many visits by the doctor.
Appendicitis in children often progresses very quickly, sometimes in only 6-8 hours, it will be necrotic. Therefore, early detection and diagnosis of appendicitis in order to perform surgery to remove the inflamed appendix is essential to avoid unfortunate things.
3. Complications due to appendicitis
Children with fever and vomiting, complaining of abdominal pain are common signs of appendicitis that parents can recognize. However, if you subjectively do not take your baby to the doctor, especially with acute cases, it is likely to lead to complications such as:Appendiceal rupture: The risk of causing an abscess around the appendix or worse, inflammation diffuse peritoneum. Intestinal obstruction: This complication is less common, occurs when inflammation around the appendix causes the muscular system in the intestinal wall to stop working, preventing the organs inside the intestine from being pushed out. Sepsis: A condition in which bacteria that cause an infection in the appendix move into the bloodstream and throughout the body. This is considered a dangerous, potentially life-threatening complication.
Trẻ bị viêm ruột thừa không được đưa đi khám kịp thời có thể đe dọa tính mạng.
4. Children with fever and vomiting should do?
Parents, grandparents, teachers around when they see the child has a fever and vomiting, complains of abdominal pain or has signs of digestive disorders such as: Full stomach, bloating, unusual loss of appetite or refusal to eat, or screams or bloody stools, difficult urination, frequent urination, painful urination, etc. At that time, it is necessary to quickly take the child to the nearest medical facility. Parents should not hesitate, should not be subjective or underestimate, look down and think that the child is pretending because these signs are likely to signal dangerous diseases.When you have not been examined and diagnosed and have not received the opinion of a treating doctor, you should not take any medicine, whether Western or Western medicine. Because if the child has been given medicine before going to the doctor, it will inadvertently make the child's abdominal pain symptoms be obscured, especially for cases of abdominal pain requiring urgent surgical emergency such as: Intussusception, acute appendicitis,...
To prevent the above symptoms, parents should supplement their children with essential micro-minerals such as zinc, Lysine, chromium, selenium, vitamin B1, ... help meet the nutritional needs of children. The addition of these essential vitamins also supports digestion, enhances nutrient absorption, improves anorexia, and helps children eat well. Parents can simultaneously apply dietary supplements and functional foods derived from nature for easy absorption. The most important thing is that improving your baby's symptoms often takes a long time. The combination of many types of functional foods at the same time or continuously changing many types in a short time can cause the baby's digestive system not to adapt and completely not good. Therefore, parents must be really patient with their children and regularly visit the website vimec.com to update useful baby care information.