Foreskin itching is one of the characteristic symptoms of posthitis (an inflammation of the foreskin). When experiencing this condition, the child may experience pain during urination, itching, burning sensations, and discomfort. Therefore, parents should closely monitor the child's health status and seek medical evaluation and treatment promptly to prevent serious health complications.
1. What Is Foreskin Itching?
The foreskin is located at the tip of the male penis, protecting the penis from harmful bacteria and dirt, helping to maintain moisture. Normally, when the foreskin is pulled down, it will expose the glans penis (the tip or top portion of the penis) and the urethra (the tube that transports urine from your bladder to outside your body). This is a rather sensitive skin area, so it is easily damaged and infected. One common condition in children is posthitis, which is inflammation of the foreskin.
An itchy foreskin is a typical symptom of posthitis. Posthitis in children can be congenital or due to other causes. Initially, posthitis presents in an acute phase. If not treated or not completely cured, it may progress to a chronic stage.
In addition to itching, children with posthitis also have other symptoms such as:
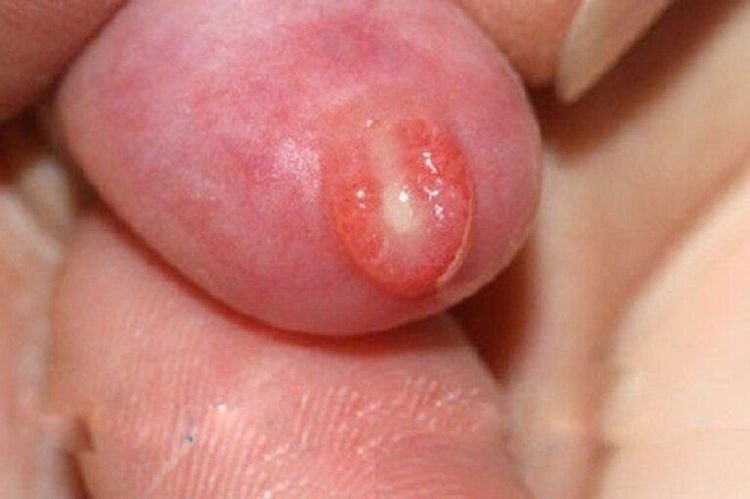
- Redness of the foreskin, blisters, or small spots on the tip of the penis. Over time, these lesions may rupture, leading to ulceration and discharge with foul-smelling fluid.
- Pain, burning, and discomfort at the tip of the penis, especially when rubbing against clothing;
- Abnormal signs of urinary tract issues, such as frequent urination or painful urination;
- Fatigue, weakness, and fever.

2. Causes of Foreskin Inflammation and Itching in Children
There are many causes of foreskin inflammation in children, leading to uncomfortable itching symptoms. These include:
- Congenital Narrowing or Long Foreskin: At birth, a child's penis and foreskin are tightly attached to protect the sensitive glans from harmful agents. However, this is also the reason why the foreskin is prone to inflammation due to the accumulation of dirt and debris. As a result, bacteria can multiply and cause infection.
- Poor Hygiene of the Genital Area: If parents do not pay attention to cleaning their child's genital area regularly, urine residue and smegma will accumulate over time, providing an ideal environment for bacteria to thrive, leading to inflammation. Since the child is young, hygiene care fully depends on the parents. Parents need to ensure they wash and clean the child’s genital area carefully.
- Incorrectly Retracting the Foreskin: For children whose foreskin is not narrow, parents may attempt to retract it at home. However, if not done correctly, it can lead to foreskin inflammation and itching. When parents pull back the foreskin to separate it from the glans, excessive force may cause damage, cracking, or tearing of the skin. Once injured, the child is more susceptible to infections. Additionally, daily activities such as wearing diapers can also cause moisture buildup, leading to foreskin inflammation.
- Urethritis (an inflammation of the urethra, the tube that transports urine from your bladder to outside your body): This is one of the causes of foreskin inflammation in young children. Poor habits like holding urine or drinking insufficient water can make a child prone to urethritis. When the urethra is inflamed, the child's foreskin is also at risk of infection (because the foreskin and urinary opening are located next to each other).
- Wearing tight, damp clothes or sharing items: These habits can also be causes of foreskin inflammation in children.
3. The Risk Associated with Foreskin Inflammation in Children
- If detected late, foreskin inflammation can have many negative effects on a child's health. In some cases, the child may experience genital necrosis (tissue death) or later suffer from premature ejaculation, cancer, infertility, and more. Below are the harmful effects that foreskin inflammation can cause in children:
- Infection: Foreskin inflammation can lead to infections of the child's penis, urethra, urinary tract, bladder, kidneys, and may even lead to kidney failure.
- Premature Ejaculation: If the foreskin inflammation persists for a long time, it can cause the glans to dry out, which may eventually result in premature ejaculation in adulthood.
- Impotence: Foreskin inflammation can damage the child's penis, and over time, it may lead to erectile dysfunction. When the child experiences an erection, the pressure can reduce the duration of the erection, and over time this could lead to impotence.
- Long-term untreated foreskin inflammation in children may cause inflammation of the testicles, epididymis (the coiled tube at the back of the testicle that stores and carries sperm), and vas deferens (sperm duct), which can reduce both the quality and quantity of sperm, posing a risk of infertility.
4. How to Treat Foreskin Itching Due to Posthitis?
If parents notice signs of foreskin inflammation in children, such as itching, discomfort, pain during urination, etc., they should take their children to a medical facility for examination and appropriate treatment.
- Topical Medication: This is a treatment for inflammation of the foreskin recommended by many doctors. The doctor will determine the cause of the inflammation and prescribe the appropriate topical medication (antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs). Additionally, the doctor may prescribe oral medication or rinses if necessary.
- Foreskin Dilation: For young children with inflammation caused by a narrow foreskin, the doctor may recommend foreskin dilation. Parents can perform the dilation at home, or, if unsure, they should take the child to the hospital for guidance.
- Circumcision: This is a procedure that removes the foreskin from the human penis. Parents can take their child to a medical facility for circumcision (in cases of congenital issues like phimosis or long foreskin) to treat the inflammation, reduce itching, and prevent the condition from recurring. Circumcision is a minor surgery, typically simple to perform, so parents do not need to worry too much.
- Proper Foreskin Hygiene: Parents should teach their children to regularly clean their genital area thoroughly, ensuring both the inside and outside of the foreskin are washed. When cleaning, the foreskin should be retracted to wash thoroughly. Children should also avoid contact with polluted environments or water sources (ponds, lakes, rivers, streams, etc.) to prevent genital infections.
When parents notice signs of foreskin inflammation in their child, such as itching, pain, or discomfort while urinating, they should promptly take the child to a reputable medical facility for a doctor's examination to determine the cause, severity, and condition of the disease, and to receive appropriate treatment.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.