This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II Huynh Thi Hien - Obstetrician and Gynecologist - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.Women will have their period once a month with vaginal bleeding for 3-7 days. This phenomenon is caused by the shedding of the uterine lining. The thickness of the uterine lining changes with each menstrual cycle.
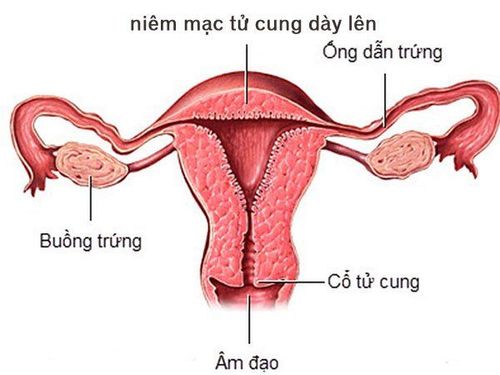
1. What is the menstrual cycle?
The menstrual cycle is divided into 2 phases:Pre-ovulatory phase (or Estrogen phase): The first phase of each menstrual cycle. At this stage, the lining of the uterus is affected by the hormone estrogen, which is counted from the start of menstruation until ovulation, usually about 14 days.
Post-ovulation phase (luteal phase or Progesteron phase): At this stage, the uterine lining is under the influence of the hormone Progesteron. The corpus luteum is the remainder after ovulation, counted from the onset of ovulation and self-regenerating until the first day of the next menstrual period.

2. How does the uterine lining change during the menstrual cycle?
Stage 1: Before ovulationAfter menstruation, the lining of the uterus will shed most of it, leaving only a thin layer of stroma, a few epithelial cells at the bottom of the glands. Then, these components will proliferate rapidly under the influence of the hormone Estrogen and be re-epithelized in 4-7 days. The uterine lining will thicken again, the glands will lengthen along with the growth of blood vessels. At the end of this period, the lining of the uterus will thicken by about 3-4mm. The glands of the cervix secrete a layer of mucus that forms a channel for sperm to move into the cervix. Therefore, around the day of ovulation, a woman will feel increased mucus secretion in the vagina
Stage 2: After ovulation
At this stage, it is not only affected by the hormone Estrogen but also under the influence of Progesteron as a result of ovulation. The endometrium thickens rapidly and secretes fluid. The glands are elongated, crooked, and filled with secretions. The blood vessels grow and twist to supply blood to the growing uterine lining. After ovulation, the uterine lining will be about 6-8 mm thick and increase until the menstrual period is equivalent to 8-12 mm. This increase makes the lining of the uterus filled with nutrients to supply the fertilized egg as it moves into the uterus.
When the egg is not fertilized, the corpus luteum degenerates. Levels of the hormones Estrogen and Progesteron will drop suddenly to very low levels. The blood supply to the lining of the uterus stops, causing the endometrium to shrink. At this time, the lining of the uterus will be thick, usually 12-15mm. After a few days, the entire lining of the uterus will be shed.
Under the effect of contraction of the uterus, the uterine lining is pushed out with a little fluid and blood. This is a menstrual period, which usually lasts about 3-5 days. The mean blood loss in each cycle was 38.13 ± 24.76 ml and menstrual blood (including blood and fluid) was non-clotting.
After the end of menstruation, the mucosa is regenerated under the effect of estrogen. The lining of the uterus plays an important role in conception, because this is where the egg implants after fertilization. The uterine lining is too thick or too thin, which is also a detrimental factor for the implantation and development of the embryo.
Trắc nghiệm: Sự hiểu biết của bạn về kinh nguyệt
Kinh nguyệt có vai trò quan trọng đối với sức khỏe sinh sản, do đó nữ giới cần chủ động trang bị kiến thức để theo dõi và kiểm soát tình trạng sức khỏe. Bài trắc nghiệm sau đây sẽ giúp bạn hiểu hơn về chu kỳ kinh nguyệt của bản thân.3. What is the effect of thick uterine lining on conception?
According to specialists, if:Uterine lining less than 6mm is considered a thin uterine lining, it will make it difficult for the implantation process to conceive. If there is a successful conception, it will be difficult for the embryo to develop and implant in the lining of the uterus and the consequences will be early miscarriage or underdeveloped embryo.
The uterine lining is thicker than 20mm: it is also difficult to conceive, because the estrogen content in the body is in excess, causing an imbalance of estrogen and progesterone, leading to consequences such as amenorrhea, menorrhagia, polycystic ovaries, Ovulation disorder, difficult embryo implantation,...
4. The phenomenon of proliferation of the uterine lining
In childbearing age, thickened endometrium causes amenorrhea, menorrhagia, prolonged menstruation, .. In menopause, thickened uterine lining may cause abnormal uterine bleeding. It is caused by too much estrogen in the body. This can cause problems related to endometriosis including uterine cancer.5. How to improve the uterine lining?
People with thick uterine lining will often be prescribed hormone therapy to re-establish the balance of estrogen - progesterone in the body, helping to increase a woman's ability to conceive and normal menstrual periods. The treatment should be examined and guided by obstetricians and gynecologists.In addition, women can also improve in other ways such as:
If you are taking estrogen after menopause, women should use it in combination with progestin or progesterone. Talk to your doctor about taking estrogen and progestin-containing medications if your periods are irregular. Losing weight in moderation because it can help prevent the risk of endometrial hyperplasia.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.