This is an automatically translated article.
The article has professional advice by Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Xuan Tinh - Anesthesiologist - Resuscitation - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General HospitalGeneral anesthesia is the strongest form, and is often used to help patients relax and relieve pain during surgery. During and after general anesthesia, there may be changes in the patient's body.
1. What is general anesthesia?
There are many forms of anesthesia such as: pre-anesthesia (initiation), general anesthesia or anesthesia - combined anesthesia. In particular, general anesthesia is a method of combining many drugs to help patients sleep, painless during surgery. This is the strongest type of anesthesia, most often used during surgery. When general anesthesia is used in surgery, doctors can perform effective treatments. Meanwhile, if the patient is awake and can feel the pain, surgery is very difficult to take place.2. General anesthesia process
First, the patient's personal information is compared, ensuring there are no errors about the patient and the procedure performed. The patient is then sedated so that the endotracheal tube can be intubated. Once monitoring devices are attached, safety procedures are met, anesthesia can begin.
When performing general anesthesia, drugs will be injected into the patient's veins or inhaled into the lungs as a gas. The muscles of the body are paralyzed, including the respiratory muscles. Therefore, the patient was intubated with an endotracheal tube and mechanically ventilated to support breathing during anesthesia.
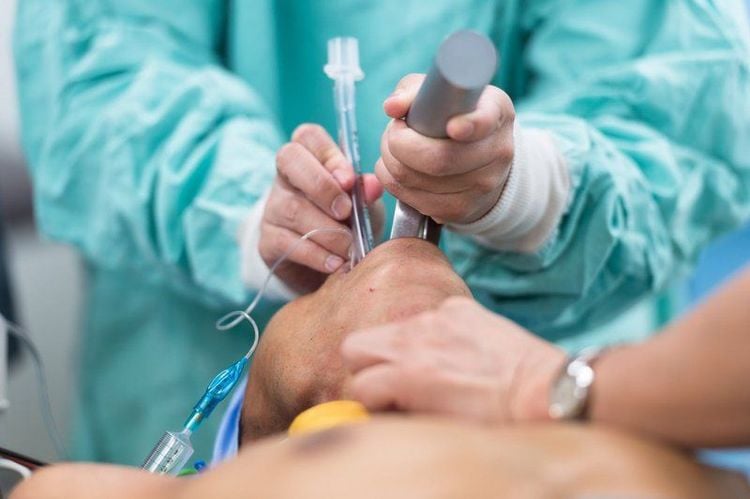
Kỹ thuật đặt ống nội khí quản trong gây mê toàn thân
During surgery, the patient is closely monitored with devices that monitor heart rate, blood oxygen, ECG and number of breaths. In addition, the patient is closely monitored by the operating room staff and the anesthesiologist. The endotracheal tube will be removed when the patient regains consciousness from surgery. With major surgery such as open heart surgery, brain surgery, patients often take longer to wake up, may need ventilation for 6-8 hours after surgery.
After regaining consciousness, the patient can drink water and maintain a diet according to the doctor's instructions. During the first day after surgery, the patient should rest and relax. In the following time, the patient is recommended not to operate heavy machinery, avoid drinking alcohol, use sedatives, ... without a doctor's prescription.
3. Body changes during general anesthesia
No pain The purpose of anesthesia is to help the patient feel no pain during surgery. The drugs that are put into the patient's body block the conduction of the nerves, preventing pain signals from reaching the brain. Therefore, the patient will not feel any pain until the effect of the anesthetic wears off.
Total loss of consciousness When under general anesthesia, the patient will be completely unconscious. As the drugs begin to work, the person will begin to feel light-headed. Within the next minute, the patient will become unconscious, the muscles relax and the patient needs respiratory support as well as measures to raise temperature because under the influence of anesthetic the respiratory system will not automatic operation, body temperature may drop. The patient will not be able to remember anything during the surgery. Therefore, general anesthesia helps to alleviate the concerns of surgery.
Sau khi gây mê, người bệnh rơi vào trạng thái vô thức
4. Common problems after general anesthesia
There are many side effects associated with general anesthesia, ranging from minor effects to serious, life-threatening risks. Side effects vary depending on the duration of surgery and the patient's background. The elderly, overweight, smoking habits, cardiovascular disease, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, kidney disease, etc. have a higher risk of having a general anesthetic than the elderly. strong.Some common problems on the body after general anesthesia include:
Drowsiness: The drugs used in general anesthesia often cause drowsiness and many patients doze off for a few hours after surgery. After that, the person may feel more comfortable; Nausea and vomiting: The most common problem after anesthesia. Postoperative nausea and vomiting can be easily prevented and treated with various drugs; Dry mouth: Due to the placement of a breathing tube, the mouth must be opened continuously during surgery, leading to the patient experiencing dry mouth. This symptom will quickly improve after the patient can eat and drink again; Sore throat and hoarseness: After prolonged surgery, patients may experience sore throat, hoarseness or pharyngitis due to irritation of the breathing tube. To overcome, patients can use throat sprays or lozenges. If hoarseness does not improve after 5-7 days, the patient should go to the doctor for examination and treatment; Tremors and chills: This is the body's natural response to the drugs used in surgery and these symptoms go away when the body gets rid of the drugs. In addition, shivering and chills can also be caused by hypothermia during surgery. If due to this cause, after warming the patient will stop shaking, chills. Patients may also experience chills if they have a fever after surgery, but this condition is quite rare and can be treated as prescribed by the doctor; Myalgia: Some of the drugs commonly used in general anesthesia can cause muscle pain. In addition, being completely immobile in one position during surgery can also cause muscle pain. In addition, the use of some muscle relaxants during surgery also causes muscle pain and muscle fatigue after surgery; Itching: Medications used during and after surgery can cause itching. Analgesics, especially those of the morphine class, cause more itching than other drugs used in general anesthesia.

Sau gây mê toàn thân người bệnh có thể gặp tình trạng khô miệng
5. Serious complications can be encountered after general anesthesia
Urinary retention: General anesthesia causes paralysis of the whole body, including the bladder. Not only affected by the anesthetic, in surgeries requiring catheterization, the bladder can also be affected. After the catheter is removed, the patient may experience pain on urination or urinary retention. The case of not being able to urinate after surgery requires immediate medical intervention; Psychosis: Altered consciousness, psychosis is a problem that can occur after general anesthesia. This condition is more common in patients who are elderly, have dementia, have Alzheimer's disease or other psychotic disorders. The combination of drugs and psychotic background increases this symptom until the body eliminates the anesthetic completely. In addition, a strange environment (hospital), due to factors that stimulated the light of day and night, the sound of machinery, the constant intervention of medical staff,... could aggravate the psychosis. , dementia;
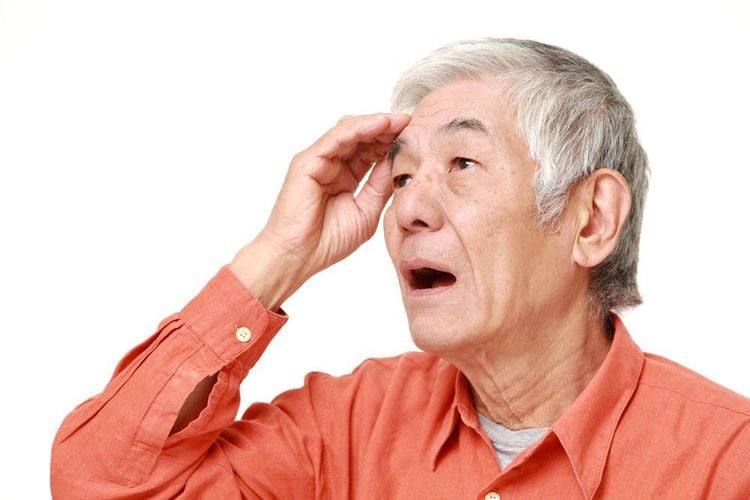

Người bệnh lớn tuổi có thể gặp tình trạng sa sút trí tuệ do biến chứng của gây mê
Difficulty weaning off the ventilator: In most patients, after surgery, the breathing tube will be removed and the patient can breathe on their own in a few minutes. Others, elderly patients, have comorbidities (especially respiratory or cardiovascular disease) will need more time to wean off the ventilator. Patients who are unsafe to remove the ventilator after surgery will be kept on the ventilator for a few hours until fully awake. In rare cases, patients are cared for in the intensive care unit until they are able to breathe on their own; Aspiration or pneumonia: A serious complication caused by aspiration of fluids and food into the lungs before, during, or after surgery. Normally, each person can cough to clear the foreign body from the airway, but during surgery, the cough reflex is lost so the patient can breathe vomit into the lungs. This condition causes pneumonia after surgery. This is a serious complication that requires antibiotic treatment or hospitalization. Therefore, patients are often advised not to eat or drink for a while before entering the operating room;
Intestinal paralysis : Anesthesia can cause the intestines to not work again for a while after surgery, causing intestinal paralysis. Patients who cannot fart after surgery will have abdominal distension and discomfort. This problem usually goes away on its own a few days after surgery. In case it does not go away, the patient should inform the doctor to find out other causes of the paralytic ileus or to use drugs that increase bowel movements. When the paralytic ileus is gone, the patient can be discharged from the hospital; Blood clots: Staying in an immobile position for many hours during surgery increases the risk of blood clot formation - postoperative deep vein thrombosis. Blood clots often form in the extremities, especially in the legs, then drift to the center causing embolism of other blood vessels, especially the pulmonary artery, which can be fatal. Therefore, after surgery, patients are advised to return to exercise as soon as possible to prevent the risk of blood clots or other respiratory complications;
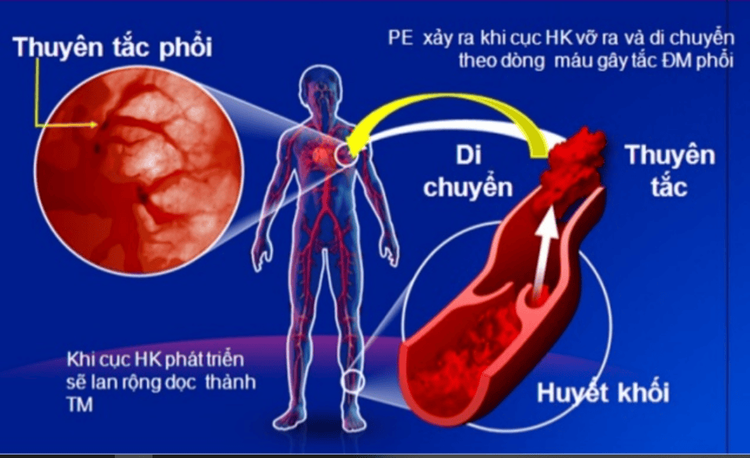
Cơ chế thuyên tắc huyết khối tĩnh mạch sâu ở người bệnh sau gây mê
Malignant hyperthermia : A particularly serious condition that occurs as a result of the body's overreaction to certain anesthetics and can be life-threatening. Elevated body temperature and muscle contractions, if not diagnosed and treated promptly, can lead to multi-organ failure. To prevent the risk of malignant hyperthermia during surgery, people with a history or family history of malignant hyperthermia should be carefully examined before anesthesia; Anesthesia awakening: Occurs when anesthetic drugs are not effective, causing the patient to lose consciousness completely. Anesthesia awakening can leave many long-term sequels for patients such as insomnia, mental disorders, depression,... Today, with modern monitoring facilities such as pain meters, monitors monitoring the depth of anesthesia,... complications from anesthesia awakening are rare. General anesthesia can lead to many unpredictable complications such as airway injury, brain damage, and even death. Therefore, when undergoing surgical anesthesia, it is necessary to carefully analyze the benefits and risks, take necessary measures to minimize the risk of complications, and help improve the patient's prognosis. Especially, if there are serious complications after surgery such as urinary retention, difficulty breathing, etc., the patient needs to be hospitalized immediately for emergency treatment.
Vinmec International General Hospital currently has a full range of modern medical equipment: Anesthesia machine, emergency resuscitation facilities, monitoring equipment: ultrasound machine, monitor, PCA, Auto bolus, machine Nervous stimulation... The hospital also has a team of doctors and nurses with many years of experience, well-trained in Anesthesiology resuscitation/analgesia treatment, and modern medical equipment to help monitor and care. customer safety. Therefore, when there are health problems, customers contact the hospital for advice and appropriate indications.
SEE MORE
Some common complications of anesthesia, anesthesia Distinguishing epidural and spinal anesthesia Anesthesia, pre-anesthesia: Things to know