This is an automatically translated article.
The article was consulted with Specialist Doctor I To Kim Sang - Internal Oncologist - Oncology Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Global Cancer Organization Globocan 2020 recognizes cervical cancer as the 4th most common cancer in women with more than 600,000 new cases and more than 340,000 deaths. Currently, medicine is increasingly developing rapidly, bringing hope to cancer patients, including cervical cancer treatment.
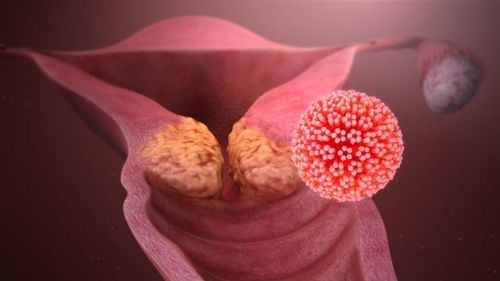
1. What causes cervical cancer?
HPV is sexually transmitted, and more than 99% of cervical cancer patients have HPV. Immunosuppression: Drugs or diseases that weaken the immune system such as HIV increase the risk of HPV infection, leading to cervical cancer. With increasing age, the risk of cervical cancer increases (the disease is usually detected between the ages of 35-44, median age is 50 years, and 20% of cases are detected after 65 years of age) Smoking, obesity, drug use long-term oral contraceptive use, unprotected sex, and a diet low in fruit and vegetables. Prevention is better than cure. Therefore, to prevent cervical cancer, women 9-26 years old, who have not had sex, should get vaccinated against HPV virus. Married or sexually active women should be screened for cervical cancer by methods such as Thinprep Pap test, HPV DNA test. Thinprep Pap test is a diagnostic and therapeutic test applied at Vinmec International General Hospital, approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to be used since May 1996. . Thinprep Pap Test has been widely used in European and American countries. This method is more advanced than the traditional Pap smear, helping to detect precancerous cells, especially adenocarcinoma, which is a type of cancer that is not easy to detect.2. How long do people with cervical cancer live?
Cervical cancer usually comes from precancerous lesions that took place 10 to 15 years earlier. The survival rate of the disease depends on many factors such as age, race and most importantly, the stage of the disease. According to statistics from the US National Cancer Institute 2011-2017, about 44% of cases of invasive cervical cancer are detected when the disease is at an early stage. At that time, the patient's 5-year survival was estimated at 92%. However, in cases where the cancer cells have spread to the surrounding area or have metastasized to the lymph nodes, this rate drops to 58% or even just 18% if the cancer cells have metastasized.Therefore, cervical cancer can be prevented by cancer screening and can be cured if detected at an early stage and treated with appropriate methods. The longer the cancer is left, the less likely it is to treat and the more expensive it is.
3. Cervical cancer treatment by stage
3.1. Treatment of cervical cancer in the precancerous stage Precancerous lesions of the cervix are lesions containing abnormal cells that appear only in the epithelial layer of the cervix, have not yet invaded through the basement membrane to the cervical tissues. deeper layer and has not yet spread to neighboring structures.At this stage, the doctor can use local treatments such as cryotherapy with liquid nitrogen, thermal ablation, laser or cone-contouring, which means that the cervix will be cut a small part in a cone shape.. .in order to limit invasiveness, preserve reproductive function but still ensure the effectiveness of treatment.

Điều trị ung thư cổ tử cung giai đoạn tiền ung thư bằng cách điều trị tại chỗ để giữ lại chức năng tử cung và buồng trứng
Treatment of cervical cancer stage I, in most cases, doctors will choose hysterectomy as the first treatment. After surgery, the patient was assessed for the risk of recurrence. If the risk of recurrence is moderate or high, additional adjuvant therapy with radiation therapy with or without chemotherapy is recommended.
For some cases of cervical cancer stage I, but the tumor is larger than 4cm, causing unfavorable surgery, the doctor will give priority to choosing a treatment method combining chemotherapy and radiation at the same time. help destroy the tumor.
When the patient refuses surgery and chemotherapy, or has a serious underlying disease that cannot be operated or chemotherapy, radical radiation therapy alone is still recommended.
3.3. Treatment of cervical cancer in stages II-III Cervical cancer stage II-III means the cancer has invaded the vagina, surrounding tissues of the cervix, pelvic wall or has metastasized to lymph nodes .
Stage II: The tumor has invaded to the upper 2/3 of the vagina or to the tissues surrounding the cervix. Stage III: Tumor has invaded to the lower third of the vagina or to the pelvic wall or has metastasized to lymph nodes. In the treatment of stage II-III cervical cancer, the main treatment method is a combination of radical concurrent chemoradiotherapy. In some cases of early invasive disease such as the tumor spreading to the upper 2/3 of the vagina but less than 4cm in size, hysterectomy may be the first method, then the patient will supported by radiation therapy to help reduce the risk of recurrence.
When the patient refuses surgery and chemotherapy, or has a serious underlying disease that cannot be operated or chemotherapy, radical radiation therapy alone is still recommended.
For invasive cervical cancer, preservation of reproductive function is almost impossible, except in very early cases when the cancer cells are only microscopically invasive. Therefore, before treatment, patients can store eggs at the Reproductive Support Center of Vinmec International General Hospital. However, this should be considered by the doctor and indicated in accordance with the actual situation of each case.
3.4. Treatment of cervical cancer stage IV Stage IV cervical cancer means the cancer has directly invaded the organs around the cervix or has spread far
Stage IVA: tumor invaded direct invasion to organs around the cervix such as bladder, rectum Stage IVB: tumor metastasizes to distant organs such as liver, lung, bone... For the case of stage IVA disease, the Treatment will be similar to that of stage II-III disease or, if the disease is considered operable, surgery and subsequent supportive treatment with concurrent chemoradiotherapy.
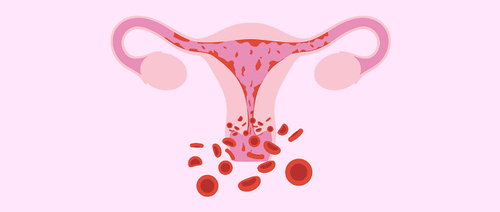
For stage IVB disease, the main treatment is to relieve symptoms and prolong survival. Systemic treatment is the treatment of choice, such as chemotherapy combined with targeted therapy and/or immunotherapy. However, temporary radiation therapy to the cervix may have a role in helping to control symptoms such as pain and vaginal bleeding.

Điều trị ung thư giai đoạn cuối phức tạp và tốn kém
Advantages of cervical cancer screening and treatment at Vinmec
Currently, with a team of highly qualified specialists Vinmec is the first private general hospital in Vietnam that can deploy cancer screening tests, the test quality is equivalent to European standards. When screening for cervical cancer at Vinmec, customers can experience the JCI gold standard, with modern testing methods and professional techniques for the most accurate screening and diagnosis results.
Screening results are then sent to your home, with specific advice and recommendations from leading industry experts.
If you need more advice and examination at Vinmec Health System Hospitals nationwide, please book an appointment on the website for service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
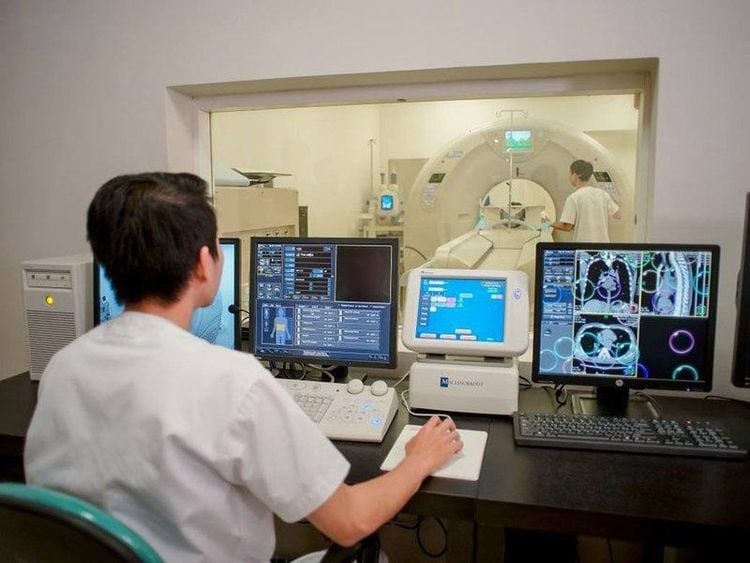
Vinmec là Bệnh viện Đa khoa tư nhân đầu tiên ở Việt Nam có khả năng triển khai xét nghiệm gen để sàng lọc ung thư ngay tại chỗ