This is an automatically translated article.
Disseminated intravascular coagulation is a condition in which blood clots develop throughout the blood stream, blocking small blood vessels. Increased clotting depletes platelets and clotting factors needed to control bleeding, causing excessive bleeding. So what causes this blood clotting disorder?
1. What is disseminated intravascular coagulation?
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a rare, life-threatening condition. In the early stages of this condition, scattered blood clots in the blood vessels cause your blood to clot excessively. As a result, blood clots can reduce blood flow and interfere with blood reaching organs in the body. As the disease progresses, platelets and clotting factors, the substances in your blood responsible for forming blood clots, are used up. When this happens, you will bleed profusely.
Watch now: Disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome
2. Causes of scattered blood clots in the blood vessels
Normally, blood clots form spontaneously at injured sites to prevent or control bleeding. When small cuts or breaks occur in the walls of blood vessels, your body activates clotting factors. The clotting factor thrombin forms long strands of the protein fibrin that clump together with platelets to form blood clots that then seal cuts or breaks. When the blood stops flowing, the body begins to break down the clots as part of the blood vessel healing process.
Disseminated intravascular coagulation is caused by another disease that causes the body's normal clotting process to become overactive. This condition progresses through two stages. In the early stages, the clotting process is overactive leading to blood clots throughout the blood vessels. Blood clots can reduce or block blood flow, damaging organs.
When disseminated intravascular coagulation progresses, it will cause coagulation disorders, the coagulation process is overactive using platelets and clotting factors, which are proteins that help blood clot normally. Without these platelets and clotting factors, DIC can cause bleeding just under the skin, in the nose, mouth, or deep inside the body.
Causes of disseminated intravascular coagulation include:
Inflammatory response to infection, injury or disease Serious tissue damage, such as burns or trauma Coagulation factors due to certain cancers cancer or pregnancy complications. Complications during pregnancy that produce clotting factors include: placental abruption, in which the placenta separates from the uterus, and amniotic fluid embolism, in which the amniotic fluid surrounding the fetus enters the mother's bloodstream.
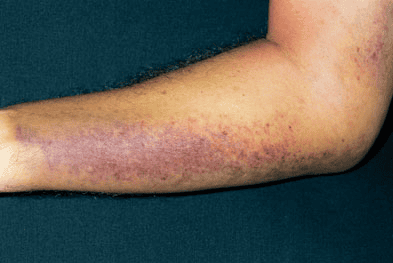
Đông máu rải rác trong lòng mạch (DIC) là một tình trạng hiếm gặp, đe dọa tính mạng
3. Risk factors for disseminated intravascular coagulation
Risk factors for disseminated intravascular coagulation include infection, trauma, lifestyle habits, and other medical conditions.
Infection: Sepsis, a systemic response to an inflammatory infection, is the most common risk factor for disseminated intravascular coagulation. Infections can be caused by parasites, bacteria, fungi, or viruses. Trauma: Major damage to organs or tissues may increase the risk of disseminated intravascular coagulation. Examples: cirrhosis, pancreatic linkage, major trauma or trauma, burns, or major surgery. Lifestyle: Using illicit drugs, such as cocaine and ecstasy, can increase the risk of disseminated intravascular coagulation. Health conditions that can increase your risk of disseminated blood clots in your blood vessels include: Vascular abnormalities, including aortic aneurysms and hemangiomas, which are growths of blood vessels. tangled blood vessels Cancer, including cancer affecting the pancreas, stomach, colon, or blood Stroke Complications during pregnancy, such as when the placenta separates from the uterus before birth, when amniotic fluid invades enter the bloodstream, or when there is severe bleeding during or after birth. Serious immune reactions, which can occur with incompatible blood transfusions, organ transplant rejection, or toxins such as snake venom. There are many causes of disseminated intravascular coagulation. You need to know the risk factors that cause the disease so that you can have an early diagnosis and timely treatment.
Follow Vinmec International General Hospital website to get more health, nutrition and beauty information to protect the health of yourself and your loved ones in your family.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.