This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II Nguyen Thi Minh Tuyet - Head of Obstetrics and Gynecology Department, Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.During pregnancy, a woman's body undergoes many physiological, anatomical, hematological, circulatory changes... One of the typical changes is cardiovascular function, heart disease during pregnancy. pregnancy can lead to many risks during pregnancy and delivery. Therefore, the monitoring, treatment, prognosis and decision of appropriate interventions for pregnant cardiovascular patients are very important.
1. Symptoms of cardiovascular disease during pregnancy
Normally during pregnancy, a woman's body will have the following changes:Blood volume and output of the pregnant woman increase by 40-50%; Blood pressure drops by about 10 mmHg as blood moves directly to the uterus; Heart rate increases 10-15 times/minute; Hypercoagulability increases the risk of thromboembolism. These symptoms lead to fatigue in women, especially in the last months of pregnancy. Pregnant women may also have hidden symptoms that signal the risk of heart disease during pregnancy such as:
Decreased exercise capacity Fatigue Difficulty breathing while sitting Fast heartbeat Fainting When having these symptoms, pregnant women should go to the hospital. Cardiac examination and check-up to avoid missing the risk of heart disease during pregnancy.

2. Objects at risk
Some high-risk subjects should actively have a cardiovascular examination and consult a doctor before becoming pregnant:
People with symptoms suggestive of cardiovascular such as chest pain, or fatigue, shortness of breath, palpitations, heart palpitations. .. Have a history of congenital heart disease Have a history of myocardial infarction, coronary heart disease Have a history of venous thromboembolism, pulmonary embolism Have heart valve disease (under treatment or have had an artificial heart valve replaced) Have heart failure Cardiomyopathy such as: dilated cardiomyopathy, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, restrictive cardiomyopathy, peripartum cardiomyopathy... Having aortic aneurysm, aortic dissection, Marfan syndrome. High blood pressure Arrhythmia (fast, slow)
3. Diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases and pregnancy
Before pregnancy:
Pre-pregnancy examination and consultation with a cardiologist on the following contents: counseling on risks for mother and child, how to monitor cardiovascular disease and pregnancy, choosing a place to give birth , vaginal delivery or cesarean section, postpartum monitoring and appropriate drug selection during pregnancy. Talk to a geneticist and get genetic testing done if you have a congenital heart disease or heart disease that puts your baby at risk. Perform an echocardiogram, electrocardiogram, or stress test before pregnancy). During pregnancy:
At 11-12 weeks pregnant, measure nuchal translucency. At 19-22 weeks of pregnancy, fetal echocardiography will help identify 45% of cases of congenital heart defects in the fetus. When pregnant at 5 and 7 months, pregnant women have an echocardiogram to plan for antenatal cardiovascular interventions (if necessary) and prepare the birthplace.

4. Common cardiovascular diseases in pregnant women
4.1. Heart valve disease About 1% of pregnant women have heart valve disease and an increased risk of serious complications for the mother and fetus. Common heart valve conditions include:
Mitral stenosis Mitral stenosis is often asymptomatic but during pregnancy can be worsened by arrhythmias (tachycardia), the need for blood supply increase... leading to common complication is acute pulmonary edema. If left untreated, there is a risk of death. Women with severe mitral stenosis should be examined and consulted by a cardiologist and directed to either dilation or mitral valve repair/replacement surgery before becoming pregnant.
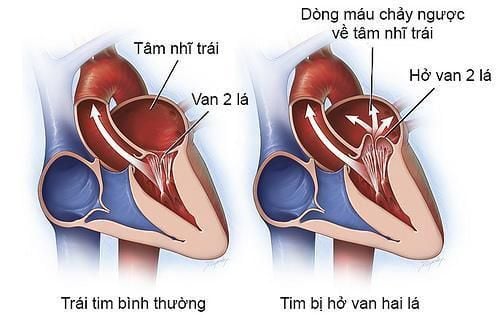
Mitral regurgitation The cause of mitral regurgitation is usually rheumatic heart disease or mitral valve prolapse. In pregnant women with well-compensated and well-tolerated heart function, sometimes pregnancy can still go on normally. However, in pregnant women with severe mitral regurgitation, accompanied by reduced heart function, pregnancy is likely to have birth complications.
Aortic stenosis Aortic valve stenosis can be congenital or a sequelae of rheumatic heart disease. If aortic stenosis is severe or if symptoms such as shortness of breath or chest pain are present, pregnancy should be postponed until surgery. Even if you are already pregnant and have early symptoms, termination of the pregnancy should be considered.
Aortic valve regurgitation When the heart function is still within limits and can be tolerated well by pregnant women, sometimes the pregnancy process can still take place normally. However, it should be noted that some drugs during pregnancy such as "ACE inhibitors" (usually used to treat aortic regurgitation) have a risk of causing fetal malformations, so they should be consulted by a doctor instead. with another class of drugs.
Mechanical valves and pregnancy Pregnant women with prosthetic heart valves often have to take anticoagulants for life, and continuously during pregnancy. However, anticoagulants such as Warfarin, Sintrom and other derivatives can lead to fetal pathology between 6-12 weeks of age, and increase the risk of miscarriage, stillbirth, and intracranial hemorrhage. . Therefore, if you continue to become pregnant, you need to talk to your doctor about the use of alternative anticoagulants and follow the appropriate course of use.
4.2. Heart arrhythmia
During pregnancy, many pregnant women have a feeling that their heart is pounding hard and fast in their chest. About 20% of women with pre-existing tachyarrhythmias will have a more severe recurrence during pregnancy. Therefore, pregnant women need to be monitored for cardiovascular disease during pregnancy.
4.3. Myocardial infarction
The risk of myocardial infarction is often increased in cases of multiple pregnancy, smoking, obesity, diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia. Myocardial infarction is most common in the third trimester of pregnancy and the risk of maternal mortality is about 20%. Treatment is similar for non-pregnant people.

4.4. Heart failure during pregnancy
Heart failure during pregnancy is common, especially in people with a history of cardiovascular disease before pregnancy. In women with a history of cardiovascular disease, during pregnancy, heart failure will become more severe. In women without a history of heart disease, having medical conditions during pregnancy can also lead to heart failure. Treatment should aim at stabilizing hemodynamic status, reducing symptoms of heart failure, and treating risk factors (anemia, arrhythmia, thyroid dysfunction...). If the condition is not monitored and improved, it can lead to death in both mother and fetus.
5. Risks of having heart disease during pregnancy
Risks to the mother:
Increased risk of blood clots, mechanical heart valve entrapment; Heart failure during pregnancy, heart function decline; prone to arrhythmia; Gestational hypertension causing preeclampsia (which can lead to death); Pulmonary arterial hypertension; Sudden death. Risks to the baby:
Fetal malnutrition; Miscarriage, stillbirth; Hemorrhage; Premature birth; Birth defects; For pregnant women in general and pregnant women with heart disease in particular, it is necessary to have regular pregnancy monitoring in accordance with regulations. Pregnant women with accompanying cardiovascular disease should be examined and combined with treatment by a cardiologist to minimize the risk of complications and complications during pregnancy, helping to ensure the health of both mother. and baby.
At Vinmec International General Hospital, there is a package maternity service as a solution to help pregnant women feel secure because of the companionship of the medical team throughout the pregnancy. When choosing Maternity Package, pregnant women can:
The pregnancy process is monitored by a team of highly qualified doctors. Regular check-ups, early detection of abnormal problems. Maternity package helps to facilitate the birthing process. Newborns receive comprehensive care.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.