This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by - Master, Resident, Specialist I Trinh Le Hong Minh - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
Computerized tomography (CT) is a technique used by doctors to look for abnormalities inside the body, plan surgery, or check if a treatment is working for a patient. are not. This technique requires the use of X-rays - radiation to capture detailed images of the inside of the body. Some people think that CT scans can lead to cancer because of the amount of radiation from the scanner.
1. What is a CT scan?
Computed tomography (CT) scan is also known as CT scan. This is a technique used by doctors to detect cancer and find out where it is, where it may have spread, and whether the tumor is affecting other parts of the body by imaging tests. . During and after cancer treatment, your doctor will also recommend CT scans to find out if the treatment is working to look for signs that the cancer has returned.
Because CT scans are repeated with a certain amount of radiation, many patients and survivors of the treatment are concerned about the safety of this procedure. With any method or technique, there are risks and certain benefits, and CT scans are no exception.
The amount of radiation emitted from a CT scan is always kept to a minimum, but your doctor will let you know about the risks and possible risks because treatment does not always take place. smooth way.

Bác sĩ sẽ tư vấn về quy trình cũng như rủi ro khi thực hiện thủ thuật
2. Radiation from a CT scan
CT scans use X-rays - which is a type of radiation, also known as ionizing radiation. X-rays can damage the DNA structure in cells and increase the chance that they will turn cancerous.
CT scans use more radiation than other imaging tests, like mammograms. For example, a single chest CT scan emits a number of X-rays between 100 and 200 mGy.cm. It sounds like a lot, but the total amount of radioactive material you get is very small.
It's important to know that everyone is exposed to ionizing radiation every day, only from naturally occurring radioactive material in the surrounding environment.
In a year, the average person gets about 3 millisieverts (mSv), which scientists use to measure radiation. Each CT scan delivers 1 to 10 mSv, depending on the dose of radiation and the part of the body you are testing for. Low-dose chest CT scan of about 1.5 mSv. The same tests at a typical dose of about 7 mSv.
The more CT scans are done, the more radiation you are exposed to. But if a CT scan is essential, you still need to opt for this method.
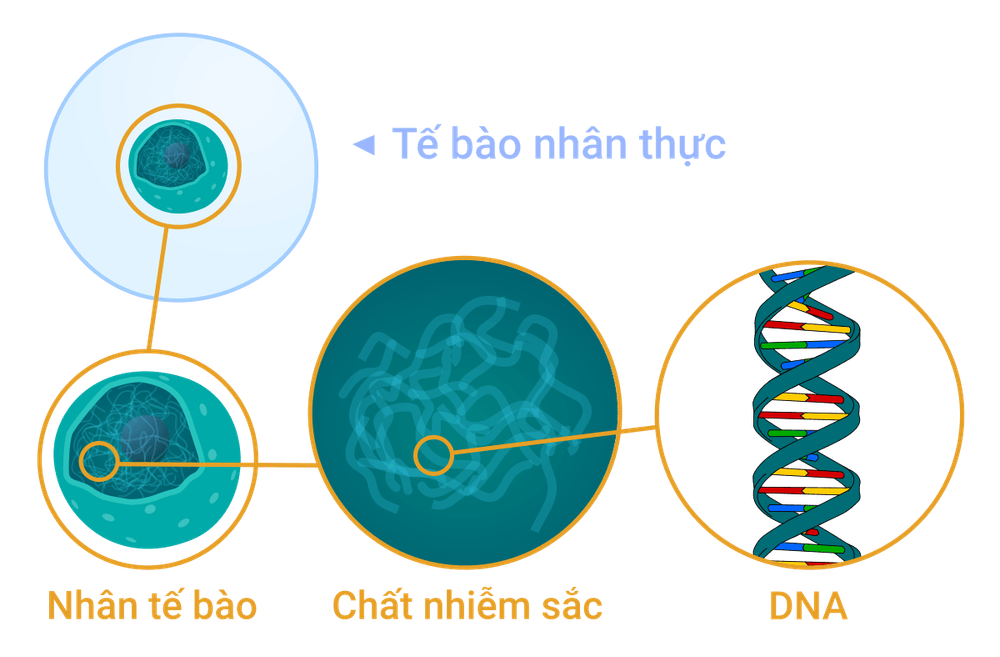
Tia bức xạ in hóa có thể làm hỏng cấu trúc DNA trong các tế bào
3. CT scans can lead to cancer
The risks posed by X-rays when performing a CT scan will depend on age, sex, and the body part being scanned. But overall, the odds are very low - the chance of getting cancer from any CT scan is about 1 in 2000.
Some patients are nervous about doing this test because radiation is known as a possible cause of cancer. However, the risk of cancer from a CT scan is very low. And the patient is only exposed to a very small amount of X-rays emitted from this method. Doctors will make sure that the benefits you get from a CT scan outweigh the risks.
Some organs in the body are more sensitive to radiation than others with a tendency to be more vulnerable to rapidly growing and dividing cells. Organs such as the chest, lungs, thyroid and bone marrow are more sensitive to X-rays than other body parts such as the brain...
Cancer is more likely in women than in men. Children are also at higher risk because they are growing and dividing faster than adults. Children can also get cancer from radiation.
If you are still worried, before having a CT scan, you can ask your doctor a few ideas:
Why do I need a CT scan? How will a CT scan affect treatment? What are the risks I may face? Can another test that does not use radiation be used, such as an MRI or ultrasound? How to protect other parts of the body during a CT scan?
Tác dụng phụ của tia X phụ thuộc vào tuổi tác, giới tính và các bộ phận cơ thể
Your doctor will use the smallest possible dose of radiation to perform a CT scan - especially if you need to have multiple scans. You should ask the technician performing the procedure if it is possible to shield other parts of the body without testing with a lead gown. This will block the X-rays from entering those areas.
You should keep the results of your CT scans to see how much radiation you received and to prevent you from repeating the test that was done.
If you're still concerned about radiation from your CT scan, your doctor will recommend another test method that's right for you.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Before taking a job at Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital, the position of Doctor of Radiology since February 2018, Doctor Trinh Le Hong Minh used to work as a resident in the Department of Radiology. at hospitals: Cho Ray, University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Oncology, People's Gia Dinh, Trung Vuong... from 2012-2015. Working officially at Cho Ray Hospital from 2015-2016, City International Hospital since 2016.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, customers can call Hotline hospitals or register online HERE.
Articles refer to sources: Webmd.com, Cancer.net