This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Master, Doctor Nguyen Nam Phong - Pediatrician - Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital.A perforated eardrum is a tear or perforation of the thin layer of tissue that separates the outer and middle ear canals. If not treated promptly, it can cause dangerous complications for hearing. These complications may include otitis media or hearing loss.
1. What is an eardrum perforation?
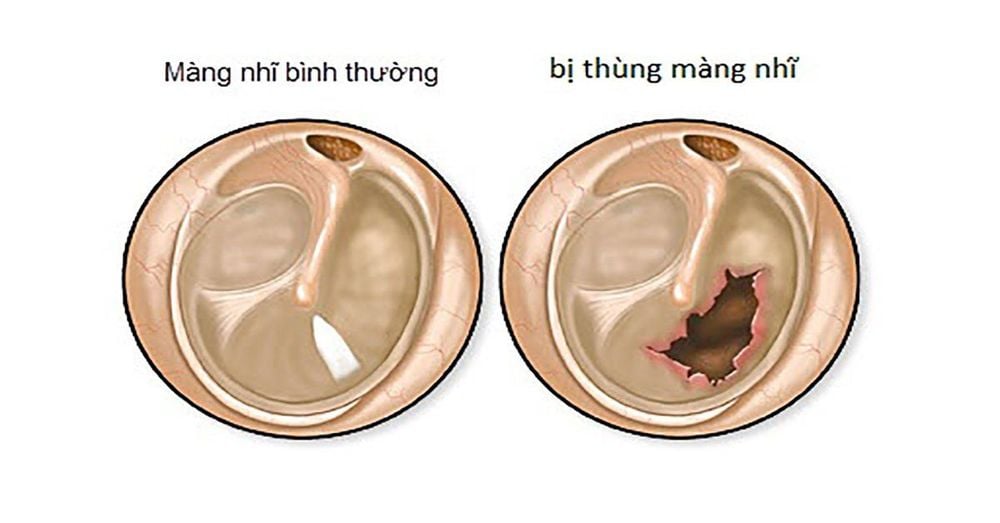
The eardrum is actually a thin layer of tissue, similar in structure to the skin tissue of the body, forming a wall between the outer ear canal and the middle ear. The eardrum is usually gray with an oval shape, slightly concave in the middle, and tends to tilt slightly behind the ear.This thin layer of tissue plays an extremely important role in human hearing. It is responsible for sensing the vibrations of sound waves from the outside, then converting them into nerve impulses and transmitting to the brain, thereby helping you hear and perceive sounds. In addition, the eardrum also helps to protect the ear from the entry of bacteria or foreign objects, and prevents water from entering the ear.
When the thin layer of tissue that separates the outer ear canal from the middle ear develops a hole or tear, this is called a perforated eardrum. A perforated eardrum can lead to a high risk of hearing loss. It can even make your middle ear more susceptible to infection.
In general, a perforated eardrum usually heals within a few weeks without treatment. In some more severe cases, the patient may need to have the eardrum patched or undergo certain surgery to heal the damage and prevent hearing loss.
2. Signs and symptoms of eardrum perforation
With a perforated eardrum, the patient may experience the following specific signs and symptoms:Ear pain that causes rapid hearing loss Severe ear pain There is a discharge from the ear that resembles mucus, pus, or blood Hearing loss Tinnitus Lightheadedness (dizziness) Nausea or vomiting may be caused by dizziness Tell your doctor right away if you experience signs or symptoms of a perforated eardrum. Your middle and inner ear are made up of delicate structures that are very sensitive to injury or disease.
Therefore, it is important to try to find the main cause of the symptoms you are experiencing, thereby determining if your eardrum is indeed perforated.
3. Causes of perforation of the eardrum
In fact, perforation of the eardrum can be caused by many different causes, the most common of which are:*Middle ear infection (otitis media): middle ear infection often leads to fluid accumulation in your middle ear. The pressure from these fluids can cause the eardrum to rupture or tear. Barotrauma: This is a stressful condition that affects the eardrum when the air pressure in the middle ear and in the environment is out of balance. If the pressure is too strong, your eardrum can rupture. Barotrauma is usually caused by changes in air pressure associated with air travel. Several other factors can cause sudden changes in pressure and lead to eardrum perforation, including scuba diving or the impact of a direct blow to the ear.
*Acoustic trauma (loud bangs or sounds): loud sounds or explosions, such as gunshots, can create pressure that can lead to perforation of the eardrum.
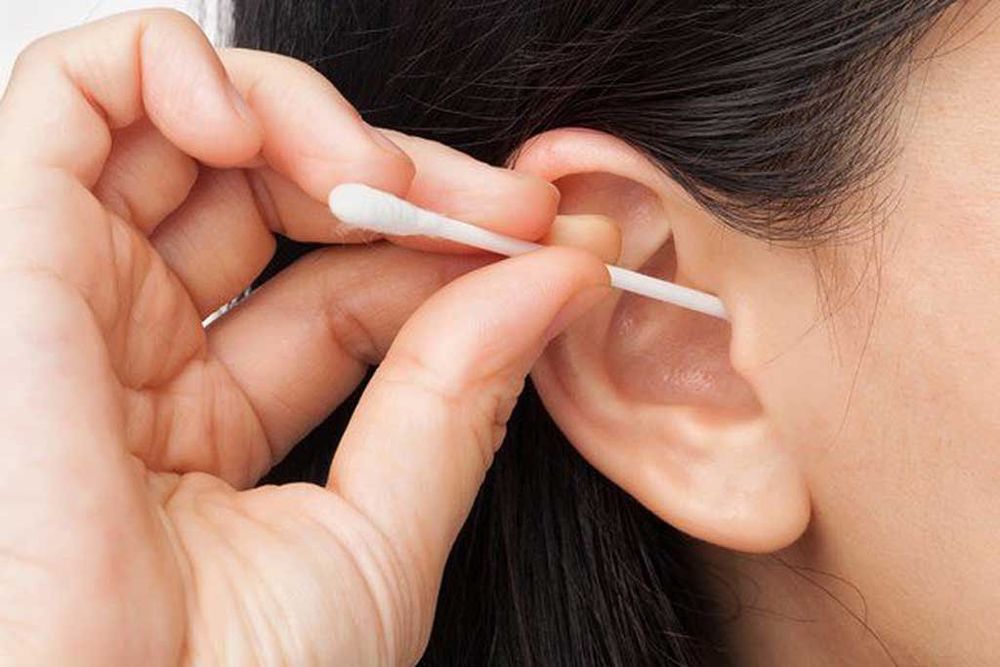
*There is a foreign body in the ear: some small objects, such as cotton swabs or bobby pins, can puncture or tear your eardrum.
*Severe Head Trauma: Some serious injuries, such as a skull base fracture, can cause dislocation or damage to middle and inner ear structures, including your eardrum.
4. Complications caused by perforation of the eardrum
The human eardrum has two main roles, including:Hearing: When sound waves hit the eardrum, they start to vibrate. This is the first step where the structure of the middle and inner ear converts sound waves into nerve impulses. Provides protection: the eardrum also acts as a barrier, helping to protect the middle ear from water, bacteria and other foreign substances. Once your eardrum is punctured or torn, it can lead to some serious ear problems, especially if the eardrum fails to heal on its own after 3-6 months. When that happens, a number of complications can occur, including:
Hearing loss: you may experience temporary hearing loss, which will only last until the hole or tear in the eardrum heals. In addition, the location and size of the tear also significantly affects the extent of your hearing loss. Middle ear infection (otitis media): When the eardrum is punctured, it can create favorable conditions for certain types of harmful bacteria to enter the inner ear. In cases where a perforated eardrum does not heal on its own, some people may be more prone to experiencing ongoing (recurrent or chronic) infections. Chronic otitis media with cholesteatoma: this condition is rare. This complication describes the growth of skin cells and debris inside the middle ear, as a long-term consequence of a perforated eardrum. Debris in the ear canal usually travels to your outer ear with the help of earwax. If the eardrum is punctured, skin debris can move into the middle ear and form a cyst. This cyst creates a favorable environment for bacteria to multiply and grow, and contains proteins that can damage the bones of the middle ear.
5. Can perforated eardrum heal on its own?
In fact, a perforated eardrum can still heal on its own if the extent and size of the hole is not too severe. A perforated eardrum will heal on its own within a week if the perforation is between 10 and 15 dB. For holes over 20dB or more, this thin film will not be able to heal on its own. The only way to do this is to patch the eardrum.
6. Diagnosing eardrum perforation
To determine if you have a perforated eardrum, an otolaryngologist will perform a visual examination using a lighted device, including an otoscope or microscope.In addition, the doctor may also order the patient to perform additional tests to find out the exact cause of your ear symptoms, or to detect the presence of any hearing loss. what hearing? These tests usually include:
Laboratory tests: if the patient has discharge from the ear, the doctor will order lab tests or perform a culture to detect a middle ear infection. by bacteria. Evaluation of the tuning fork: a tuning fork is a metal instrument with two ends that produces sound when struck. Through some simple tests with tuning fork can help doctors detect the patient's vision loss. In addition, tuning fork evaluation can also reveal whether vision loss is caused by damage to the vibrating parts of the middle ear (including the eardrum), damage to the inner ear's sensors or nerves. or hurt both. Tympanometry: A tympanometer uses a device inserted into your ear canal to measure the response of your eardrum to small changes in air pressure. Through certain types of reactions, it is possible to show whether the eardrum has perforated or not. Audiometry test: this is a series of rigorously calibrated tests that measure how well you hear sounds at different volumes and pitches. These tests are usually done in a soundproof chamber. The technique of monophonic audiometry and tympanometry at Vinmec is performed by a team of well-trained and experienced medical doctors, with a system of modern equipment to help improve diagnostic efficiency. For detailed information on audiometric technology at Vinmec, please go directly to Vinmec medical system or register for an online examination on the website.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
7. Treatment of perforated eardrum
Most eardrum perforations heal on their own within a few weeks without the need for treatment. Your doctor may prescribe antibiotic drops if an ear infection is found.In cases where a tear or hole in the eardrum does not heal on its own, treatment may include procedures to mend the tear or hole. These treatments usually include:
Patching of the eardrum: if a tear or hole in the eardrum does not heal on its own, an otolaryngologist will seal them with a paper patch (or patch). made of other materials). With this procedure, your doctor can apply a chemical to the edges of the tear to help promote healing of the eardrum, and then apply a patch over the hole. This may need to be repeated several times until the puncture is completely closed. Surgery: If patching the eardrum is not effective, the doctor may ask the patient to perform surgery. The most common surgical procedure is tympanic surgery. During surgery, the doctor will graft a piece of tissue from other parts of the patient's body to close the hole in the eardrum.
8. Home remedies for perforated eardrums
A perforated eardrum may heal on its own within a few weeks. In certain cases, healing can take months. To help the eardrum heal quickly, you can do some of the following measures:Keep your ears dry: you can put waterproof silicone earplugs or kerosene cotton pads in your ears when showering . Limit cleaning the ear: at this time, you should give the eardrum to have time to heal completely on its own. Avoid blowing your nose: The pressure created when blowing your nose can interfere with the healing of this thin layer of tissue.

9. Measures to help prevent perforation of the eardrum
You can follow these tips to prevent a perforated eardrum, including:*Treatment of otitis media: first, be aware of the signs and symptoms of otitis media, including fever , earache, stuffy nose and hearing loss. Children with otitis media are often fussy and may stop eating. Inflammation of the middle ear can lead to a perforated eardrum, so you should pay attention to the symptoms to detect and treat it early.
*Ear protection during flight: you should not fly if you have a cold or allergies that cause stuffy nose/ears. In the case of airplanes, you should keep your ears open with the pressure regulator, yawn, or chew gum. Alternatively, you can also do the Valsalva maneuver, which gently pushes air into your nose as if blowing your nose, while pinching your nostrils and closing your mouth.
*Avoid getting foreign objects into the ear: you should never try to remove earwax with items such as cotton swabs, or bobby pins. These items can easily tear or puncture your eardrum.
*Limit exposure to loud noises or explosions: avoid activities that expose your ears to explosions. If you are reluctant due to the nature of your work, you can protect your ears from unnecessary damage by wearing earplugs or covering your ears.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: mayoclinic.org