This is an automatically translated article.
This article is expertly consulted by Master, Doctor Vu Huu Thang - Emergency Medicine Doctor - Emergency Resuscitation Department - Vinmec Ha Long International General Hospital.Breathing oxygen through a mask is a method of increasing the concentration of inhaled oxygen (FiO2) by a mask, providing enough oxygen for the body's metabolic needs. This oxygen therapy plays a very important role in emergency resuscitation.
1. Overview of oxygen therapy
Respiration is the activity of gas exchange between the body and the outside environment (absorption of oxygen from the environment and expulsion of carbon dioxide from the body). The respiratory process consists of four stages: ventilation, diffusion, transport, and organized respiration. These stages are closely related and influence each other. If one of the above stages is disturbed, it will cause respiratory disorders, leading to lack of oxygen for the whole body.
1.1. Learn about hypoxia
Causes of hypoxia include:
● There are obstacles in the respiratory tract: It causes narrowing of the air inlet and outlet, reducing the oxygen content in the body, increasing the carbon dioxide content. . Obstacles include: pharyngitis, respiratory tract tumor, choking, diphtheria, bronchitis, pneumonia, asthma, increased secretion of respiratory mucus, edema of bronchial smooth muscles, ... ;
● Decrease in thoracic volume: Due to paralysis of respiratory muscles (spine injury, spinal nerve damage), thoracic trauma (rib fracture, scoliosis), diseases that cause effusion, pneumothorax pleura ;
● Diseases that interfere with air diffusion in the lungs: Acute pulmonary edema, emphysema, pneumonia, bronchopneumonia,...;
● Diseases causing disturbances in oxygen transport by blood and circulation: Anemia, heart failure, congenital heart disease (also known as ductus arteriosus, ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect,...).
Regarding symptoms, when there is a lack of oxygen, all patients show respiratory failure with the following signs:
● Shortness of breath;
● Anxiety, panic, restlessness;
● Struggling, stimulating;
● Consciousness drowsy, confused;
Decreased vision;
● Decreased muscle tone and coordination of muscle groups;
● In the early stages of respiratory failure, blood pressure, pulse, respiratory rate and heart rate increase;
● In the post-respiratory failure stage, the patient has cyanosis, shortness of breath, respiratory contractions, and a decrease in pulse and blood pressure;
The arterial blood gas analysis showed a decrease in oxygen saturation (SpO2) and oxygen pressure (PaO2).
1.2. What is oxygen therapy?
Lack of oxygen can damage the body's tissues, especially those vital to life such as brain cells. Therefore, when the body is deprived of oxygen, the patient is assigned to perform oxygen therapy. Oxygen therapy is a method of providing breathing air to a patient with an oxygen concentration higher than the concentration of oxygen in the air by more than 21%. Oxygen is an important measure in the treatment of respiratory failure.
There are different methods of oxygen breathing treatment: Breathing oxygen through a nasopharynx, breathing oxygen through a mask, breathing oxygen using an oxygen cage, an oxygen tent. In particular, breathing oxygen through a mask is being widely used today. This is a technique to increase the concentration of inhaled air with a mask, providing enough oxygen needed for the body's metabolic needs.
Specifically, a mask is a device that covers the patient's mouth and nose, used for patients to breathe oxygen in an emergency or when the patient has damage to the nose and throat, so it is not possible to perform oxygen breathing techniques. through the nasopharynx. Oxygen inhalation can provide the patient with breathing air with a higher concentration of oxygen compared to nasopharyngeal catheterization.
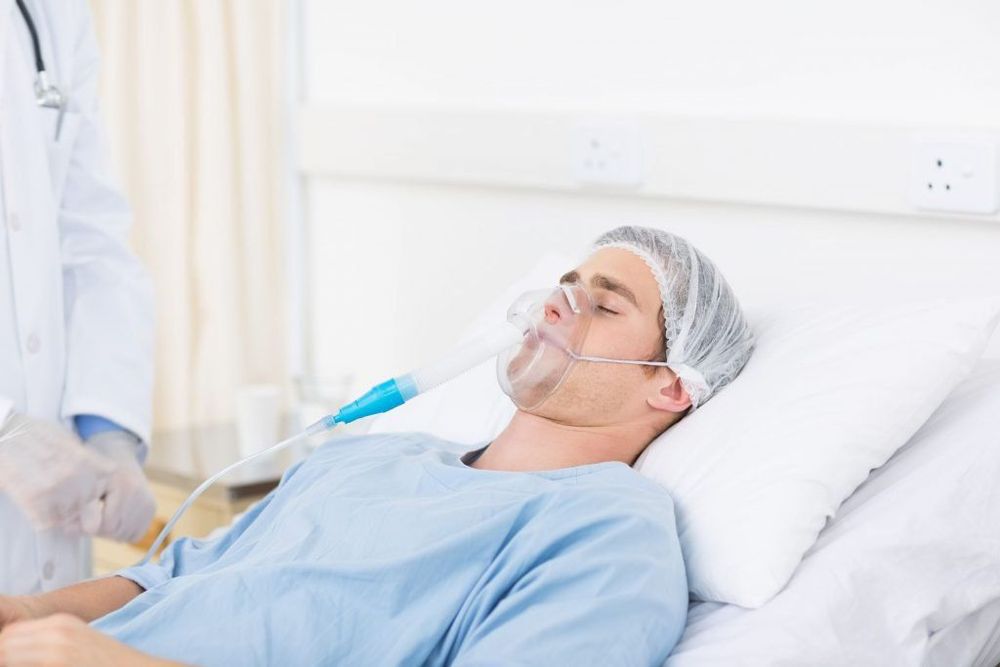
Thở oxy qua mặt nạ đang được ứng dụng rộng rãi hiện nay
1.3. Regulations when practicing oxygen therapy
When using oxygen in clinical practice, it is necessary to be very careful and follow the correct technical procedures to reduce complications during treatment. Some notes to remember are:
● Oxygen is a flammable and explosive gas, so it is necessary to prevent fire and explosion by banning smoking, fire in areas with oxygen tanks, oxygen tanks must be placed in places. dry, clean, securely fixed, and limited in transport of oxygen cylinders. If you need to transport oxygen tanks, you should use a separate trolley, move gently;
● Oxygen therapy uses dry gas, when breathing, it is necessary to moisten first to avoid damage to the respiratory mucosa;
● The concentration of oxygen in the breathing air needs to be suitable in terms of time, method of breathing, air flow and concentration (oxygen concentration). Avoid excessive oxygen concentration in breathing air, long-term use causes many eye and lung complications for patients;
● Ensure hygiene, prevent infection, use sterile tools, clean the patient's mouth as indicated.
2. Indications/contraindications for oxygen mask ventilation in emergency resuscitation
2.1. Indication
● The patient breathes on his own and has a high need for inspiratory oxygen (FiO2 over 40%);
● There are contraindications or complications when breathing oxygen through the nasopharynx;
● Patients with arterial hypoxemia: The specific pressure of oxygen in the arterial blood (PaO2) is lower than normal;
● The patient has clinical manifestations of hypoxia;
● Emergency situations: Choking, bleeding, convulsion, hypothermia,...;
● Short time oxygen: After anesthesia, after surgery.
2.2. Contraindications
● Patients with severe facial injuries, pressure is not allowed;
● Less effective for anemia, circulatory failure.
3. Perform the technique of breathing oxygen through the mask
3.1. Preparation
● Implementation personnel: Medical staff;
Necessary facilities: Flow meter, oxygen lead, SpO2 meter, mask appropriate for the patient's age and oxygen needs (simple mask, mask with reserve balloon - no valve 1-way, mask with reserve ball - 1-way valve);
● Patient: Informed about the upcoming procedure, placed on the emergency bed next to the oxygen source, cleared the upper airway, checked for clinical signs (breathing rate, SpO2 measurement, pulse, signs) exercise effect, mental assessment, skin mucosal condition,...);
● Medical records: Fill in the patient's personal information and health status before giving oxygen.
3.2. Procedure
● Wash hands, wear gloves;
● Install the flow meter to the oxygen supply;
● Install the humidifier in the flow column;
● Insert the oxygen lead into the outlet of the flow column or the humidifier;
● Attach the mask to the conductor;
● Adjust the oxygen flow through the mask to suit each different case according to the indications;
● Check oxygen connections, make sure they are not open;
● Put a mask over the patient's nose and mouth;
● Fix the mask to cover the patient's nose and mouth but not cause discomfort.
3.3. Monitoring
● During the first 30 minutes of breathing oxygen through a mask, it is necessary to continuously monitor the patient with a SpO2 meter and heart rate, assess breathing rate, level of exertion, skin color and spirit in order to adjust the amount of oxygen accordingly. fit;
● Observe the patient's facial skin in the area where the mask is placed to see if it is irritated or allergic to the mask's material;
● After 1-2 hours of oxygen breathing, the mask should be removed, dried on the mask and wiped the patient's face;
● When the patient is on stable oxygen, monitor every 3 hours for issues such as leaky oxygen junction, patient response status, SpO2 index;
● Adjust oxygen flow, ensure SpO2 index within allowable limits;
● Change mask, leads and humidifier daily.

Chú ý theo dõi bệnh nhân trong quá trình thở oxy qua mặt nạ
4. Some complications and ways to handle when performing oxygen breathing through a mask
Dryness of the airways: Need to be treated by humidifying the air that is inhaled;
● Oxygen poisoning: Should be managed by adjusting the amount of oxygen accordingly;
● Bacterial superinfection from oxygen breathing apparatus: To prevent, it is recommended to use disposable masks and leads, and change tools (masks, leads and humidifiers) daily;
● Some other complications: Hypoventilation due to oxygen, atelectasis, retinopathy,... perform proper treatment according to standard protocol.
The technique of breathing oxygen through a mask in emergency resuscitation plays an important role in the patient's health. When being assigned to perform this procedure, the patient needs to strictly follow the doctor's advice to ensure the best treatment effect and minimize the possible complications.
Customers who have any questions needing advice about the lack of oxygen in the body and the measures to deal with this situation can go directly to Vinmec Medical System for support and answers, or contact to book an appointment. Check online HERE.
SEE MORE
How does the body react when there is a lack of oxygen to the brain? Signs the body is lacking oxygen Causes of the body lack of oxygen