This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by MSc Nguyen Thuc Vy - Radiologist, Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.Brain perfusion MRI is a technique used to evaluate the distribution of blood to the brain parenchyma. Using this technique helps to differentiate some neurological diseases and to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment as well as to monitor the disease.
1. Distinguish between cerebral perfusion MRI and cerebral artery MRI
MRI of cerebral arteries provides information about cerebral arteries such as whether there is stenosis, blockage, aneurysm or thrombus in the lumen. Cerebral perfusion MRI to assess the distribution of blood to the brain parenchyma, eg in the setting of a stroke, cerebral artery MRA to assess cerebral artery stenosis/occlusion, and cerebral perfusion MRI to assess post-stenosis/embolism whether to reach the parenchyma or not.
These two techniques provide complementary information in the evaluation of nervous system pathologies. For example, there are cases of narrowing/occlusion of a small cerebral blood vessel that cannot be seen on MRI of cerebral arteries, but ischemic brain parenchyma can be seen on cerebral perfusion MRI and conversely, there are cases of MRI. Cerebral artery stenosis/obstruction but normal cerebral perfusion due to stenosis/occlusion is a chronic process, with compensatory development of collateral circulation leading to normal perfusion of brain parenchyma.
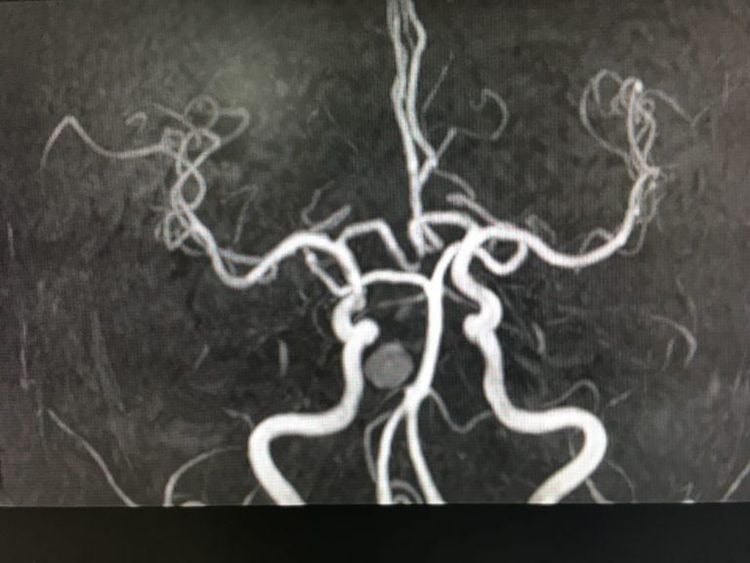
Hình ảnh cộng hưởng từ động mạch não
Technically, there are two main methods for measuring cerebral perfusion on MRI: the contrast-enhanced technique and the non-contrast technique. The most commonly used contrast-enhanced technique today is Dynamic susceptibility contrast-enhanced MRI perfusion (DSC MRI perfusion) with intravascular injection of Gadolinium-based contrast and the use of T2* pulse sequences on conventional MRI. through algorithms and the support of computer system to calculate cerebral perfusion parameters such as CBF, CBV, MTT, Tmax and display by color coding brain parenchymal perfusion. The arterial spin labeling (ASL MRI perfusion) technique provides only CBF and color coding information for cerebral perfusion.
Both of these methods have their own advantages/disadvantages and are being applied at Vinmec. Contrast-free brain perfusion imaging is simple, easy to perform, can be repeated many times, and provides initial information for clinicians to make a diagnosis. In case of pathology, the doctor will prescribe cerebral perfusion technique with contrast injection to confirm the diagnosis.
2. Purpose/meaning of technique
Main clinical application of cerebral perfusion MRI in acute stroke and brain tumor.
In acute stroke with onset before 6 h, the role of cerebral perfusion MRI is still limited, only when non-drug MRI/CT and cerebral angiography do not provide sufficient information, doctors will appoint Brain perfusion MRI.
In acute stroke in the period 6-24 hours, the American Stroke Association (AHA stroke guideline 2019) recommends using cerebral perfusion MRI or cerebral perfusion CT to select patients who can still undergo endovascular intervention. thrombosis .
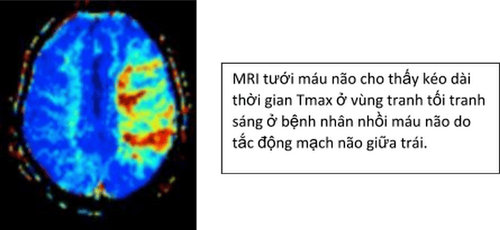
In brain tumors, cerebral perfusion MRI is used for diagnosis, staging, prognosis, and monitoring response to treatment. For example: assessment of tumor malignancy based on CBV parameter, high-grade malignancy with high CBV, post-treatment follow-up: distinguishing between necrotic areas due to hypoperfusion radiation therapy and infiltrated tumor tissue with increased perfusion blood...

3. Indications/Contraindications
Indications: Brain perfusion MRI is indicated in many nervous system diseases such as stroke, brain tumor, differentiating brain tumor from brain abscess, assessing vasoconstriction leading to cerebral ischemia of subarachnoid hemorrhage , in the trauma setting to evaluate traumatic angioedema and cytotoxic edema, altered cerebral perfusion due to hematoma, and for prognosis. Contraindications: Similar to magnetic resonance imaging techniques: pacemaker insertion, magnetic metal implants, metal foreign bodies in the eyeball, intracranial vascular clips, claustrophobia Claustrophobia is contraindicated in patients with impaired renal function eGFR < 30 ml/min due to the risk of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. .
Vinmec Nha Trang uses a modern magnetic resonance machine (3.0 Tesla) with a silent MRI program to limit noise during magnetic resonance imaging.
Contrast-free perfusion technique is safe, easy to perform, can be repeated many times, and the snapshot time is being implemented at Vinmec Nha Trang to provide useful information on cerebral perfusion support for patients. clinicians in the diagnosis and treatment of patients.
Customers can go directly to Vinmec Nha Trang to visit or contact hotline 0258 3900 168 for support.