This is an automatically translated article.
This article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Vu Huy Hoang - Radiologist - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International Hospital.1. What is cerebral perfusion computed tomography?
Computerized tomography is a technique that uses a computer and an X-ray machine to create cross-sectional images of the body. These images will provide more detailed information than conventional X-rays. Computed tomography (CT) scans show images of soft tissues, blood vessels, bones, and other body components.Brain perfusion computed tomography is used to investigate the perfusion of brain parenchyma, by using contrast dye (mainly iodine) injected into the blood vessels, then taking pictures by machine, and then record the images into the computer, thereby helping to clearly see the cerebral blood vessels, measure cerebral blood flow and help evaluate brain parenchymal damage.
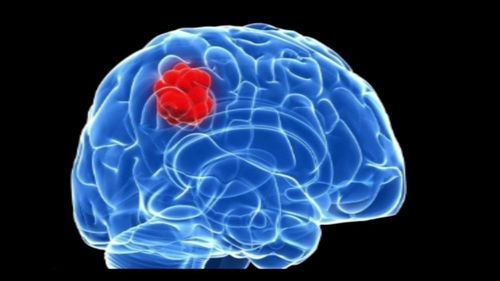
When receiving the information after the assessment, the doctor will assess the extent of brain parenchymal damage in stroke diseases, clearly identify the ischemic brain tissue that can still be saved. From there, doctors make quick and appropriate treatment decisions. In addition, cerebral perfusion computed tomography can further evaluate vascular abnormalities in dilated, narrowed, and occluded cerebral vessels and vascular proliferation in brain tumors.

2. Brain perfusion computed tomography scan
2.1 Indications and contraindications IndicationsCerebral stroke: Cerebral infarction in fulminant stage, acute stage; Brain tumors require assessment of vascular proliferation; Cases of cerebrovascular stenosis suspected of affecting cerebral perfusion; Follow-up after treatment with arterial thrombosis or after treatment with fibrinolytic drugs. Contraindications:
Relative contraindications: In the examination area (cranium) there are many metals that interfere with the image, pregnant women. The patient has a contraindication to contrast media, has a history of allergy to contrast. Have kidney failure. History of hyperthyroidism. 2.2 Computerized tomography procedure Preparation
Performer: doctor and specialist radiologist. Means used for brain perfusion computed tomography include: Multi-segment computed tomography machine, contrast agent pump; Film, printers and image storage systems; Water-soluble iodinated contrast agent; Supplies: Syringes, needles, syringes for contrast dye pumps, antiseptic solutions, physiological saline, gloves, masks, trays, cotton swabs; Box of drugs and equipment to manage complications in case of abnormality when injecting contrast agents. Patients: Patients are clearly explained how to take pictures and possible complications when taking films to be able to coordinate with the photographer; Remove items such as earrings, necklaces, hairpins (if any); Need to fast, drink before 4 hours. Can drink but not more than 50ml of water; Patients who are overstimulated, cannot lie still: Need to give sedation before the scan.

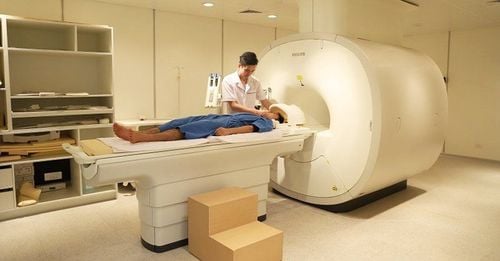
Patient lying supine on the table, move the table into the machine with light beam positioning for the examination area. Shooting techniques Positioning capture; Set the craniocervical field according to a schedule for the upper and lower areas of the tent, the thickness of the layer under the tent is 2-3 mm, and the layer above the tent is 7-8 mm; Preliminary assessment of lesions, assessment of need and necessary value for cerebral perfusion imaging; Carry out intravenous placement with an 18G needle, connect a 2-barrel electric injection pump (1 barrel of medicine, 1 barrel of physiological saline); Place the scan layer at the location of the lesion that needs to be assessed for perfusion; Next capture the machine's default setting program; Image processing on workstation screen, measurement of blood flow, blood volume, mean transit time, time to peak of the examination area. Evaluation of the results: The brain parenchyma can be seen as dark and light in the pathology of cerebral infarction. The large vascular structures in the skull base are shown. The doctor then reads the lesion, describes it on an internal computer, and prints the results to the patient.
3. Complications and how to handle them
Patient feels scared, agitated: Encourage and comfort the patient. Excessive anxiety, fear: Can give sedatives. Contrast-related complications: Anaphylaxis: After injection, within 1 hour, symptoms such as itching, acute urticaria, rash, angioedema, vomiting, bronchospasm causing difficulty in breathing and breathing will appear. hissing, laryngeal edema, chest indrawing, hypotension, shock, loss of consciousness. It is necessary to treat according to the anti-anaphylactic regimen of the Ministry of Health. Contrast-induced renal failure: A condition in which acute renal failure or increased renal failure occurs after contrast media administration, in which other causes affecting renal function should be excluded. Usually occurs within 24-48 hours of contrast medium administration. Thyroid storm: A serious condition in patients with underlying hyperthyroidism. There is a risk of harm to the fetus, so pregnant women need to consider carefully before taking and taking X-rays, they often have lead vests to protect them. Some cases have allergic-like reactions such as mild itching, but these reactions quickly disappear. Before taking a CT scan of the brain with contrast, the patient needs to inform the doctor about the previous medical history and unusual reactions if the previous scan is done to limit the risk of complications. Contrast-induced variation.Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital is equipped with a 640-slice CT scanner Aquilion One manufactured by Toshiba that is capable of supporting diagnosis on an area up to 16 cm wide, fast speed allows one rotation to capture the image. whole heart (up to 0.275s), helping to optimally diagnose coronary, cerebrovascular and whole body. In particular, this machine can reduce up to 90% of radiation dose, so it can be taken for pregnant women when indicated.
Doctor Vu Huy Hoang has 10 years of experience working in the field of diagnostic imaging, formerly a Doctor at the Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Thai Nguyen Central Hospital. Currently, the doctor is working at the Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Times City International Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.