This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Specialist Doctor I Vu Thi Hanh - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Hai Phong International General HospitalMagnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is considered the optimal non-invasive cranial assessment method, helping doctors detect and evaluate abnormalities of the skull. Usually, brain MRI does not need contrast injection, but in some pathologies, radiologist often prescribes imaging and contrast injection to clarify damaged structures.
1. Do all brain MRI scans require the use of contrast media?
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is considered the most optimal non-invasive cranial assessment method, helping to detect and evaluate many diseases or abnormalities of the skull due to its clear, detailed, and observable images. whole brain circuit. Most cranial magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) examinations do not require contrast injection, but in certain conditions such as vascular abnormalities, brain tumors, encephalitis, meningitis, radiologists are often ordered. imaging, concurrently injecting contrast agent to clarify the lesion structures, or evaluate the drug kinetics, the perfusion status of the lesion to obtain more information for diagnosis.
2. Cases requiring the use of contrast agents
Cases of magnetic resonance imaging with contrast injection are as follows:
Evaluation of anatomical structure: Brain vascular anatomy, anatomical variations, cerebral vascular malformations, brain aneurysms... drug enhancement, drug kinetics in tumor lesions (Meningiomas, cranial nerve tumors, Dynamic imaging in pituitary tumors, Perfusion for grading in brain tumors..). Evaluation of the enhancement of lesions in encephalitis, meningitis..
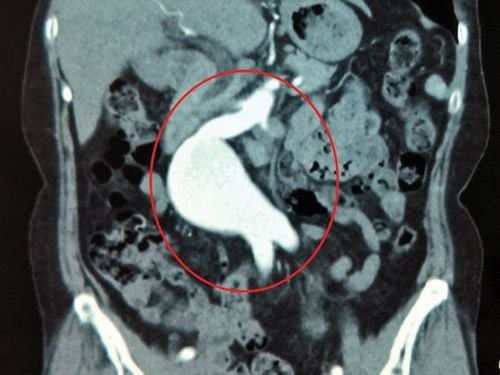
HÌnh ảnh phình mạch não trên kết quả chụp cộng hưởng từ
3. Effects of magnetic contrast drugs on patients
The contrast medicine used in MRI called Gadolinium is less likely to produce an allergic reaction than the iodine-based materials used for x-rays and CT scans. Very rarely, the patient is allergic to the contrast agent. Reactions are usually mild and easily controlled with medication. Severe reactions are very rare.
Accordingly, renal fibrosis (NSF) is a rare complication in patients with renal disease undergoing contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Gadolinium-based contrast agents may be withheld in some patients with severe kidney disease.
Some evidence suggests that small amounts of gadolinium can be retained in various organs of the body, including the brain, after a contrast MRI. Although there are no known negative effects from this, it is recommended that you consider multiple contrast-enhanced MRIs.
Undesirable effects of contrast agents: when using gadolinium contrast drugs, there may be adverse drug reactions (ADRs).
Mild common: Sensation of heat intravenously from the injection site to the neck and face, itching, hives, nausea, vomiting, taste disturbances, sneezing, anxiety. Moderately uncommon: The above-mentioned signs are at a higher level, especially urticaria, vomiting, dyspnea and anxiety. Bronchospasm increases shortness of breath, lowers blood pressure. Severe rare: The signs described above are very severe, especially dyspnea, bronchospasm, hypotension, generalized convulsions. Consciousness disturbance, glottis edema. Cardiovascular collapse may occur with pulmonary edema; arrhythmia leading to cardiac arrest. The rate of severe reactions is about 0.2% of the cases of using contrast agents, there are cases of death.

Tình trạng nổi mề đay thường gặp trên một số bệnh nhân sau dùng thuốc thuốc tương phản
4. Management of undesirable effects of contrast agents
Manage side effects of contrast agent in the following ways:
Immediately stop using contrast agent Mild anaphylaxis (urticaria, angioedema): intravenous injection of Solumedrol 40mg and/or Dimedrol 10mg, transfer the patient Go to the emergency department for follow-up for timely treatment if severe anaphylaxis occurs. In case of severe and critical anaphylaxis, adrenaline injection is required. Rehydrate with 0.9% sodium chloride 1000-2000ml for adults or 10-20ml/kg body weight for children. Let the patient lie on the table, with the head low, the legs high, and let the patient lie on his side if vomiting occurs.
Depending on the degree of difficulty breathing, measures can be used: Give the patient oxygen 6-10 liters/minute for adults, 2-4 liters/minute for children. Intubation, artificial ventilation, tracheostomy if glottis edema.
Vinmec International General Hospital has applied magnetic resonance technology to medical examination and treatment, and image diagnosis. In particular, the cranial magnetic resonance imaging technique with injection and without contrast injection at Vinmec is performed methodically and according to standard procedures by a team of highly skilled doctors, modern machinery, and equipment. Thanks to that, it gives accurate results, contributing significantly to the identification of the disease and the stage of the disease. From there, come up with the most effective treatment plan for the patient.
Hệ thống máy chụp MRI hiện tại Bệnh viện Vinmec
If you have a need for medical examination by modern and highly effective methods at Vinmec, please register here.