This is an automatically translated article.
The article was consulted professionally with Master, Doctor Do Thi Hoang Ha - Doctor of Biochemistry - Laboratory of Laboratory - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.Inflammation is a protective response of the body's immune system (innate immune response) against an attack by an external agent (microorganism, chemical, or physical agent) or by an external agent. internal (ischemic necrosis, autoimmune disease...) and inflammatory manifestations are usually seen only locally. The human body often has inflammation caused by many agents such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites, ... . When inflammation occurs, the body will produce substances that are released into the bloodstream and move to the inflammatory site to fight the inflammatory agents.
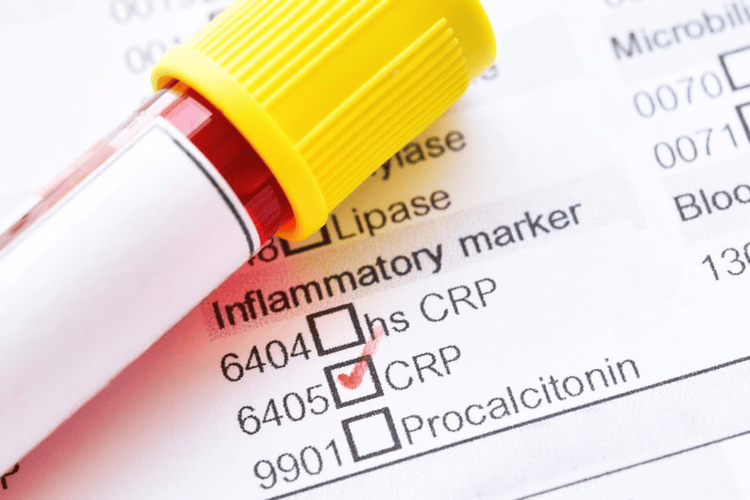
1. CRP . test
CRP (C - Reactive Protein) C-reactive protein is the classical acute phase protein of inflammatory reactions. It is synthesized by the liver and consists of five identical polypeptide chains forming a five-part ring with a molecular weight of 105000 daltons. CRP is the most sensitive acute phase reactant and its concentration increases rapidly during inflammation. Complex CRP activates the classical complement pathway and is a nonspecific acute inflammatory protein in response to inflammatory agents, infection, and tissue damage. The elevation of CRP is influenced by many factors, and is not always increased in sepsis with agranulocytosis.CRP response often precedes clinical symptoms including fever. In normal healthy individuals, CRP is a trace protein in concentrations up to 5 mg/L. After the onset of an acute phase response, serum CRP levels rise rapidly and dramatically. The increase begins within 6 to 12 hours and peak values are reached within 24 to 48 hours after the onset of infection. Concentrations above 100 mg/L are associated with serious irritation such as severe trauma and severe infection (sepsis). The CRP response may be less pronounced in patients with liver disease. The biological half-life is 19 hours, reducing concentrations by 50% per day after the acute inflammatory stimulus has resolved. And when the acute inflammatory process ends, CRP quickly disappears.
Application:
Elevated levels of CRP in the blood suggest an acute infection, a decrease in CRP levels in the blood means better patient condition and reduced inflammation. When combined with other clinical and laboratory data, mass-measured CRP values are a useful means of monitoring and can contribute to reducing unnecessary antibiotic use, as well as as to evaluate the treatment of bacterial infections with antibiotics; to detect intrauterine infection concurrently with premature rupture of membranes; CRP levels can jump thousands of times in response to inflammation and will be valuable in monitoring disease progression. CRP testing is also used to differentiate between active and inactive forms of concomitant infection, for example in patients with lupus erythematosus or ulcerative colitis, to monitor the outcome of certain treatments. arthritis and evaluate anti-inflammatory therapy, autoimmune diseases, and pelvic inflammatory disease (Pelvic Inflammatory Disease), to determine the presence of postoperative complications in the early stages, such as wound infection. injury, thrombosis, and pneumonia, and to distinguish between infection and rejection of bone marrow transplantation, appendicitis, cardiovascular disease, etc.
2. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) test
Normal blood is a plasma suspension containing red blood cells. Blood sedimentation (VSS), also known as erythrocyte sedimentation (the rate at which the red blood cells of the blood clump together), is caused by the action of gravity combined with a very complex interaction of physical force and is made up of all blood components and certain proteins. This is a blood test that is not specific to any particular disease, but is a test used to screen for many diseases to assess inflammation in the body. This test measures the height of a column of red blood cells (in mm) of a volume of anticoagulated blood in a special graduated tube over a period of 1 hour. This height may be affected by the red blood cell count and the concentration of high-molecular-weight proteins in the blood because changes in blood proteins lead to agglomeration of red blood cells and red blood cells. agglomeration in inflammatory and necrotic conditions causes it to "settle" faster than when cells stand alone.Application: Measuring erythrocyte sedimentation rate is a test performed to monitor an inflammatory condition or monitor a certain malignancy, although it does not indicate the exact source of this condition. Although this is a routine blood test, screening, it is very necessary in detecting and monitoring tuberculosis, monitoring the process of tissue necrosis in the body, other pathological disorders belonging to the lower body. Pathology (pathology of joints, tendons, striated muscles, ligaments,... and related structures), can even help detect diseases where clinical symptoms are vague and unclear. .
3. White blood cell count test
White blood cells play an important role in diagnosing infections: When we suspect that a patient has an inflammatory state of the body, we often test a blood count to evaluate the number and percentage of different types of white blood cells in the blood. The white blood cell count test is a simple, inexpensive test that gives quick results for 2 parameters including total number and percentage of white blood cells. Leukocytes have the following types: neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils.White blood cells are important components of the immune system. In the presence of inflammation, infection, or trauma, white blood cells (BCs) secrete CSF (colony-stimulating factor). This substance stimulates the marrow to increase BC production, also known as left-passing BC (when young BC have a larger amount than mature BC), so the amount of BC can double in a few hours. BC's defense against foreign agents is through phagocytosis. That phagocytosis is only temporary different from BC disease (phagocytosis is always occurring and progressive).
The white blood cell count test is indicated in inflammatory and infectious diseases, blood cancers, lymphoma and bone marrow abnormalities. Any acute infection or stress can increase BC production. BC has a normal value of 4500-10000/microliter of blood. BC has a variable quantity with age: increase in young children, pregnant women, decrease in the elderly. BC is reduced in myelosuppression, cytotoxic collagen-producing diseases (eg, lupus erythematosus), liver and spleen diseases, radiation, viral infections, and severe infections. BC is increased in infectious and inflammatory diseases (eg, allergies, rheumatoid arthritis), and non-infectious diseases such as anemia, blood cancers, severe physical and mental stress, and tissue damage.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space. Customers when choosing to perform tests here can be completely assured of the accuracy of test results.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.