This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Master, Doctor Pham Thi Mai Thanh - Department of General Internal Medicine - Vinmec Times City International General HospitalColonic diverticulum is a common disease in the elderly, often without symptoms, Hemorrhagic complications occur due to rupture of a blood vessel in the colonic diverticulum. Fresh blood comes out from the anus or sometimes dark, mahogany stools, when bleeding occurs in the right colonic diverticulum.
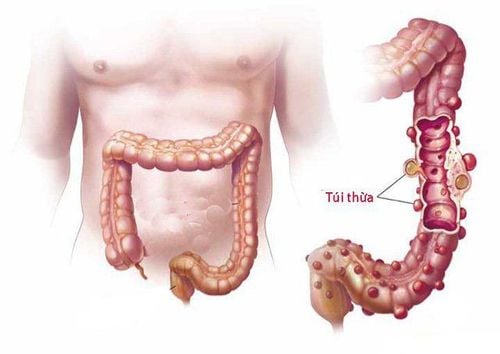
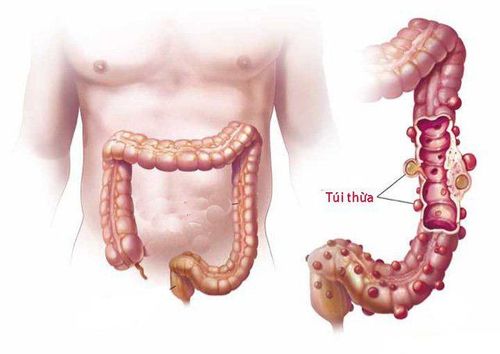
1. What is a bleeding colonic diverticulum?
Bleeding colonic diverticulum is one of the common causes of bloody stools (brown or bright red stools). 15% of patients with colonic diverticulum have diverticulitis, of which a third is major bleeding. Most diverticulitis occurs in the right colon (50-90%)
Diverticulitis spontaneously stops bleeding in 75% of patients but there is a risk of recurrent bleeding as high as 50% after the second bleeding Although many patients with diverticular bleeding are elderly and have multiple comorbidities, the mortality rate from bleeding colonic diverticulum is only about 10-20%.
Symptoms : Blood in the stool without abdominal pain is the typical symptom of diverticulitis, however, some patients present with abdominal distension, abdominal cramps, or urgency.
Clinical: Patients usually have normal blood pressure if bleeding has stopped. However, patients may have a rapid pulse and low blood pressure if they are bleeding or bleeding profusely. Dry, lax skin, less urination, and altered consciousness are signs of severe blood loss.
Test: Initially, the hemoglobin (hemoglobin) of the patient with gastrointestinal bleeding is usually normal (due to the total blood loss of the patient) but after a while, the hemoglobin begins to decrease due to dilution by extra blood. intravenous infusion or infusion of fluids during resuscitation.
2. Treatment of bleeding colonic diverticulum
Emergency resuscitation: intravenous fluids, red blood cells, treatment of coagulation disorders if any, hemodynamically unstable patients need to be monitored in the intensive care unit. Interventional hemostasis: if bleeding does not stop spontaneously: + If colonoscopy detects bleeding site or exposed blood vessels => endoscopic hemostasis intervention: epinephrine injection, electrocautery, site clamp endoscopy Bleeding with clip, rubber band ...
+ If the bleeding site cannot be detected by colonoscopy or endoscopic hemostasis fails, alternative methods are angiography and embolization ( embolization )
+ If both colonoscopy and angiography fail or are hemodynamically unstable despite aggressive resuscitation, surgical intervention is required.
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has implemented the method of laparoscopic right colectomy and lymph node dissection. Accordingly, the doctors will cut the inflamed colonic diverticulum with many advantages as follows:
No visual restriction like traditional, optimal quality images with higher accuracy. Less pain after surgery. Colon function recovers quickly. Small surgical scar. Minimize the risk of wound infection. Guaranteed aesthetics. Fast postoperative recovery, short hospital stay. Quickly return to normal activities. The system of modern equipment such as the modern endoscope system Olympus CV 180 allows to detect very small lesions (only a few millimeters) and accurately locate the lesions, endoscopic methods with frequency range Narrow light (NBI) has made a breakthrough in the screening and diagnosis of cancers of the gastrointestinal tract (esophagus, stomach, duodenum and colon and rectum) at early and very advanced stages. Soon. The level of anesthesia, anesthesia and postoperative analgesia is very good, leading in the application of the world's leading anesthetic - anesthetic methods. If you have a need for consultation and examination at Vinmec Hospitals under the national health system, please book an appointment on the website for service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.