This is an automatically translated article.
Spina bifida (spinal spina bifida) causes serious consequences for the development of the fetus. Pregnant women need to learn more about this issue during pregnancy to minimize the risk of their baby having neurological problems.
Children with spina bifida are at risk of generalized paralysis and many other dangerous problems with the development of the nervous system. You can prevent your baby during pregnancy by supplementing with essential micronutrients.
1. What is birth defect spina bifida?
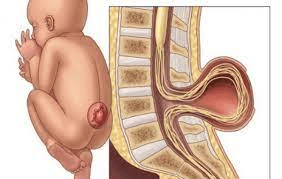
Spina bifida occurs when there is an abnormality in the development of the spinal cord in an infant. The spinal cord is the organ that connects the body's nervous system to the brain. In the case of spina bifida, the spine does not close completely, leaving a gap. Spina bifida means the spine splits into two halves.
Spinal fissures are divided into 2 basic types:
Hidden vertebrae: This is the most common and mildest form. An occult spina bifida forms when there is a small space between the vertebrae. Often, occult spina bifida has no symptoms or very mild symptoms, and thus the patient is unaware that they have it. Spina bifida: The most visible sign of spina bifida is a sac-like appearance on the back, like a large blister covered by thin skin. Spina bifida is further divided into two types: herniation of the spinal cord - meningeal and herniation of meninges. Infants with spina bifida often experience nerve damage or paralysis in some areas. The child may have total paralysis or be unable to control urination. Most neonates with medullary hernias are often associated with congenital hydrocephalus.
Spina bifida occurs during the third and fourth weeks of pregnancy when part of the fetal spinal cord does not close properly. As a result, the baby was born with part of the spinal cord exposed in the back.
Although scientists believe that genetic and environmental factors can together cause spina bifida, up to 95% of babies with spina bifida are born into families with no money. medical history. Women with certain chronic health problems, including diabetes and epilepsy (treated with certain antiepileptic drugs), have an increased risk (about 1 in 100) of having a baby with spina bifida. living.
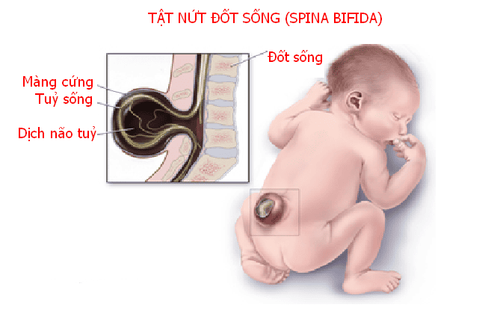
Tật nứt đốt sống xảy ra khi có bất thường trong sự phát triển của tủy sống ở trẻ sơ sinh
>> See also: Birth defects from statistics to causes – Article written by Doctor Do Phuoc Huy, Vinmec High Technology Center
2. Signs of spina bifida
The three most common types of spina bifida are:
Hidden spina bifida: The most common condition and does not cause problems or require treatment. Some children with the disease cannot see the defects, but some children often have dimples, birthmarks or patches of hairy skin on their backs; Meningeal hernia: A rare and serious form of the disease. Cerebrospinal fluid will escape from the spine and extrude under the skin. Parents may see a raised area in the child's skin; Meningeal hernia: This is the rarest and most serious form. Symptoms of the disease in a child will depend on the severity of the defect. For severe cases of spina bifida, the child often has many serious problems with the spinal cord and brain such as:
Little or no feeling in the legs, feet, arms, so the child cannot move the parts this part of the body; Bladder or bowel problems, such as urine leakage or difficulty having a bowel movement; Even with treatment, your baby may still have seizures, which affect learning or vision; Scoliosis .
3. Complications of spina bifida
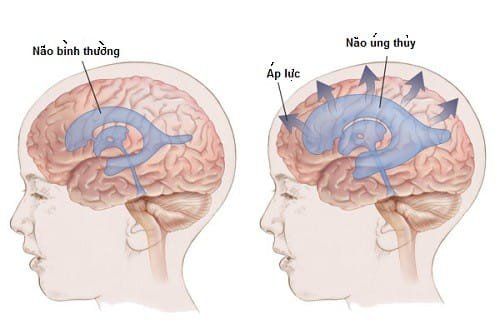
Paralysis of the legs: The nerves that control the leg muscles do not function correctly below the area of the spinal defect, causing weakness in the leg muscles, sometimes associated with paralysis. Whether a child can walk normally depends on the location of the disability, its size, and the care received before and after birth. Leg and spine problems: Children with myelopathy can have many problems in their legs and spine because of weak muscles in their legs and back. Possible problems include a curved spine (scoliosis), abnormal growths or dislocations of the hip, muscle cramps, etc. Bowel and bladder problems: The nerves that supply the bladder and the intestines often don't work properly when a child has bone marrow failure. This is because the nerves that supply the bowel and bladder come from the lowest level of the spinal cord. Fluid accumulation in the brain (hydrocephalus): Babies born with myelomeningocele often experience a buildup of fluid in the brain, a condition known as hydrocephalus. Shunt malfunction: The shunt may stop working or become infected. Some warning signs of a shunt not working include headache, vomiting, drowsiness, irritability, swelling or redness along the shunt, confusion, changes in the eyes (fixed gaze down), difficulty eating or contracting jerk. Infection in the tissues around the brain (meningitis): Some children with myelodysplasia can develop meningitis, an infection of the tissues around the brain. This infection is potentially life-threatening. Sleep disorders: Both children and adults with spina bifida can have sleep apnea or other sleep disorders. Skin problems: Children with spina bifida can injure their legs, buttocks, or back. They cannot feel the blistering or pain. Sores or blisters can turn into deep wounds or infections that are difficult to treat. Latex allergy: Children with spina bifida have a higher risk of latex allergy, an allergic reaction to natural rubber or latex products. A latex allergy can cause hives, sneezing, itching, watery eyes, and a runny nose. It can also cause anaphylaxis, a potentially life-threatening condition in which swelling of the face and airways, can make breathing difficult. Therefore, it is best to use latex-free gloves and equipment during childbirth and when caring for a baby with spina bifida. Other complications: Many problems can arise as a child with spina bifida grows, such as urinary tract infections, gastrointestinal (GI) disturbances, and depression. Children may have learning disabilities, such as attention problems, difficulty learning to read and do math.
4. Diagnosis of birth defects spina bifida
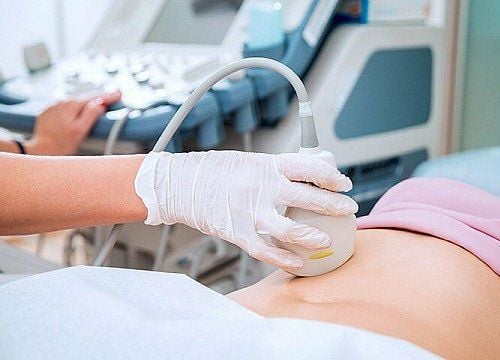
Thông thường, bác sĩ có thể nhìn thấy nứt đốt sống thông qua siêu âm
Doctors can diagnose spina bifida in the fetus or after the baby is born.
Diagnosis of fetal spina bifida: The doctor will conduct screening tests (prenatal screening) in pregnant women to check for spina bifida and other birth defects. Talk to your doctor about any questions or concerns you have about this prenatal test.
Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) test : A protein produced by the fetus. This is a simple blood test that measures how much AFP has entered the mother's blood. Babies have spina bifida when AFP levels are high. The AFP test is part of the Triple test to screen for neural tube defects and other problems; Ultrasound: Usually, the doctor can see spina bifida through ultrasound; Amniocentesis: The doctor will take a small amount of amniotic fluid surrounding the baby in the womb for testing. If the level of AFP in the amniotic fluid is high, the baby will have spina bifida. Diagnosing spina bifida in babies: Sometimes, there is a patch of hairy skin or dimples on a baby's back after birth. The doctor may take an X-ray, MRI, or CT-scan to get a better look at your baby's spine and back bones.
5. Treatment of spina bifida
The treatment for each spina bifida patient is different. People with spinal meningoceles and meningoceles will have more complicated treatment than people with occult spina bifida. Children with severe spina bifida need surgery to repair the holes in the first two days after birth. born. However, there are some doctors who will not use surgery but rather let the area heal on its own. After surgery, the doctor will develop a care plan for your baby's specific needs. The doctor will also update the care plan as the child grows. This plan may include:
Treatment of hydrocephalus; Physical therapy; Treatment of joint problems.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.