This is an automatically translated article.
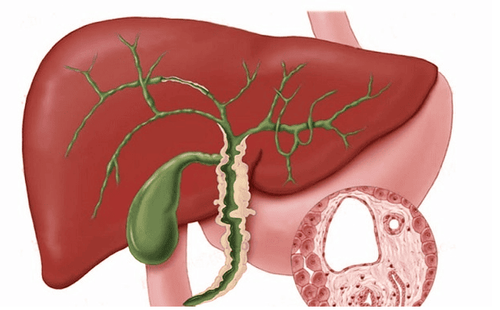
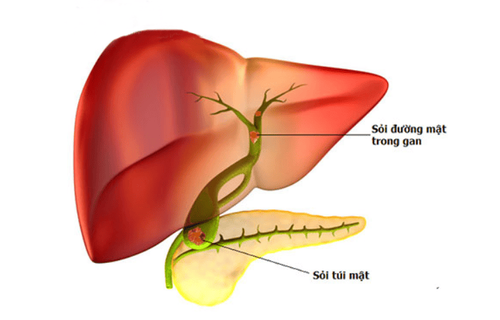
Gallstones in the liver are actually gallstones, because they often appear in the hepatic ducts, so they are also called liver stones. This condition needs to be vigilant because stones can cause biliary obstruction leading to many dangerous complications, even life-threatening.
1. Why get gallstones in the liver?
The main component of gallstones is bilirubin. Bilirubin is one of the substances in bile produced by the liver and is also a product of the breakdown by old red blood cells, creating a yellow-green bile pigment. Therefore, gallstones in the liver are also called pigment stones.
Causes of gallstones are thought to be due to:
Parasites carry bacteria from the intestine to the bile ducts and change the solubility of bilirubin, then eggs and worms combine to form stones. The composition of bile is unbalanced due to disordered liver function (hepatitis, cirrhosis, ...) Bile duct is impaired due to physical inactivity, obesity.
2. Manifestations of gallstones in the liver
Gallstones in the liver manifest through two stages, in which the first stage has symptoms similar to digestive disorders such as flatulence, abdominal distension, dyspepsia. In the later stages, gallstones cause complications and have common manifestations such as:
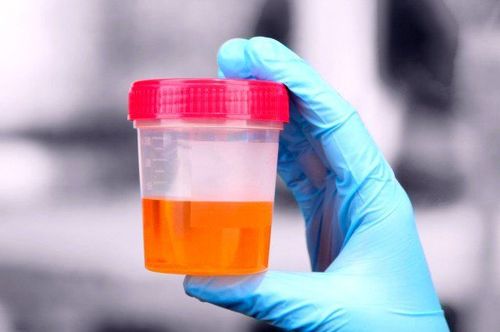
Abdominal pain: If the patient eats too much, he may experience a sudden and intense abdominal pain, making the patient unable to move. Cramping pain can last from a few minutes to several hours cyclically. High fever: Accompanied by liver cramps, the body sweats, feels chills and has a high fever. Jaundice, dark urine: Gallstones in the liver can block the bile duct, thus delaying bile fluid in the liver. At that time, the patient showed jaundice, yellow eyes, dark urine.
Sỏi đường mật trong gan thực ra chính là sỏi mật
3. Beware of gallstones in the liver
Compared with gallstones in other locations, gallstones in the liver can cause many dangerous complications such as hepatitis, liver abscess, cirrhosis, biliary tract infection, sepsis, cholangiocarcinoma in the liver. liver.
Hepatitis: Gallstones in the liver cause bile obstruction, stagnation of bile and create conditions for bacteria to invade, causing hepatitis, forming liver abscesses. Cirrhosis: After hepatitis, liver parenchyma is severely damaged and difficult to recover, leading to cirrhosis complications. Biliary tract infection: Gallstones in the liver can cause a dangerous complication of biliary tract infection. Typical symptoms of an infection include high fever, chills, infected bile ducts, and severe obstruction, which can cause fatigue and lightheadedness. Sepsis: The complication of sepsis is especially serious and requires prompt emergency treatment so as not to affect life. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Intrahepatic cholangiolithiasis can cause intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in 3 to 10% of cases. This is the most dangerous complication of liver stones and the survival time of patients after detection is very little, only from a few months to a few years.
4. Diagnosis and treatment of gallstones
Compared with stones located in other locations such as the common bile duct or gallbladder, intrahepatic bile duct stones are difficult to detect and diagnose. Patients may need to perform many tests including blood tests, liver function ultrasound, CT scan or magnetic resonance to get the most accurate conclusion and prognosis.
As with diagnosis, intrahepatic cholangiolithiasis is difficult to treat because the stones are scattered and deep in the hepatic ducts. In particular, biliary obstruction due to stones in segments, stagnation of bile is affected when performing procedures for therapeutic intervention. Besides, some common gallstone treatment methods are
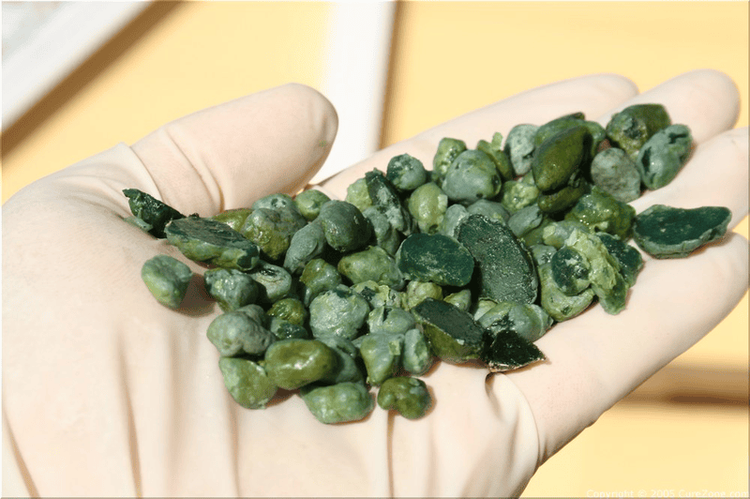

Sỏi đường mật trong gan có thể gây biến chứng nguy hiểm là nhiễm trùng đường mật
Some common gallstone treatment methods are not suitable for the treatment of intrahepatic bile duct stones such as lithotripsy or endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Lithotripsy is mainly used to treat cholesterol stones, not to treat pigment stones like liver stones. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography is mainly used to treat extrahepatic stones.
To treat gallstones in the liver, can apply surgical treatment, open surgery to remove the liver or remove stones. However, this method is not suitable for elderly patients because this is a major surgery, patients may have slow recovery and a lot of pain after surgery.
Currently, the method of treating intrahepatic gallstones that is suitable and gives high results is percutaneous transhepatic endoscopy to remove stones. This is a minimally invasive procedure that allows the patient to recover quickly after surgery.
Gallstones in the liver can cause dangerous complications that need to be alerted and detected early for timely treatment. Therefore, when you see abnormal liver-related symptoms such as jaundice, yellow eyes, dark urine, abdominal cramps with high fever, go to a reputable medical facility for examination and treatment advice.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.