This is an automatically translated article.
Cholecystitis as the name implies is an inflammatory disease in the gallbladder and is mostly related to stones. Patients with cholecystitis due to stones need to be hospitalized for treatment with drugs such as pain relievers, antibiotics or intravenous fluids... and most patients respond to the treatment regimen. However, people with gallstones are prone to recurrent inflammation of the gallbladder, when cholecystectomy is required for future prevention.
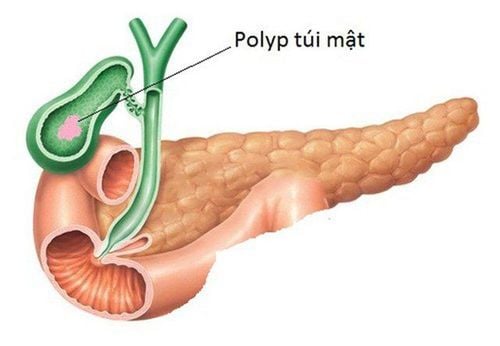
1. Anatomy and physiology of the gallbladder
Bile is essentially a digestive fluid, produced in the liver. Bile juice contains many different components, among which are prominent bile pigments, bile salts and cholesterol... Bile juice after being excreted by the liver will follow small tubes, called bile ducts or bile ducts, after being excreted by the liver. It is stored in the gallbladder or excreted directly into the small intestine to digest food. The small bile ducts inside and outside the liver will fuse together to form the main bile duct (also known as the common bile duct).
The gallbladder is a small structure, located below the liver, located on the right side of the upper half of the abdomen. The role of the gallbladder is to store bile, then when we consume food, the gallbladder will contract to pour bile into the common bile duct and then into the duodenum (the first part of the small intestine followed by the bile duct). stomach). Bile helps in the digestion of nutrients found in food, especially fats.
2. What is gallstone cholecystitis?
Many people have gallstones with a type of stone formed by the deposition of bile, the composition of which is mostly fat (similar to cholesterol) that thickens and hardens. Some other types of gallstones form due to the deposition of bile pigments or calcium.
We can get gallstones in different amounts, which can range from a few to a lot of stones or sometimes just form 1 large stone. According to statistics, about 1⁄3 of women and 1⁄6 of men have gallstones of varying degrees during their lifetime. However, gallstone formation mainly occurs in older people.
Fortunately, most cases of gallstones do not cause any symptoms and we are sometimes unaware of their presence. Most gallstones will exist in the gallbladder peacefully, not harmful to human health. However, a small number of patients develop gallstones and experience various health problems, the most common of which is gallstone cholecystitis.
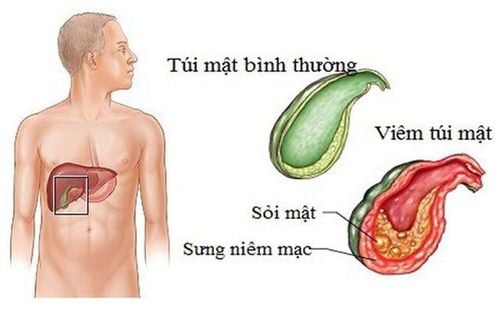
Cholecystitis is a term that describes an inflammation of the gallbladder due to many different causes, most of which are caused by gallstones. Statistics show that the rate of cholecystitis due to stones is very high, accounting for 19/20 cases. The pathogenesis is when a stone forms and becomes lodged in the cystic duct (or neck of the gallbladder, the structure that carries bile from the gallbladder to the common bile duct). At that time, the bile will be stagnant, causing the gallbladder to swell, leading to the condition of the gallbladder wall being inflamed, even infected. In particular, cholecystitis if accompanied by an infection will be very dangerous, the risk of many complications will appear.
Only 1 in 20 cases of cholecystitis are not associated with stones. At the same time, inflammation and infection of the gallbladder in this group are difficult to determine the exact cause.

Viêm túi mật do sỏi là tình trạng thường gặp
3. Treatment of cholecystitis caused by stones
Acute cholecystitis is a disease requiring hospitalization for both medical and surgical treatment.3.1. Medical treatment of cholecystitis
To give the gallbladder a temporary rest, the patient should temporarily not eat or drink anything. Your doctor will prescribe fluids, energy, and pain relievers to relieve symptoms. With such treatment measures, in most cases, the patient will quickly relieve the symptoms of gallstone cholecystitis. This is because the obstructing stone has usually returned to the lumen of the gallbladder and the inflammation will go away. In cases of suspected gallbladder infection, the doctor must prescribe appropriate antibiotics intravenously.
3.2. Surgical treatment of cholecystitis
Gallstone cholecystitis most of the time is indicated for cholecystectomy. This is not an emergency surgery, which can be delayed several days from the time of admission. Some patients may be able to delay it for a longer time so that the cholecystitis goes away completely. There are many different types of cholecystectomy, the indications for which depend on many factors. Which may include:
Laparoscopic surgery : Most commonly indicated to remove inflammatory cholecystitis. The advantage of laparoscopic surgery is that the incision is small, leaving little scars on the abdominal wall. Surgeons use small laparoscopes, inserted into the abdomen through small incisions in the abdominal wall. Modern instruments help the surgeon see the gallbladder clearly, then remove and remove the gallbladder easily. Laparoscopic surgery for cholecystitis due to stones can be applied to all patients; Traditional open surgery: A small number of patients who cannot use laparoscopic surgery will have traditional surgery to remove the gallbladder. Gallstone cholecystitis is completely treatable medically and recovery is still very good. However, because the stone still exists, the chance of cholecystitis recur is very high. That is why patients with gallstone cholecystitis should undergo cholecystectomy after medical therapy.
4. Some notes after cholecystectomy
Physiologically, the existence of the gallbladder is not important, we can still digest food without the gallbladder. Bile is still excreted by the liver, then follows the bile duct to the small intestine to digest food. At this point, the bile will have nowhere to store it.
Patient still eats and digests food as usual after cholecystectomy. However, about half of all cholecystectomy patients will develop mild abdominal pain or distention, which increases over time. In particular, the above symptoms often appear after high-fat meals.
Besides, some cases after cholecystectomy often increase the number of bowel movements, similar to mild diarrhea symptoms. This problem can be related to the liver not excreting enough bile to digest fat and can be easily overcome with anti-diarrheal medications.

Phẫu thuật nội soi điều trị viêm túi mật do sỏi
5. Prevention of cholecystitis
Most cases of cholecystitis are caused by stones, so the risk of cholecystitis can be reduced by the following measures to prevent stones:
Do not skip meals: Try to maintain a regular eating habit every day . Bad habit of skipping meals increases the risk of gallstone formation; Create a daily exercise routine: Physical activity limits the risk of gallstones, so we should create a habit of exercising about 30 minutes a day; Maintain ideal weight: For overweight and obese people, it is necessary to have an appropriate and gradual weight loss regimen. Do not lose weight too quickly because of the possibility of gallstone formation. The ideal goal is to lose 0.5 to about 1kg per week. Cholecystitis as the name implies is an inflammatory disease of the gallbladder and is mostly associated with stones. Diseases do not cause any symptoms and we are sometimes unaware of their presence. Prevention by maintaining a lifestyle and implementing a reasonable diet, exercising regularly. When unusual symptoms appear, you need to go to medical centers for examination and treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.