This is an automatically translated article.
This article is professionally consulted by Master, Resident Doctor Dang Thi Ngoan - Pediatrician - Neonatologist - Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital.The first month after birth, also known as the neonatal period, is the period when the baby changes from the water environment to the air environment. Therefore, at this time, children are learning to adapt to the outside environment. The development of a 1-month-old baby is always a matter of concern for many mothers.
1. Neonatal period
1.1 Physiological characteristics
The neonatal period is the period from birth until the baby is 1 month old. At this stage, the baby mainly learns to adapt to the environment outside the uterus, due to the transition from the water environment to the air environment. As soon as the baby is born, along with the birth cry, the baby begins to breathe on its own with its own lungs. At this time, the circulation cycle begins to officially work instead of the placental circulation. The baby begins to suckle, and the digestive system begins to work, the kidneys will now take over the function of regulating the internal environment of the body. Replace all previous tasks performed by placenta.In the period 1 month after birth, the baby's body is still very immature, the structure and function of the organs have not been fully completed. The child's nervous system is always in an inhibited state, so the child sleeps all day.
In addition, a number of physiological phenomena may occur in the 1-month-old baby period, including:
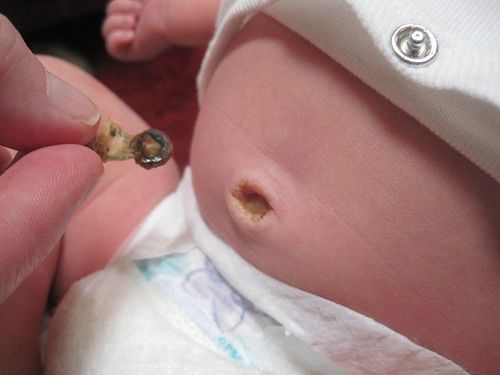
Physiological jaundice: Jaundice appears on the 3rd - 4th day after birth, slight yellowing in the chest area, no What are the accompanying symptoms? The child still eats, sleeps, and urinates normally. End when the baby is 10-14 days old. Physiological redness: Due to the development of blood vessels under the child's skin, the subcutaneous fat layer is still thin, so when the baby moves, twists and turns, the skin will turn red. This phenomenon will decrease or go away when the baby is still. Physiological peeling: Common in children at birth, pregnant, and old. Physiological weight loss: Children lose weight due to loss of water through the skin, excretion of meconium and urine. After about 7-10 days, the baby will return to birth weight. Decrease in height Physiological increase in muscle tone: Lasts a few seconds, mainly in the extremities. While the child is still breathing, his lips are pink. It will go away when the baby is about 2.5 months old. Umbilical shedding: After 7-10 days, the umbilicus will shed three meconiums. Unstable body temperature
Trắc nghiệm: các chỉ số cần chú ý về sự phát triển thể chất của trẻ
Chiều cao, cân nặng của bé ở từng giai đoạn nên là bao nhiêu là bình thường, bao nhiêu là bất thường? Cùng ThS.BS Ma Văn Thấm điểm lại xem bạn đã nắm được các chỉ số phát triển thể chất của bé chưa nhé!The following content is prepared under supervision of Thạc sĩ, Bác sĩ y khoa, Ma Văn Thấm , Nhi , Phòng khám Đa khoa Quốc tế Vinmec Dương Đông(Phú Quốc)
1.2 Pathological features
Because the child's body is still immature and weak, so the child is susceptible to diseases and often has a severe course and can easily lead to death. This is the age with the highest mortality rate. The leading diseases in infancy are infections such as umbilicus tetanus , umbilicus , pneumonia , sepsis , and other infections,...
In addition, diseases can be encountered due to too many disorders. The process of formation and development of the fetus such as: premature birth, teratogenicity, congenital malformations, cleft lip, cleft palate, congenital heart, anal defect, bladder exposure,... Finally, the diseases related to childbirth such as asphyxia, fractures, serous tumors, bleeding in the brain, meninges,...

2. Physical development
The physical development of the first 1 month old baby after birth will be based on many factors such as weight, height, head circumference, bust, fontanel:Weight : Normal newborn weight at new average birth weight from 2.8-3 kg. If less than 2.5kg is called preterm or low birth weight/fetal malnutrition, and over 4kg or more means the baby is too big. A baby's weight in the first 6 months will increase on average 700g per month. This is the period when children grow up very quickly. Mothers can chart their weight each month to track their baby's growth. Height: The average height at birth is 48-50cm, less than 45cm is considered premature. In the first trimester, a baby can grow 3.5 cm per month. Head circumference : Newborn's head circumference is 34cm Bust : Bust 32cm Font: Anterior fontanel has an average size of 2cm in each dimension. For premature babies, they will be larger in size. The posterior fontanelle is triangular in shape and is usually closed immediately after parturition.
3. Children's mental and motor development
Newborns often sleep a lot, can sleep up to 22-23 hours/day. Sometimes babies laugh while sleeping, this action is considered the language of the child. At this time, the baby's 5 senses are active:The baby hears the sounds and voices of everyone. The baby likes sweet drinks, doesn't like bitter drinks The baby recognizes the smell of breast milk, so he can find the mother's breast to suckle every time to be held Child knows pain when pinching, injecting Fine motor: Knows how to see light without moving, knows how to look at mother. Babies in the first month of life only have spontaneous, unconscious movements. As a result, movements often appear sudden, uncoordinated, and sometimes aimless.
Newborns have natural reflexs including:
Swallowing reflex, sucking reflex Robinson reflex: Bringing an object to the palm of the hand, the baby grips it very tightly, Faucet reflex: When touching the cheek, or position Which side of the mouth is close to the baby's mouth, the baby's lips will turn to that side to suck on Moro reflex: When patting the edge of the bed where the baby lies, or there is a loud noise, the baby will startle his arms outstretched to hug his body. In addition, children make personal-social adaptations by observing the things around them.
4. Care and nurture

Breastfeeding as soon as possible, breastfeeding right after birth Feeding the baby properly Feeding the baby on demand, day and night Keeping the baby clean: Hygiene umbilical cord, skin, diapers are clean Keep children warm in the cold season and cool in the hot season Take their children to be vaccinated fully and on time. In addition, mothers need to know how to monitor their children's physiological phenomena in 1 year. the first month to be able to recognize abnormal signs such as absence of natural reflexes, abnormal stools, refusal to breastfeed,...
In short, the first 1 month after birth is an adaptation period for babies. From the water environment to the air environment, the child may appear some physiological signs. Therefore, mothers need to be aware of abnormal signs so that they can take their children to a medical facility in time.
Doctor Dang Thi Ngoan used to be a lecturer in the Department of Pediatrics - Hai Phong University of Medicine and Pharmacy. Having been granted certificates in Pediatrics at home and abroad such as: Westmead Hospital, Australia; Hai Phong Medical University. Currently, Doctor Ngoan is a pediatrician - neonatologist at the Department of Neonatology at Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital.
Pediatrics department at Vinmec International General Hospital is the address for receiving and examining diseases that infants and young children are susceptible to: viral fever, bacterial fever, otitis media, pneumonia in children, ... With modern equipment, sterile space, minimizing the impact as well as the risk of disease spread. Along with that is the dedication from the doctors with professional experience with pediatric patients, making the examination no longer a concern of the parents.