This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Dr. Phan Dinh Thuy Tien - General Internal Medicine - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.An arterial blood gas test is a test that measures the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood and helps diagnose and assess the severity of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
1. What is an arterial blood gas test?
An arterial blood gas test is a test that measures the acidity, oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the arterial blood.The test is taken from arterial blood after the blood has passed through the body's tissues where oxygen has been used up and carbon dioxide is produced. A blood sample may be taken from the radial, femoral, or brachial arteries. If the arm is used for dialysis or if there is infection or inflammation in the area where the needle was inserted, do not use it to draw blood.
Steps to perform an arterial blood gas test:
Clean the site to be drawn with alcohol. In some cases, a local anesthetic may be injected to numb the area. Insert the needle into the artery, which may require more than one needle stick. Fill the syringe with blood. It should be noted that the patient is certainly breathing normally while the blood is being collected.
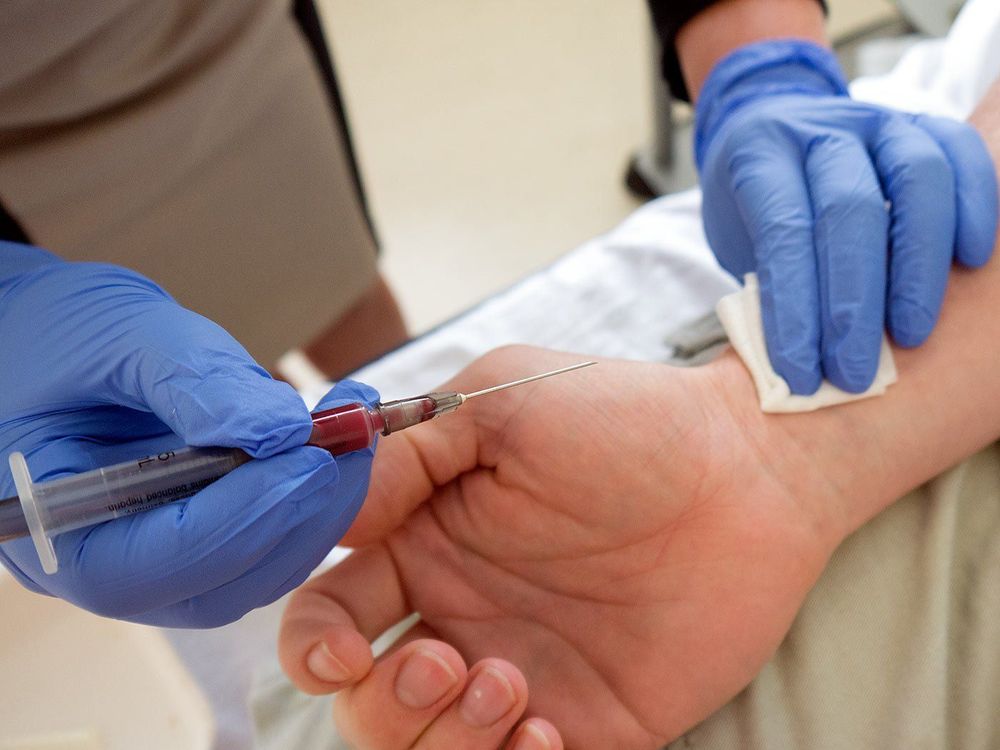
Lấy mẫu xét nghiệm khí máu động mạch
Fever or hypothermia Severe anemia or polycythemia Smoking.
2. What is chronic obstructive pulmonary disease?
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease is a form of obstructive pulmonary disease that is characterized by chronic insufficiency of ventilation. The main cause of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is the harmful effects of smoking.Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease reduces breathing flow, one of the characteristic physiological disorders of the disease. Because chronic airway inflammation thickens the airway subepithelial layer, increases the quantity and irritation of mucus, increases bronchial microvasculature, increases airway smooth muscle mass. Airway remodeling results in airway narrowing, increased mucus production, increased peripheral airway resistance, and an irreversible decrease in airflow.

Thuốc lá là nguyên nhân chính gây ra bệnh phổi tắc nghẽn mạn tính
Chest X-ray, CT chest, respiratory function test, Arterial blood gas.
3. Arterial blood gas test in the diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
An arterial blood gas test is used to check how well the lungs are able to move oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the blood. As blood passes through the lungs, oxygen moves into the bloodstream while carbon dioxide moves out of the blood into the lungs.An arterial blood gas test uses blood drawn from an artery in which the levels of oxygen (PaO2) and carbon dioxide (PaCO2) can be measured before they move into the tissues of the body.
Pressure of oxygen (PaO2): measures the pressure of dissolved oxygen in the blood and how well oxygen can move from the lungs into the blood. Pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2): measures the pressure of dissolved carbon dioxide in the blood and how much carbon dioxide can move out of the body.
Mẫu xét nghiệm khí máu động mạch được lấy từ máu động mạch
In severe cases, it will lead to acute or chronic respiratory failure. This leads to a decrease in PaO2 in the blood and an increase in PaCO2. The decrease in PaO2 in blood is mainly due to alveolar hypoventilation and imbalance between ventilation and circulation.
In a nutshell, an arterial blood gas test is a test that measures the level of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood. One of the important tests in the diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Especially for critically ill patients requiring mechanical ventilation, arterial blood gas testing will help in adjusting ventilator parameters.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.