This is an automatically translated article.
Tooth tumor is considered one of the serious dental diseases. If not detected and treated promptly, it can cause dangerous complications such as jaw and face deformities, hindering chewing and swallowing functions. So are tooth tumors dangerous?
1. What is a tooth tumor?
Are tooth tumors dangerous? Dental tumor is a benign tumor related to tooth growth. Specifically, it is a dental cyst, consisting of abnormally growing tooth tissue.
There are two main types of odontomas, which are composite and complex:
Multifocal odontoid : This condition still has three distinct tooth tissues (enamel, dentin and bone), which may appear lobar, where there is no defined boundary of distinct tissue between the small teeth. This condition usually occurs in the upper jaw; Complex dentin : This condition as an area of contrast contrast with varying densities, usually occurs in the back of the upper or lower jaw. In addition to the above forms, dilated dental cysts are an infrequent growth that occurs in any area of the dental arch and can affect primary teeth, permanent teeth, and supernumerary teeth. Intradental eruption is an abnormality that results from receding in part of the arch formed in the enamel organs. The most serious form of an ingrown tooth is dilated dental cysts.
2. Types of tooth tumors
Dental cysts have 3 types:
Root cysts: caused by infected teeth, cavities or trauma. The patient has no symptoms of pain or discomfort, the only sign to detect the disease early is discoloration of the teeth. Only when the disease is severe will symptoms such as pus discharge, pain in the tumor area, loose teeth, facial swelling in the jawbone,...
Crown cyst: originates from an underground tooth, then develops develop into cysts, so the disease is difficult to detect at first. It can only be detected by regular check-ups.
Yeast cyst: is a phenomenon where the dentin enamel germs that have existed since birth form a tumor. The characteristic of this type of tumor is that it is very easy to recur. When it grows, it will spread into surrounding tissues such as soft tissue, jawbone, temporomandibular joint, skull floor, causing the patient's face to be completely deformed, making it difficult to chew, swallow, speak and breathe. .. In this case, the doctor was forced to cut the jaw bone, remove the joint
3. Causes of tooth tumor
Dentists believe it is caused by an infection or related injury, genetic or genetic mutation. An example of an inherited syndrome that can cause tooth tumors is Gardner syndrome, which causes a variety of tumors in the body, including those in the teeth.
Tumors in teeth are the second most common after enamel tumors of the jawbone, accounting for about 20% of all tumor cases in teeth. Currently, there are no factors that can increase the risk of having a tooth tumor. If you experience a strange phenomenon on your teeth, visit your dentist immediately for detailed advice and know the exact cause to prevent.
4. Signs to recognize tooth tumor
Ever-onset is not known because it causes no symptoms. Root cysts are usually caused by an infected tooth, decay or trauma. Tooth discoloration is an early sign of disease, but it is often overlooked and only when signs of serious illness such as pus discharge, pain in the tumor area, loose teeth, swelling of the face are noticed by the patient. mind and go to the doctor. The crown cyst originates from an underground tooth, then develops into a cyst, making it difficult to detect at first. Cystic cysts are very easy to recur because the dentin germ cells that are still present at birth form the tumor.
5. Treatment of tooth tumor
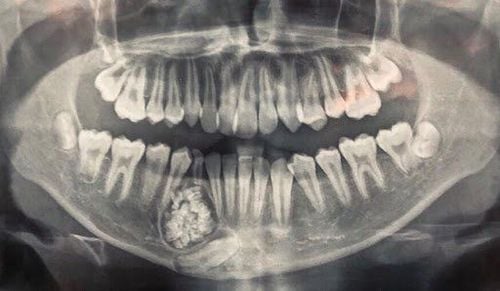
Tumors often have no outward symptoms, these tumors are only detected on x-rays, although delayed teething or the absence of a certain tooth can be a warning sign. needed to conduct a more in-depth examination.
When a tooth tumor appears, you will first need further examination to determine what type of tumor it is. In addition, histological diagnosis of tissues provides valuable information for dentists:
Histology of dental tumors:
Dentists do not know why the tumor occurs, possibly due to trauma and/ or infection in the network of teeth, genetic or genetic mutation. An example of an inherited syndrome is Gardner syndrome. This syndrome causes tumors in the body, including dental tumors. When examined at the cellular level, all tooth tissues were found to be in an abnormally coherent state.
The pulp, dentin, enamel and bone can sometimes look like a composite odontoid structure. These tooth cells are found in a surrounding support layer of fibrous cells. Since enamel has lost calcium, it looks like the space around small tooth structures. If you look closer, you can see calcified structures that are solid masses or many small teeth that can be seen on X-rays. Because enamel can easily detach from bone, it can be distinguished from other tumors (if present).
Complex dentition has no specific tooth tissue sequence and is not similar to normal tooth structure. At the cellular level, complex dentinomas mostly take the form of tubular dentin containing voids, these calcium-depleted circular spaces that once contained enamel. The edges may have a thin layer of tooth bone forming a tissue-like capsule around the tumor;
CT scan for tooth tumor :
This method helps dentists see inside the tumor before performing surgery to remove it. Occasionally, complex odontomas can progress into the nasal cavity. At this point, besides the X-ray, you need to conduct other tests to be aware of this condition. Occasionally, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is also used for in-depth analysis of complex tumors.
Treatments for tooth tumors:
The definitive treatment for tooth tumors is surgery. Early detection and treatment will benefit the patient. The tumor is benign and made of tooth tissue, so the surgery is quite simple, and you will also recover very quickly. Some complex tumors can lead to complications after surgery. So, keep in touch with your doctor after surgery to prevent complications.
6. Prevention of tooth tumor
Currently, the cause of the disease is unknown, so it is difficult to take preventive measures. It is suspected that tooth decay, tooth infection, or trauma to the tooth are predisposing to a tooth tumor. Therefore, to prevent disease, it is necessary to avoid these injuries. Children with delayed teething, missing teeth... need to take a scan to check where the teeth are located, whether there are tumors inserted into the teeth or not.
In particular, when there are any abnormal manifestations such as: loose teeth, deviated jawbone, sinusitis, rhinitis, ... also need to take X-rays to check. It is necessary to visit the dentist every 6 months or once a year for early detection and timely treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.