This is an automatically translated article.
Appendicitis in children occurs due to a blocked appendix or other intra-abdominal infections infecting the appendix, with signs such as abdominal pain, fever, vomiting, loss of appetite, and loss of appetite. It can be difficult to diagnose appendicitis in children, especially young children. Early diagnosis and surgery give good results and limit complications.
1. What is appendicitis?
Appendicitis is an inflammation and infection of the appendix, a small, hollow, finger-shaped organ located at the first part of the large intestine. This inflammation and infection can happen when bacteria get trapped in the appendix because hard stools or a large lymph node compress and block the opening. Once the appendix becomes infected, it must be removed to prevent it from bursting and spreading the infection into the abdomen.
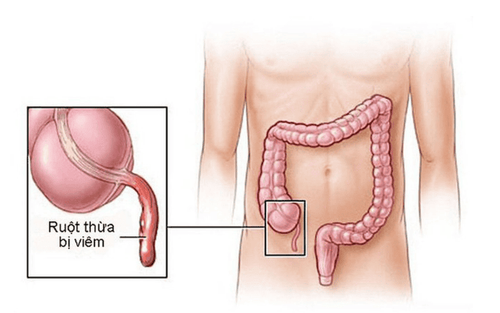
Bệnh viêm ruột thừa cần được cắt bỏ sớm
2. How common is appendicitis?
Appendicitis is the most common cause of emergency abdominal surgery. In Western countries, about 7% of the population suffers from appendicitis. The age with the highest rate of appendicitis is from 10 to 30 years old
Currently, the number of appendicitis cases is on a decreasing trend. This may be because people are tending to include more fiber in their diets and it can help prevent the blockage that causes appendicitis.
3. Risk factors for appendicitis
People with a family history of appendicitis are more susceptible than others. The number of appendicitis cases is higher in men. If your child has cystic fibrosis (an inherited disease that causes digestive and respiratory problems) it makes them more likely to develop appendicitis.

Trẻ tăng nguy cơ bị viêm ruột thừa khi có ba hoặc mẹ bị đau ruột thừa
4. How to recognize appendicitis in children?
Appendicitis is a very rare condition in infants, but it can happen. The illness can be difficult to diagnose by a child's parents because at first it may seem like the stomach flu with the common signs being abdominal pain, fever and vomiting, in rare cases it also can cause diarrhea.
A child with appendicitis has an abdomen that is distended and painful to the touch. The child may bend to the right if the inflamed appendix irritates the muscles leading to the leg. For older children, you can ask them to describe signs that they feel like abdominal pain that progresses from the navel to the right lower abdomen to identify the disease.
5. What should be done when the child has appendicitis?
The first thing you should do is contact your doctor immediately and you will be instructed what to do. The child may need to be taken to the emergency room. If left untreated, appendicitis can rupture and infect the baby's abdominal cavity. Be careful not to give your child laxatives or enema, as these can cause the appendix to burst. You just need to try to keep the child calm.
During the examination of the child, tests such as X-rays, ultrasounds or CAT scans and painless procedures may be used to help the doctor better visualize the baby's appendix. The doctor may also do blood tests to see if there is an infection and a urine test to make sure that the child has a urinary tract infection. The doctor will then see if the child needs surgery.
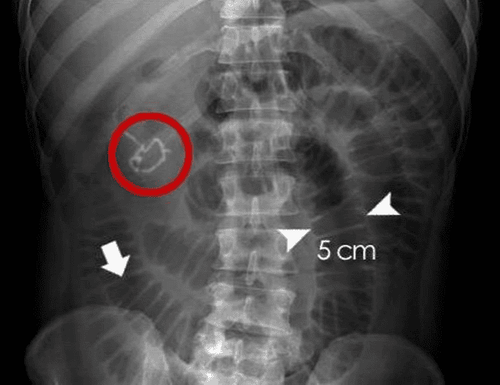
Chụp X-quang giúp chẩn đoán tình trạng viêm ruột thừa
6. How is appendicitis surgery?
First, the child will be given general anesthesia and the surgeon will make an incision in the abdominal wall. The appendix will then be separated from the large intestine and drained of any fluid that has accumulated due to the infection.
Some surgeons perform the procedure using a laparoscope that has a small camera attached to the transducer to allow internal images to be viewed without having to make a large incision in the abdomen. Then, the doctor will give the child antibiotics to prevent the incision from becoming infected. Your child will need to stay in the hospital for one to three days after appendicitis surgery for observation.
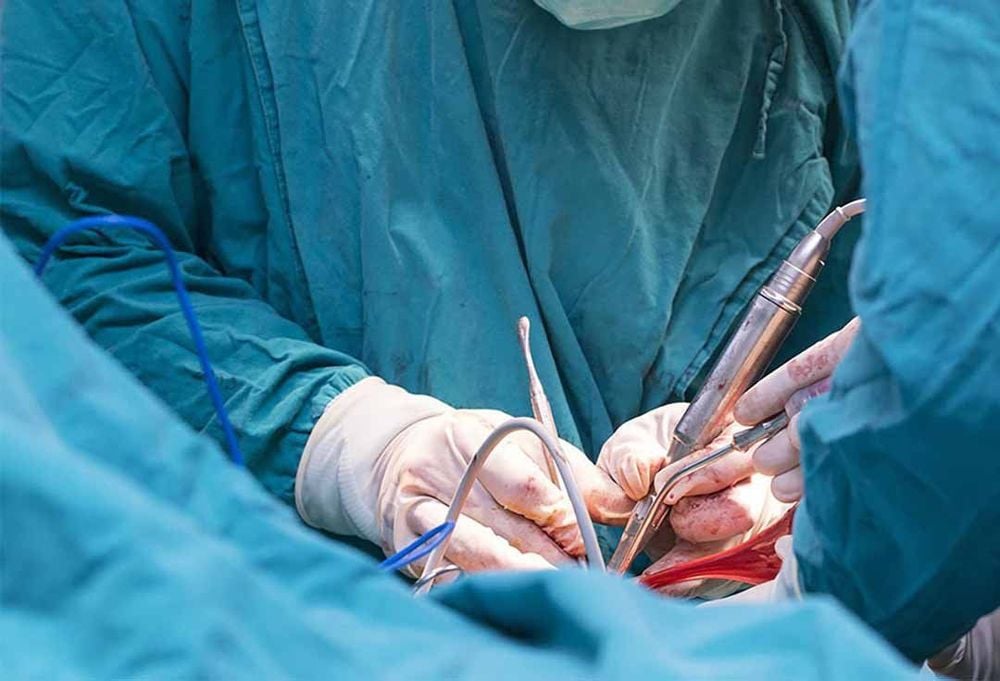
Trẻ có thể được chỉ định phẫu thuật viêm ruột thừa
7. What happens if the appendix ruptures?
If the infection becomes severe, the appendix can burst and spill bacteria from the infected organ into the abdominal cavity. Once this happens, the child will be admitted to the hospital and given an injection to deliver antibiotics directly into the bloodstream to fight the infection. However, surgery is still necessary after that.
To keep your baby safe, as soon as your baby has signs of appendicitis, you should take him to a reputable medical facility for early examination. Early surgical intervention to remove the inflamed appendix will help prevent dangerous complications. The surgical process, if the inflamed appendix is not completely removed and the post-operative care is not good, will very easily cause infection, inflammation, and greatly affect the health of the baby. Therefore, you should choose reputable medical facilities to perform examination and treatment.
Vinmec International General Hospital is chosen by many customers to treat digestive-related diseases in children, including appendicitis. The medical team is not only highly qualified and experienced, but also understands young psychology, is constantly trained, participates in specialized seminars with the world's leading experts, helps patients access to the most advanced and effective treatments.
In particular, Vinmec is one of the few hospitals with a team of specialists: gastroenterology, respiratory, neurology, cardiology, nutrition... right at the Pediatric Department. Therefore, during the treatment process, if any diseases or complications arise, the baby will be treated at the department, shortening the treatment time and saving costs.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: babycenter.com