This is an automatically translated article.
Signs of HIV in women and HIV symptoms in men are mostly similar, but because each individual is unique, the presentation will vary from patient to patient. So how are HIV signs in men and women different?
1. Common signs of HIV in men and women
In the early stages of the disease, about 2 to 4 weeks after infection, the patient will feel flu-like symptoms. It is a sign that the body is responding to the virus, and symptoms can last up to several weeks.
With acute HIV infection, symptoms may appear:
Chills. Tired. Fever. Genital ulcers. Mouth sores. Muscle pain. Night sweats. Rash. Throat ulcers. Swollen lymph nodes. Some people don't show early symptoms of HIV, so get tested if you suspect you've been exposed to HIV.
One reason to get tested for HIV early is to prevent the risk of infecting others. Knowing that you have HIV early will help in the treatment and care of yourself, as well as help your partner know to get tested early and take preventive measures.
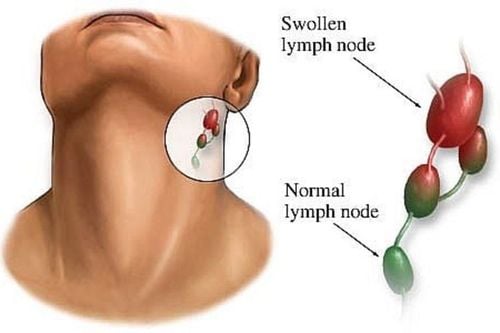
Sưng hạch bạch huyết có thể là dấu hiệu của nhiễm HIV cấp tính
2. Signs of HIV in women but not in men
While both men and women often experience the same symptoms when infected with HIV, there are some signs of HIV in women that are not found in men:
Change in menstrual cycle: menstrual flow may be less or increased, missed periods or had a bad premenstrual syndrome. Stress or sexually transmitted diseases (which are common in HIV-infected patients) can cause changes to the menstrual cycle. However, these changes may also be due to the effect of HIV on the immune system leading to hormonal effects in the body. Pain in the lower abdomen: this is one of the manifestations of an infection of the uterus, ovaries and fallopian tubes, called pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). For many women, it is one of the first red flags that they have HIV. In addition to lower abdominal pain, pelvic inflammatory disease can cause: Abnormal vaginal discharge. Fever. Irregular menstrual cycle. Pain during sex. Pain in the upper abdomen. Vaginal yeast infections: Many women with HIV have frequent vaginal yeast infections, up to several times a year. Sometimes it is the first symptom that the body has HIV infection. When infected with a fungus, the symptoms may be: Milky white vaginal discharge. Pain during sex. Pain when urinating. Vaginal itching, burning. Both men and women with HIV can get oral thrush, which causes swelling and a thick, white plaque that covers the mouth, tongue, and throat.
3. What to do when you suspect you have been exposed to HIV?
If the body shows one or more of the above symptoms, it is not necessarily HIV infection. Many other illnesses, such as the flu, can cause similar symptoms. Therefore, if you suspect that you have been exposed to HIV, whether you have symptoms or not, you should take an HIV test for sure results.
Another very important thing is to see a specialist as soon as possible, or go to the emergency room right away if you think you have been exposed to HIV, for HIV prevention treatment. However, the effectiveness of the treatment is limited to 72 hours from the time of exposure. Your doctor will prescribe a prophylactic dose taken once or twice daily for 28 consecutive days.
Nếu nghi ngờ bản thân đã phơi nhiễm HIV thì nên đi làm xét nghiệm HIV để có kết quả chắc chắn
4. What happens after the initial phase of HIV infection is over?
After the first few weeks of flu-like symptoms disappear, the disease progresses to the asymptomatic stage or chronic HIV infection. This stage is characterized by the disappearance of symptoms, the patient's body seems to be better, but HIV continues to multiply incessantly. And most HIV patients at this stage do not have any symptoms.
If HIV-infected patients are treated with antiretroviral therapy every day, the progression of the disease can be stopped and the patient's survival time can be extended nearly as much as that of the general population. Therefore, early detection and timely treatment are extremely important, both to control the progression of the disease, and to help prevent the transmission of HIV to others.
If infected with HIV, to prevent transmission to others, in addition to using antiretroviral therapy, the patient must also take many other methods, including being open about his or her medical condition to others. partners and use condoms correctly every time you have sex.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: Web MD