This is an automatically translated article.
After being exposed to HIV, many people often have the mentality of wanting to be tested for HIV immediately because they want to know if they are infected with HIV soon. However is this really true? And exactly how long after exposure to HIV does it take to test for HIV?
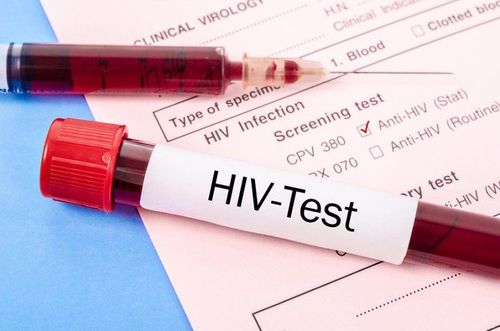
1. When to get tested for HIV?
As recommended by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), everyone between the ages of 13 and 64 should get tested for HIV at least once as part of their health care. periodically, because about 1 in 7 Americans have HIV without them knowing they have it.
People at higher risk should get tested more often. If you tested negative for HIV the last time, or the test was done more than a year ago, and you have one of the following characteristics, you should get tested for HIV as soon as possible:
Person in a gay relationship. Have had anal or vaginal sex with an HIV-positive person. Has had multiple sex partners since the last HIV test. Sharing needles or other items such as water or medical cotton with others. Used to sell sex. Have ever been diagnosed/treated for another sexually transmitted disease. Have been diagnosed/treated for tuberculosis or hepatitis. Have had sex with someone with at least one of the above characteristics. In addition, pregnant women also need to be tested for HIV so that they can protect both mother and baby from HIV infection.
Trắc nghiệm: Bạn có phân biệt được chính xác cảm lạnh và cúm mùa?
Cảm cúm và cảm lạnh là hai khái niệm mà chúng ta thường đánh đồng nó giống nhau, không phân biệt rõ ràng. Dưới đây là một số câu hỏi trắc nghiệm, giúp bạn có thêm những kiến thức phân biệt cảm lạnh và cảm cúm. Từ đó, có những biện pháp điều trị bệnh phù hợp.2. After exposure to HIV, how long does it take to test for HIV?
There is no HIV test that can detect HIV immediately after exposure. Therefore, if you think you have been exposed to HIV within the last 72 hours, talk to your doctor about post-exposure prophylaxis right away.
The time from when a person may be exposed to HIV until a test can definitively detect HIV infection is called the “window” period. The length of this phase varies from person to person and depends on the type of test used to detect HIV.
Several types of tests are commonly used to detect HIV:
Nucleic acid test (NAT): usually can detect HIV infection within 10 - 33 days of exposure to HIV. An antigen-antibody test done with intravenous blood can detect HIV infection 18 to 45 days after exposure to HIV. An antigen-antibody test done with blood from a finger may take longer to detect HIV, usually 18 - 90 days after exposure to HIV. In case it is necessary to do a test to confirm that you are not infected with HIV, the antigen - antibody test by intravenous blood will be preferred.
Antibody tests usually take 23 - 90 days to reliably detect HIV infection. Most rapid tests and home tests are antibody tests. In general, antibody tests that use venous blood can detect HIV earlier from infection than tests with blood from the finger or with an oral solution.
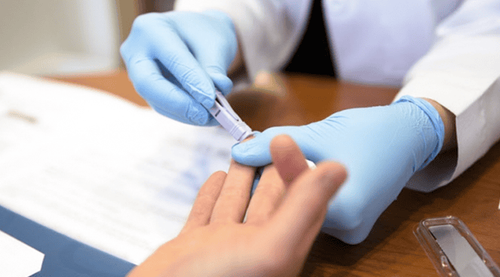
Cần trao đổi kỹ với bác sĩ chuyên khoa trước khi tiến hành làm xét nghiệm
You need to talk to your doctor about your health and the window period for the examination. If you take an HIV test after a latent HIV exposure and the result is negative, you need to get tested again after the test period, to know for sure if you have HIV according to the following schedule:
If If you are using a venous antigen-antibody test, you should retest 45 days after your last exposure. If you have other tests, you should get tested again at least 90 days after your last exposure. As such, HIV testing should not be performed immediately after exposure to HIV. How long after HIV exposure should be performed depends on the individual patient and the type of test used. That's why you need to talk to your doctor before taking the test.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)