This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Le Xuan Thiep - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital
Sinusitis is a common disease, the disease easily recurs in cold, dry weather or when the living environment has a high amount of smoke and dust. With the development of modern medicine, X-ray of the skull and sinuses helps to observe the inside of the sinus cavity, thereby accurately diagnosing the type of sinusitis for appropriate treatment.
1.Structure of the craniofacial region
The structure of the craniofacial region consists of many small bones, similar in size with many different shapes, between the bones connected by immovable joints. The only movable joint in the craniofacial region is the temporomandibular joint, so the only movable bone is the mandible.
The midfacial layer includes many bones arranged in layers and creates many different natural cavities and sinuses. Therefore, when patients have conventional radiographs (including cranial and sinus X-rays, X-rays of the brain, X-rays of the face, etc.), it is difficult to detect abnormalities due to many overlapping images.
Craniofacial diseases such as sinusitis or maxillofacial fracture are relatively complicated. In order to make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to combine the results of clinical examination to orient and assign appropriate cranial X-ray positions.
Cranial X-ray techniques are very complicated with many different imaging positions depending on the location of the lesion, different signs and symptoms, but first, the patient needs to take a whole skull X-ray to do it. comparison benchmark.
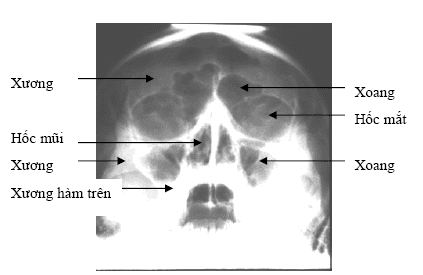
Hình ảnh x quang sọ não
2.The role of diagnostic imaging in sinus diseases
X-ray of the skull and sinuses evaluates features such as opacity, sinus size and sinus wall continuity. However, because these bones are small, stacked and have poor resolution, it is difficult to evaluate brain sinuses such as sphenoid and ethmoid sinuses. Therefore, the value of X-ray of the skull and sinuses is relatively limited and needs to be combined with clinical practice to make the most accurate diagnosis. Computed tomography CT-scan with multiple thin slices has the advantage of reducing overlap and increasing the detail of bones. CT scan can examine structures such as bones, soft tissues, nasal cavities, eye sockets, intracranial structures... In particular, computed tomography is very valuable in diagnosing and treating chronic sinusitis. or recurrent sinusitis. Cranial sinus MRI is difficult to clearly examine the bone structure.
3. Common cranial sinus X-ray positions
3.1. X-ray of the skull and sinuses in Blondeau position (nose - chin - film) Indications for X-ray of the skull and sinuses in Blondeau position include diseases such as: frontal sinusitis, sinusitis or sinusitis. When taking this position, the patient lies on the stomach, nose and chin touch the film, and the mouth is maximally open. The X-ray beam is projected from the back to the front. An important requirement for the most accurate and clear X-ray results is that the film must be balanced.
X-ray results of normal skull and sinuses will clearly observe the light space on both sides of the nasal cavity, the bone walls are clear. The maxillary and frontal sinuses are evenly lit when compared with the orbital lumen.
On the contrary, when a patient has sinusitis, the image of the maxillary sinus or frontal sinus will be blurred due to inflammation, swelling, and mucosal edema. In addition, the associated images that may be encountered are loss of the nasal cavity, excessive nasal peduncle or narrowing of the nasal peduncle.
In addition, on the X-ray film of the skull and sinuses, the degeneration of the mucosa, the thickening of the mucosa, or the pus-filled sinuses are also factors that make the sinuses blurry. The presence of discontinuous or poorly visualized bone walls suggests a high risk of malignancy.
When a foreign body is suspected, the patient should have a Blondeau position cranial X-ray combined with a tilted skull to determine the exact location of the foreign body. On the other hand, when the patient is suspected of having a tumor or polyp in the maxillary sinus, the combination of contrast agent injection and X-ray film can be taken for the clearest and most accurate image.
Sử dụng chất cản quang khi chụp phim X quang để hình ảnh rõ ràng, chính xác nhất
3.2. Hirtz X-ray (chin - top of film) Hirtz X-ray is indicated to diagnose sinusitis in locations such as anterior ethmoid sinus, posterior ethmoid sinus or sphenoid sinus. This postural cranial radiograph requires the patient to lie supine with the head protruding from the table so that the top of the head is in contact with the film and the X-ray beam goes from top to bottom.
Normally these sinuses on the film have a bright image, clearly observing the cell septum. Conversely, if the sieve cells are dense or opaque, it may be due to thickening of the mucosa or pus-filled sinuses or polyps.
3.3. Schuller position Cranial X-ray Schuller position skull X-ray (also known as the temporal - tympanic position) is valuable in diagnosing mastoiditis. The patient lies on his side, the X-ray beam is projected at an angle of 25-30 degrees from the axis of the two ears, so the X-ray will pass through the ear canal on the side of the shot, the most basic requirement is that the auricle must always be bent forward to image. The image taken is not over the mastoid.
Normally, the X-ray film will clearly see the septum and the cells. When the patient has acute mastoiditis, the image of the septum and septum will be blurred, no longer as clear as usual. In particular, when mastoiditis becomes chronic, the septum will completely disappear and the septum will be greatly blurred.
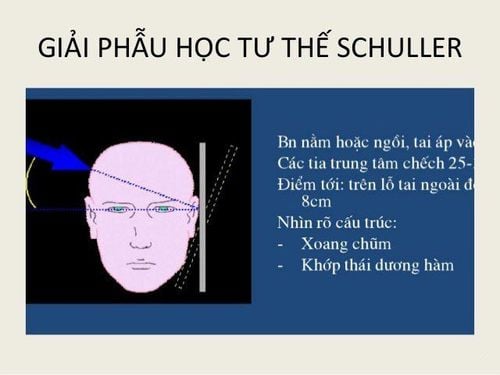
Giải phẫu học tư thế Schuller
3.4. Cranial X-ray Stenvers position Stenvers cranial-sinusoidal X-ray is used in cases of traumatic brain injury causing transverse scapula fractures, stony osteitis or tumors in the cerebellar pons...
The required position when taking this position is that the patient lies on his stomach, facing the film at the edge of the orbit, cheekbones and nose on the side to be photographed. The X-ray beam is directed from the nape of the neck, with the central beam perpendicular to the major axis of the scapula, going from the occipital bone to the cheekbone.
Normal Stenvers position skull X-ray film will show parts such as cochlea, inner ear, inner ear canal, vestibule, superior and outer semicircular canal and scapular process. The unobservable structure is the posterior semicircular canal. If the patient breaks the stony bone, the fracture line will be observed. Nerve tumor of VIII, the image of the inner ear canal will be dilated.
Is the cranial sinus X-ray able to evaluate features such as opacity, sinus size and sinus wall continuity? However, patients should inform their doctor about their own health status, so that the doctor can understand and have clear indications before conducting a cranial sinus X-ray to avoid unnecessary consequences. this.
Vinmec International General Hospital has applied X-ray techniques in examining and diagnosing many diseases. X-ray technique at Vinmec is carried out methodically and according to standard procedures by a team of highly qualified medical professionals, modern machinery system, thus giving accurate results, making a significant contribution to diagnosis and staging of the disease.
If you have a need for medical examination by modern and highly effective methods at Vinmec, please register for an online examination.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.