This is an automatically translated article.
Post of MSc. Nguyen Dac Tu, Product Quality Evaluation Team Leader and MSc. Pham Thi Thanh, Product Quality Assessment Specialist, Vinmec
CNC Center
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is known as a safe and effective autologous therapy when it is widely applied in many different medical fields. With those advantages, platelet-rich plasma is now also chosen by doctors to treat muscle damage.
1. Muscle damage and effects
Muscle damage is one of the most common forms of osteoarthritis, accounting for 45-55% of all sports injuries. In particular, inflammation and muscle tension are the two most common forms, accounting for 90%. When a muscle is damaged, inflammation can cause pain and swelling, which is markedly painful when moving or touching the muscle. Muscle pain can be mild (nearly uncomfortable) or so severe that the muscle cannot be used. Muscle pain can cause fatigue and limit mobility and make everyday activities like climbing stairs and lifting objects painful.
Muscle damage can be caused by acute or chronic injuries, often as a result of repetitive activities: rowing, tennis, baseball, golf, even poor posture. posture. Muscle pain or tension occurs when a muscle is overstretched, or even torn, often as a result of fatigue, excessive muscle movement, and irrationality. Depending on the extent of muscle damage, there are appropriate treatments, however, the standard treatment is to minimize bleeding or pain, swelling.
Mild to moderate muscle strain can be effectively treated at home with ice or heat, rest, exercise, and anti-inflammatory medication. Severe strains or muscle tears may require medical intervention. Mild to moderate strains will resolve on their own in a few weeks, while severe strains can last for months. Injuries involving muscles are one of the major challenges for medicine because the healing process of muscle damage is often slower than that of other injuries, and the recovery is not complete. Some studies show that the use of anti-inflammatory drugs helps reduce pain, but can interfere with the healing process of muscle tissue.

Điều trị tổn thương cơ do các chấn thương cấp tính hay mãn tính
2. Platelet-rich plasma – effective therapy for muscle damage
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is known as a safe and effective autologous therapy when it is widely used in many medical fields ranging from dental surgery. to the treatment of hair loss and baldness. In orthopedic surgery, PRP has been shown to be effective in treating lateral epicondylitis, knee osteoarthritis, rotator cuff tear, patellar tendonitis, Achilles tendonitis, plantar fasciitis. Basic scientific studies have demonstrated that the process of muscle tissue regeneration and formation involves growth factors in PRP involved in the healing process such as IGF-1, HGF, FGF-2, TGFβ-1, TNF-α, PDGF. Therefore, PRP is considered as one of the potential therapies in the treatment of muscle damage.The results of studies at both in vitro, in vivo and clinical levels show that PRP stimulates the formation of muscle tissue (myogenesis), regulating muscle fibrosis during wound healing. At the 2nd World Congress of Regenerative Medicine, Sanchez reported the effectiveness of PRP in treating 20 professional athletes with varying degrees of muscle damage. For small muscle tears, only 1 injection of PRP is needed, while for larger tears, 2-3 times of PRP are needed under ultrasound guidance. The results showed that the injured muscle area was no longer swollen, painful, and the recovery time was twice as fast as expected [5]. Rossi and colleagues conducted a study comparing recovery time and risk of disease recurrence for 72 athletes with grade 2 myositis. The results showed that the group treated with PRP (34 people) had a longer time. Mean recovery was 21.1 days, while the control group (38 people) had a recovery time of 25 days. The group treated with PRP significantly reduced pain and swelling compared to the control group [2]. Similar to Delos' report, the athletes who received PRP injections had no complications, and the recovery time was also shortened by half compared to the group that did not receive PRP [3].
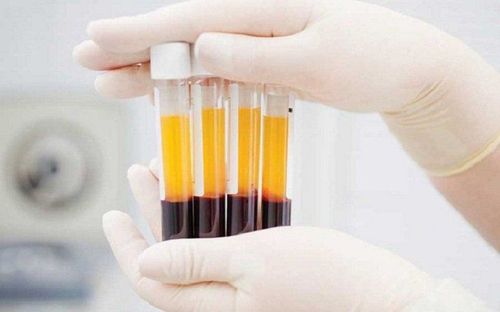
Ứng dụng huyết tương giàu tiểu cầu trong hỗ trợ và điều trị tổn thương cơ
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has a treatment package for musculoskeletal diseases with platelet-rich plasma, applying PRP (also known as platelet-rich plasma) technology in the treatment of musculoskeletal diseases. joints, including:
Tendon disease and tendinitis; Achilles tendinitis Inflammation of the plantar fasciitis (common in golfers and tennis elbows) Plantar fasciitis Tendonitis and knee tendonitis (1-sided for player injuries: soccer, basketball, ball) throw) Shoulder rotator cuff syndrome Sports injuries Injury and compression of nerves Osteoarthritis in the early stages In addition, there are many other musculoskeletal diseases, so when suffering from musculoskeletal diseases, Injury patients can go to Vinmec International General Hospital for examination and treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References
Setayesh K, et al (2018), “Treatment of muscle injuries with platelet-rich plasma: a review of the literature”, Current Reviews in Musculoskeletal Medicine. Rossi L.A., et al (2016), “Does platelet-rich plasma decrease time to return to sports in acute muscle tear? A randomized controlled trial”, Sports Medicine. Delos D., et al (2013), “Muscle injuries in athletes: enhancing recovery through scientific understanding and novel therapies”, Sports Health, 5(4), 346-352. Hamid M.S.A., et al (2014), “Platelet-rich plasma injections for the treatment of hamstring injections”, Am J Sports Med, 42(10), 2410-2418. Sanchez M., et al (2005), “Application of autologous growth factors on skeletal muscle healing”, Presented at 2nd World Congress on Regenerative Medicine, May 18-20, Leipzig, Germany. Terada S., et al (2013), “Use of an antifibrotic agent injury the effect of platelet-rich plasma on muscle healing after”, J Bone Joint Surg Am, 95(11), 980-988.