This is an automatically translated article.
Antidepressants, including SSRIs and SNRIs, can help you improve your symptoms of depression for a while. However, stopping these drugs can lead to antidepressant discontinuation syndrome and a number of health problems. Ideally, you should consult your doctor if you intend to stop using the drug.
1. Antidepressants, including SSRIs and SNRIs, can help you improve your symptoms of depression for a while. However, stopping these drugs can lead to antidepressant discontinuation syndrome and a number of health problems. Ideally, you should consult your doctor if you intend to stop using the drug
Antidepressant discontinuation syndrome usually occurs in about 20% of patients after abrupt discontinuation of antidepressants for at least six weeks. Certain types of antidepressants, including serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).
Typical symptoms of antidepressant discontinuation syndrome usually include:
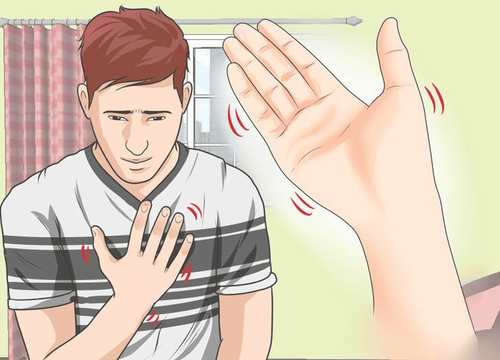
Nausea . Feeling dizzy. Overbalance. Difficulty sleeping or insomnia. Sensory disturbances. Feel worried. Cuong yang. These symptoms are usually mild, lasting 1 to 2 weeks and are quickly extinguished when the antidepressant is reintroduced. Antidepressant discontinuation syndrome tends to be more likely with longer duration of treatment and shorter half-life of the treatment.
When you stop taking them, some antidepressants leave the body quickly (short half-life), while others leave the body more slowly (long half-life). Symptoms of antidepressant discontinuation can occur in either case, especially when you stop taking them suddenly.
Before prescribing antidepressants, physicians should warn patients of potential problems associated with abrupt discontinuation of the drug. Alerting patients to common clinical events will help prevent future episodes and reduce the risk of misdiagnosis.

Ngưng uống thuốc chống trầm cảm đột ngột có thể gây ra tác dụng phụ nghiêm trọng.
2. What are SSRIs and SNRIs?
SSRIs are a type of antidepressant that includes sertraline (Zoloft), paroxetine (Paxil), and fluoxetine (Prozac). These drugs help stimulate the production of the neurotransmitter serotonin in the brain. Using SSRIs can help reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety, and regulate mood.
SNRIs are another class of antidepressants, including venlafaxine (Effexor) and duloxetine (Cymbalta). These drugs work on 2 main neurotransmitters, norepinephrine and serotonin.
Overall, these two antidepressants are both groundbreaking. In the past, older antidepressants can cause many difficult-to-tolerance side effects such as fatigue, dry mouth, dry eyes, and difficulty urinating. In contrast, SSRIs and SNRIs are generally well tolerated by the body. However, like other drugs, they still have some minor side effects, including the risk of affecting your sexual functions. Ideally, you should consult with your doctor to be able to make the right choice of medication for you.
Treating depression with medication can help you get better. In addition, cognitive-behavioral therapies, social activities, and exercise have also been shown to be very helpful for depression.
3. Some notes when stopping taking antidepressants
Let's say you've been taking an SSRI such as paroxetine for a few years and find your depression is getting better. At this point, you feel ready to stop using the drug, but are concerned about the symptoms of possible antidepressant withdrawal syndrome. To avoid this, you should consult with the doctor who prescribed the medicine for you.
Some antidepressants can be stopped immediately, however, most SSRIs and SNRIs need to be tapered off slowly. You should reduce your dose to once a week, every two weeks, or even once a month. If you have been taking a higher dose of an antidepressant, which can last up to 6 months, you should not reduce the dose too quickly to avoid the appearance of withdrawal symptoms.
Please follow the website: Vinmec.com regularly to update other useful information.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: health.harvard.edu, aafp.org