This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II Nguyen Binh - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital.Suture surgery to restore the diaphragm is a major surgery, requiring double-lumen endotracheal anesthesia combined with lung collapse to control the patient's breathing during surgery and resuscitation after the end. surgery.
1. In what cases is anesthesia indicated?
When the patient received the indication for laparoscopic surgery to suture the diaphragmatic perforation. Surgery is caused by perforation or rupture of the diaphragm or by trauma or hernia of the diaphragm.The cause of the injury can be:
Through the tear of the diaphragm, the visceral organs in the abdomen get into the chest after an accident or after a while, causing a diaphragmatic hernia. Diaphragm perforation due to thoracic and abdominal trauma, it may be accompanied by other abdominal and thoracic injuries. Cases of relative contraindications to anesthesia: The patient does not agree to perform surgery. Failure to ensure adequate surgical facilities as well as anesthesia and resuscitation equipment. The technician is not well versed in surgical manipulations.
2. Prepare for anesthesia
2.1. Performers Performers are specialists and nurses with experience in the emergency department.
2.2. Implementation means A system of machines to help anesthetize and support breathing for the patient, life function monitor, hand squeeze oxygen source, defibrillator, suction machine,...
Máy theo dõi chỉ số sinh tồn cần được chuẩn bị trong quá trình gây mê
In addition, indispensable laryngoscope, and endotracheal tube type 2 caliber 32F to 39F, mask, suction tube, bulb, Magill pliers, oropharyngeal cannula, soft mandrin.
Lidocaine 10% spray and Salbutamol spray.
Means used for difficult intubation cases: laryngeal mask, Cook tube, flexible bronchoscope, mouth opener, tracheostomy kit,...
Means used for arterial blood pressure or central venous catheterization.
2.3. Patients with diaphragmatic perforation should be given endotracheal anesthesia to avoid complications of lung compression, due to air entering the pleura through the perforated area of the diaphragm during abdominal surgery. .
Patients need to be examined under anesthesia before surgery to detect and prevent potentially life-threatening risks, it is necessary to explain to the patient and family members to cooperate.
Evaluation of difficult intubation, and associated chest trauma, pneumothorax, effusion. Use sedation the night before surgery if the patient has a session.
3. Steps to administer anesthesia in laparoscopic surgery to suture diaphragmatic perforation
Check the patient's record: The tests performed must be within the allowable limits for surgery (pay attention to tests to assess the respiratory status such as: pulmonary ventilation, blood gases). Check the patient: Make sure the patient's name is correct, the department, what type of surgery, which side... Technical implementation: Prepare the patient:
Install monitoring equipment including: BP, electricity heart, SpO2... Prepare fully stethoscope, and suction machine. Make peripheral transmissions with a minimum of 18G needles. Before that, more pleural drainage should be placed on the side of the lesion to ensure the safety of the patient during induction of anesthesia. Prepare anesthetics and resuscitation drugs. Give the patient 100% oxygen before surgery, at least 3 minutes.
Cần chuẩn bị đầy đủ cơ số thuốc sử dụng trong quá trình gây mê
Initiating anesthesia:
Pain relievers for patients: fentanyl, sufentanil, alfentanil... Drugs that cause drowsiness (thiopental, propofol, ketamine). Muscle relaxants (succinylcholine, pavulon, arduan, tracrium) pay attention to only inject muscle relaxants into patients when mask breathing has taken effect. Technique:
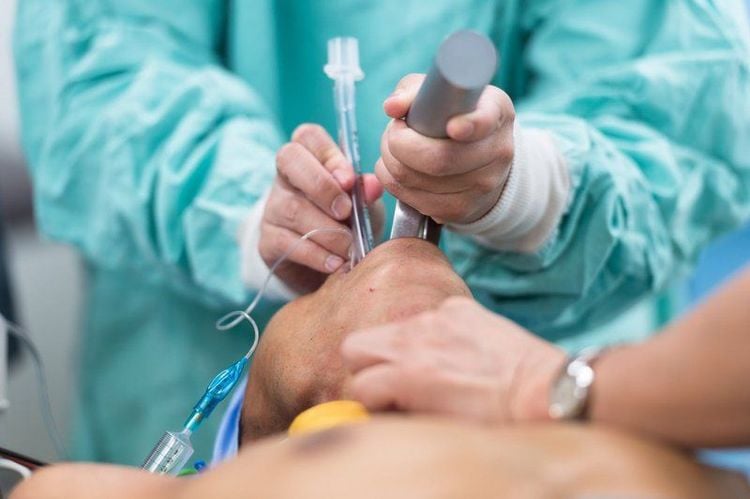
After induction of anesthesia with sufficient depth and muscle relaxation, help the patient to lie on his back. Bring the endotracheal light up and move forward to push the patient's tongue to the left, if the glottis is visible, local anesthetic is used by using 5% xylocaine sprayed 3-5 times into the air. manage. Use the right hand to immediately insert the double-bore endotracheal tube with the spur posteriorly for direct insertion through the glottis. If the tip of the tube and the spur both pass through the vocal cords, withdraw Mandrin and rotate the endotracheal tube 90 degrees counterclockwise. Carry out inflating two Cuff balloons, pay attention not to inflate more than 5ml of air in cases of bronchial Cuff. Connect the 2 tubes of the endotracheal tube with a Y-shaped raccord to help with ventilation. Two Y-branch clamps are performed in turn to help control the ventilation of each lung. A flexible endoscope can be used to help check the position of the endotracheal tube. Secure the endotracheal tube with two adhesive tapes. Place the cannula in the patient's mouth to avoid biting the tube, and insert a nasogastric tube.
Maintain anesthesia:
Endotracheal anesthesia when breathing is controlled. Maintain ventilation in both lungs as much as possible.
Respiration by a machine that helps maintain anesthesia with anesthetic drugs for the airways, muscle relaxants by injection or maintained with a continuous infusion pump.
Before the end of the operation, the dose of volatile anesthetics that is being administered into the patient's body must be reduced. Remove all sputum from both branches of the endotracheal tube, and fully expand the lungs before performing chest closure.
If inhaled anesthetics are used, the drug must be stopped at the end of the surgery, fully opened the valve, increased ventilation, and compressed the reserve balloon to release the amount of anesthetic in the patient. enchantment ring.
In addition, it is necessary to monitor parameters when maintaining anesthesia: blood pressure, pulse, SpO2, EtCO2, blood gases and prevent cases of endotracheal intubation, or tube folding, and the tube being pushed deep.
Gây mê nội khí quản được duy trì khi hô hấp được điều khiển
4. Caring for patients after surgery
After completing the surgery, the patient will be transferred to the emergency department to continue monitoring the health status. Note:
Keep your body warm, keep your head high and provide respiratory support if needed. Use intravenous antibiotics for about 7-10 days. Fasting for the gastrointestinal tract to recover, complete intravenous feeding for 2-3 days, then eating by mouth or using a nasogastric tube. Take care of the wound every day, can proceed to cut sutures after 7 days.
5. Things to note after surgery
If the following complications occur after surgery, it is necessary to quickly and safely handle:
Pneumothorax: put the patient on mechanical ventilation, drain the pleural space. If the patient has sepsis, pneumonia, urinary tract infection, etc., it is necessary to conduct an antibiotic chart or receive antibiotic treatment in time. Bleeding, leaking in the patient's abdomen: open the abdominal wall to re-examine and stop the bleeding. Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consulting services. and comprehensive, professional medical treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Doctor Nguyen Binh has more than 20 years of experience in the field of anesthesia - resuscitation in thoracic surgery, anesthesiology resuscitation for elderly patients... Currently a Doctor of General Surgery, National General Hospital Vinmec Ha Long International.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.