This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Ta Quang Hung - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec International General Hospital Da Nang.Peripheral iridotomy is the treatment of choice for people who have or are at risk of acute, chronic, or narrow-angle glaucoma. Optical iridotomy will facilitate the circulation of aqueous humor from the back room to the front room to resolve pupillary blockage.
1. Overview
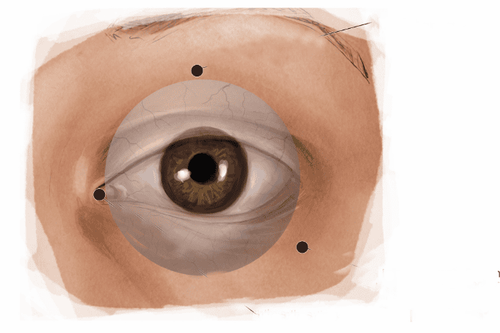
Paraocular anesthesia is a technique of injecting local anesthetic into the eye socket outside the muscle apex, distal optic nerve, distal eyeball, sclera, and visual hole. The two sites of application of injection are the junction between the medial and 2⁄3 of the superior border of the orbital bone and the junction between the medial 1⁄3 and the medial 2⁄3 of the inferior border of the orbit. In paraocular anesthesia, the anesthetic is injected directly onto the nerve endings and nerve trunks around the eyeball, helping to inhibit pain sensation and stop eyeball movement.Advantages of anesthesia near the eyeball:
Anesthesia technique is simple and easy to perform. Good anesthetic effect. Good pain relief. Rapid decrease in eyeball movement. Low cost. Disadvantages of para-ophthalmic anesthesia:
Risk of mistakenly injecting into blood vessels or eyeball (especially when the axis of the eyeball is over 26mm). May cause glaucoma if large amounts of local anesthetic are injected. Causes more pain if compared with subtenonal anesthesia.
2. Indications and contraindications
Indication caseParaocular anesthesia is used for patients who need optical iridotomy according to the classic method.
Contraindications
Para-ocular anesthesia is not applied in the following cases:
People with blood clotting problems. People who are allergic to anesthetics. The patient is uncooperative.
3. Prepare for anesthesia
Implementation teamAnesthesiologist Anesthesiologist Resuscitation Medical equipment:
5ml or 10ml syringe (25G needle, 25mm long). Kim withdrew the drug. Antiseptic cotton swab. Antiseptic solution (Betadine 10%). Local anesthetic solution: Lidocaine 2%; Hyaluronidase 180UI/ml; Bupivacaine 0.5%. Bars or overrides.
Confirm the correct name and condition of the eye requiring surgery (optical iridotomy). Instruct the patient to wear the correct medical clothing. The patient is explained to work with the doctor to help ensure success and increase the safety of the procedure. Preparation of medical records, complete tests, paraclinical investigations to support diagnosis and surgical anesthesia, legal approval of surgery, written commitment before surgery under anesthesia and resuscitation.
4. The process of anesthesia next to the eyeball to treat retinal detachment
Check patient informationCheck records: identify issues related to the anesthetic procedure through laboratory tests and investigations.
Check the patient with the right name, right pathology, right eye that needs surgery.
Steps to take
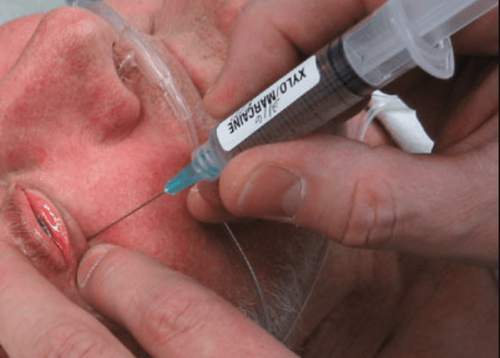
Get local anesthetic: 3-4ml Lidocaine 2% and 3-4ml Bupivacaine 0.5%, Hyaluronidase 180UI/ml. Put the patient in supine position, eyes straight, disinfect the injection site and the area around the eyes with a cotton swab dipped in 10% Betadin solution. Locate the 1st injection: The junction between the external 13 and the 2⁄3 in the lower border of the orbit, pointing the needle upwards. Locate the 2nd injection: The junction between the 1⁄3 inside and the 2⁄3 outside the upper border of the eye socket, pointing the needle down. When the needle penetrates the skin of the eyelid, combine gently pushing the eyeball up and at the same time by pressing the finger into the groove between the eye socket and the eyeball. When the needle is in the correct area of the equator of the eyeball, slowly pass the needle over the equator of the eyeball and hold the tip of the needle outside the muscle tip. Ask the patient to squint and gently aspirate the piston to check the position of the needle. When making sure that the needle is in the correct position, slowly inject local anesthetic combined with palpation to control the estimated eye pressure. If after injection, there is a feeling of fullness and drooping of the eyelids, it means that the anesthetic operation next to the eyeball has been performed well. When the patient's eyes are completely closed, apply pressure on the eyeball with a pressure bar or bulb for about 5-10 minutes to spread the anesthetic, help reduce intraocular pressure and reduce local edema. Stop squeezing the eyeball and check for eye motion. If the eye is motionless and the pupil is slightly dilated, it is an indication that the periocular anesthesia is good.
5. Accident monitoring and handling
Injected into a blood vessel by mistake: Perform respiratory and circulatory resuscitation as in the case of anesthetic poisoning. Hematoma at the injection site: treated by applying light pressure on the conjunctival edema to avoid edema spreading to the surrounding area. Orbital hematoma : Postponing optical iridotomy and treating as contusion eye trauma. Eyeball Needle: Postpone optical iridotomy and treat as transocular trauma. If you are experiencing vision problems, go to a medical facility immediately to be examined and treated by a doctor as soon as possible. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has vision-related service packages such as:Refractive error screening package Cataract examination and consultation package Ortho-K Master package. Doctor Ta Quang Hung has over 10 years of experience in teaching and practicing in the field of Anesthesia and Resuscitation. Currently, he is an Anesthesiologist, General Surgery Department - Vinmec International Hospital Da Nang.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.