This is an automatically translated article.
Located in the main oral cavity, the human tongue is a muscular mass covered by mucosa, with the characteristic of easy mobility. The normal human tongue plays an important role for chewing, swallowing, tasting and talking.
1. Tongue structure and function
Tongue is a muscular taste organ located in the oral cavity, covered with pink moist tissue called mucosa. The structure of the tongue consists of two main parts, the tongue frame and the muscles.
In terms of external appearance, behind the dorsal surface of the human tongue there is a V-shaped groove, called the terminal groove. V-shaped apex has a small pit, also known as the foramen, this is a relic of the thyroid duct from the embryonic period. One of the three major salivary glands located under the tongue, helping to pour saliva into the oral cavity, contributing to the digestion of food and keeping the oral mucosa moist.
The tongue is attached to the back of the oral cavity and protrudes anteriorly by means of a network of hard tissues and mucous membranes. The part that holds the front of the blade is called the blade brake (frenum). At the back of the mouth, the tongue is anchored to the U-shaped hyoid bone in the neck.
The human tongue is a very important organ for chewing and swallowing food, as well as helping us to talk. The tip of the tongue moves freely and is very flexible thanks to the coordination of the transverse and longitudinal muscles in the tongue, neck and jaw. When not eating or talking, the normal human tongue will fit in the mouth and rest the tip of the tongue against the front teeth.
Small papillae give a rough texture to the tongue. There are thousands of taste buds covering the surface of the papilla. This is a collection of nerve cells, connected to the nerve and transmitted to the brain. The number of taste buds on the adult tongue is about 5000, but children and the elderly will be much less. Like skin cells, taste buds are also constantly being replaced and diminished over time.

Lưỡi người có vai trò nhai và nuốt thức ăn
There are four common tastes that the tongue can taste: sweet, sour, bitter and salty. When we taste the glutamate in MSG, we get a fifth flavor called umami. Actually, spicy and acrid are not the same taste. The spicy sensation that makes you choke and water your eyes is due to capsaicin, mainly because the nose smells it rather than the tongue. And acrid is just the feeling when the mucosa is hunted and the saliva astringent in the tongue.
The normal human tongue has many nerves that detect and transmit taste signals to the brain. All parts of the tongue can detect these four common tastes. Therefore, the "taste map" - the specific part on the human tongue to taste certain tastes, mentioned by many documents is not really accurate.
The normal human tongue will not properly perceive the taste and heat of food when having a cold, fever or difficulty in digestion. The cause is that the taste buds are covered with turbidity and are not activated. Therefore, sick people often do not want to eat. In addition to taste receptors, the nerves of the normal human tongue also have branches to sense touch, temperature, and motor muscles.
2. Possible problems with the human tongue
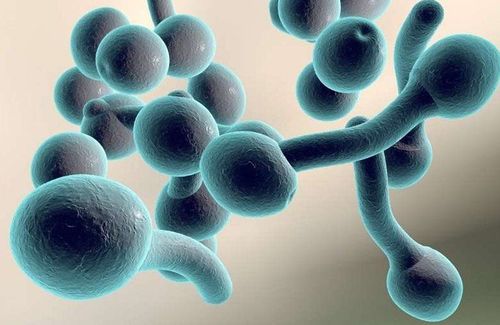
Thrush (candidiasis) A yeast called Candida albicans, usually grows on the surface of the mouth and tongue. It can happen to anyone, but is more common if you take steroids or have a suppressed immune system, as well as young children and the elderly.
Oral cancer A growth or sore that appears on a person's tongue and grows steadily. Oral cancer is more common in people who smoke and/or drink a lot of alcohol.
Macroglossia This condition is divided into different categories based on the cause, which can be congenital, inflammatory, traumatic, cancerous and metabolic disorders. Thyroid disease, lymphoma, and birth defects are among the common causes of an enlarged tongue.

Lạm dụng thuốc tăng nguy cơ mắc bệnh ung thư miệng
Map blade Tongue appears as large, dark colored spots with clear boundary edges. This condition causes the normal human tongue to look like a geographical map, with images of continents. These spots are not permanent, but change their appearance periodically. However the map blade is a harmless condition.
Burning mouth syndrome This is a relatively common problem, where the tongue feels burning or burning, and has an increasing strange taste or sensation. In general, burning mouth syndrome is harmless and can be caused by a mild neurological problem.
Atrophic glossitis The structure of the tongue loses its roughness and roughness, on the contrary, it becomes smooth. Sometimes the cause of this condition is anemia or vitamin B deficiency.
Mouth ulcers / Canker sores Small and painful sores that periodically appear on the tongue or mouth. This is a relatively common condition, but the cause is unknown. This aphthous sore is also unrelated to the sore caused by the herpes virus. Mouth sores, canker sores are not contagious.
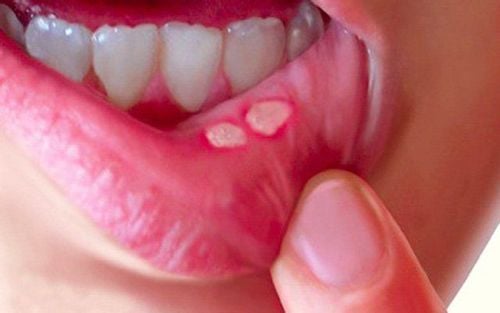
Nhiệt miệng là bệnh lý thường gặp ở miệng
Oral leukoplakia White patches appear on the tongue, which can be scraped off easily. Oral leukemia can be benign, but it can also progress to oral cancer.
Tongue hair The papillae of the normal human tongue can be overgrown, producing an unusually white or black surface, instead of a pinkish red. Removing the papilloma will help correct this harmless condition.
Herpes stomatitis Herpes virus can cause cold sores on a person's tongue, or cold sores on the lips and mouth.
Oral lichen planus This is a harmless condition that can affect the skin or mouth. The cause of lichen planus is unknown, but it is possible that the immune system attacks the skin and lining of the mouth.
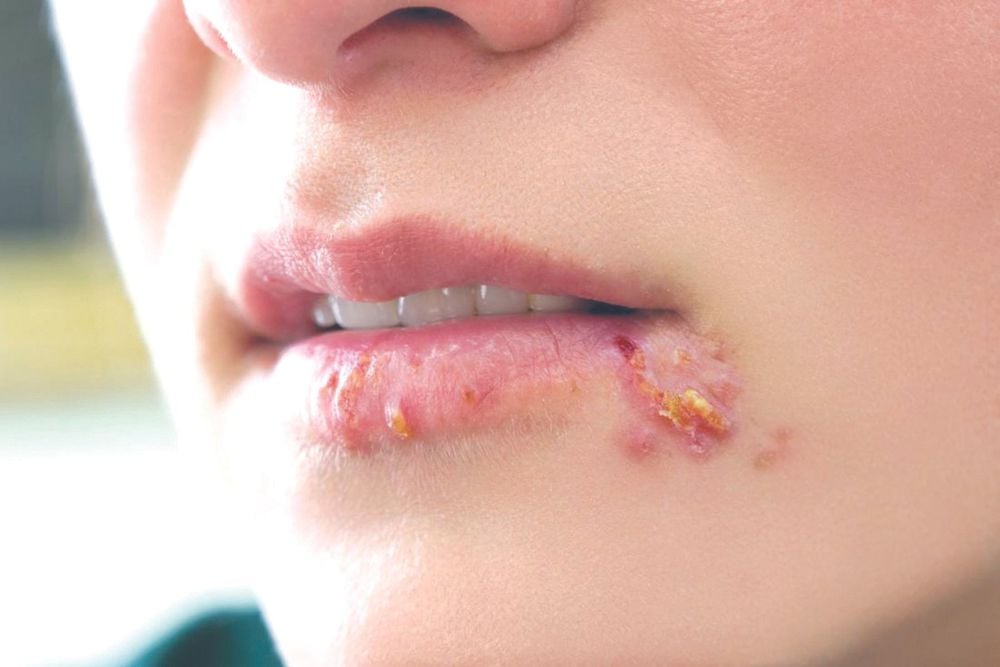
Viêm miệng herpes là bệnh lý truyền nhiễm gây ra do một loại virus có tên là HSV
3. Diagnosing and Treating Tongue Problems
3.1. Test
Biopsy: Usually done to check for oral cancer. Your doctor will take a small tissue sample from an abnormal area on your tongue to take to a lab for testing. Taste Discrimination Test: Four different sweetener solutions were used to assess the ability of the normal human tongue to perceive flavors and odors.
3.2 Treatment
Steroid gel: Applying a steroid gel prescribed by your doctor (like Lidex) will help speed up the healing process of mouth sores. Silver nitrate: Your doctor may apply this chemical to an ulcer to speed healing and reduce pain. Anesthesia gel (lidocaine): When applied to the tongue, lidocaine gel provides immediate pain relief by its ability to numb, but the effect is only temporary until the drug wears off. Antifungal drugs: Medicines that can get rid of the fungus Candida albicans, the type that causes thrush. Additionally, mouthwashes and antifungal tablets are equally effective. Tongue scraping: This is a simple way to remove overgrown papillae that cause a black or white hairy tongue. Vitamin B: Supplementing with B vitamins can correct symptoms experienced by people with this nutrient deficiency. Surgery: May be indicated to remove tumors in patients with oral cancer or leukemia.

Chế độ ăn giàu vitamin B giúp ngăn ngừa các bệnh lý về lưỡi
The normal human tongue is an important part of life, especially some diseases can be expressed through the tongue. Therefore, it is necessary to actively protect the tongue by cleaning the teeth daily, ensuring a complete and balanced diet so as not to lack vitamins. In addition, you should also have regular check-ups to detect abnormalities early. When suffering from tongue disease, it is necessary to follow the treatment regimen of the doctor.
Vinmec International General Hospital is a high-quality medical facility in Vietnam with a team of highly qualified medical professionals, well-trained, domestic and foreign, and experienced.
A system of modern and advanced medical equipment, possessing many of the best machines in the world, helping to detect many difficult and dangerous diseases in a short time, supporting the diagnosis and treatment of doctors the most effective. The hospital space is designed according to 5-star hotel standards, giving patients comfort, friendliness and peace of mind.
To register for an examination at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact the nationwide Vinmec Health System Hotline, or register online HERE.
Reference source: .webmd.com