This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II Pham Thi Tuyet Mai - Obstetrician and Gynecologist - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Vinmec Hai Phong International General HospitalThe term sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) - a sexually transmitted infection (STI) or a venereal disease (VD) is used to refer to a condition that is primarily transmitted from one person to another. through sex.
1. Symptoms of STDs in Men
People can live with STDs without developing symptoms. But some STDs cause obvious symptoms. In men, common symptoms include:
Pain or discomfort during sex or urination. Sores, lumps, or rashes on or around the penis, testicles, anus, buttocks, thighs, or mouth. Abnormal discharge or bleeding from the penis. Testicles are painful or swollen.
2. Symptoms of STDs in Women
In many cases, STDs do not cause noticeable symptoms. Some of the common STD symptoms in women include:
Pain or discomfort during sex or urination. Sores, bumps, or rashes on or around the vagina, anus, buttocks, thighs, or mouth. Unusual discharge or bleeding from the vagina. Itching in or around the vagina.
3. Types of STDs
Many different types of infections can be sexually transmitted. The most common STDs are described below.
3.1 Chlamydia A bacteria that causes chlamydia. Many people with chlamydia have no noticeable symptoms. When symptoms develop, they usually include:
Pain or discomfort during sex or urination. Green or yellow discharge from the penis or vagina. Lower abdominal pain. If left untreated, chlamydia can lead to:
Infection of the urethra, prostate or testicles. Pelvic inflammatory disease. Difficulty conceiving. If a pregnant woman has been infected with chlamydia, she can pass it on to her baby during delivery. Children can get diseases:
Pneumonia. Eye infection. Blind. Antibiotics are the most effective treatment for chlamydia commonly used.
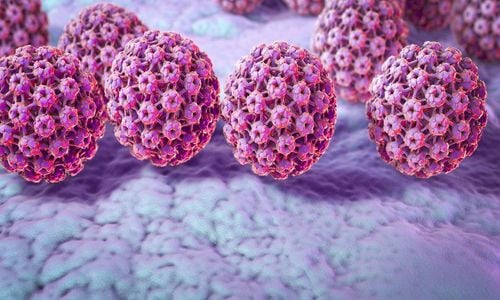
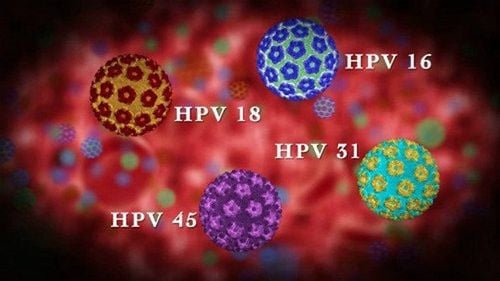
3.2 HPV (human papillomavirus) The human papillomavirus (HPV) is a virus that can be passed from person to person through skin contact or sexual contact. There are different strains of viruses, some more dangerous than others.
The most common symptom of HPV is warts on the genitals, mouth or throat.
Certain strains of HPV infection can lead to cancer, including:
Oral cancer Cervical cancer Vulvar cancer Penile cancer Rectal cancer While most viral infections do not develop into cancer, there are still some strains of viruses that are capable of causing cancer. According to the National Cancer Institute, most HPV-related cancers in the United States are caused by HPV 16 and HPV 18. These two strains of HPV account for 70% of all cervical cancer cases.
3.3 Syphilis Syphilis is a bacterial infection. The disease often has no obvious symptoms in the early stages, so it is rarely detected.
The first symptom to appear is a small round sore, called a chancre. It can develop on the genitals, anus, or mouth. It is painless but very contagious. Later symptoms may include: rash, fatigue, fever, headache, joint pain, weight loss, hair loss.
If left untreated, late-stage syphilis can lead to: vision loss, hearing loss, memory loss, mental illness, brain or spinal cord infection, heart disease, even death .
3.4 HIV HIV can damage the immune system, increasing the risk of infection with other viruses or bacteria and some cancers. If left untreated, it can lead to stage 3 HIV, known as AIDS. But with today's treatment, many people with HIV do not progress to AIDS.
3.5 Gonorrhea Gonorrhea is another common bacterial cause of STDs. It is also known as "clapping".
Many people with gonorrhea develop no symptoms. But when present, symptoms may include:
White, yellow, beige or green discharge from the penis or vagina. Pain or discomfort during sex or urination. Urinating more often than usual. Itching around the genitals. Sore throat. If left untreated, gonorrhea can lead to:
Infection of the urethra, prostate or testicles. Pelvic inflammatory disease. Difficulty conceiving. A mother can pass gonorrhea to her infant during childbirth. When that happens, gonorrhea can cause serious health problems in the baby. That's why many doctors encourage pregnant women to get tested and treat for STDs if they have one. Gonorrhea can usually be treated with antibiotics.
3.6 Head lice Pubic lice are another name for pubic lice. They are tiny insects that can reside on pubic hair. Like head and body lice, they feed on human blood.
Common symptoms of head lice include:
Itching around the genitals or anus. Small pink or red bumps around the genitals or anus. Mild fever. Lack of energy. Irritability. You may also see lice or their small white eggs around the hairline. Using a magnifying glass can help spot them.
If left untreated, lice can be spread to others through skin contact or through shared clothing, bed linen or towels. Scratched bites can also become infected. Therefore, it is best to detect and treat head lice as soon as possible.
3.7 Trichomonas According to the CDC Trusty Source, less than a third of people with Trichomonas develop symptoms. As symptoms develop, they may include:
Discharge from the vagina or penis. Burning or itching around the vagina or penis. Pain or discomfort when urinating or having sex. Urinate frequently. The discharge usually has an unpleasant or fishy odor. If left untreated, Trichomonas can lead to: urethral infection, pelvic inflammatory disease, difficulty conceiving. Trich can be treated with antibiotics.
3.8 Herpes Herpes is a shortened name for the herpes simplex virus (HSV). There are two main strains of the virus, HSV-1 and HSV-2. Both can be transmitted sexually. It is a very common STD.
HSV-1 mainly causes cold sores in the mouth. However, HSV-1 can also be passed from one person to another during oral sex. From there, causing genital herpes.
HSV-2 mainly causes genital herpes. The most common symptom of herpes is blistering sores. In the case of genital herpes, these sores develop on or around the genitals. In oral herpes, they develop on or around the mouth.
3.9 Other STDs Chancroid, lymphogranuloma venereum, granuloma inguinale, molluscum contagiosum, scabies.

4. STDs from oral sex
STDs can be transmitted from one person's genitals to another by mouth or throat and vice versa.
When oral STDs cause sore throat symptoms or sores around the mouth or throat. Many STDs are curable. For example, the following STDs can be cured with antibiotics or other treatments: chlamydia, syphilis, gonorrhea, lice, trichomoniasis. The following STDs are currently incurable: HPV, HIV, herpes.
However, even if an STD cannot be cured, it is still manageable. It is important to detect and diagnose the disease early. Treatment options are often available to help ease symptoms and reduce the risk of passing the STD on to others.
5. STDs and pregnancy
Pregnant women can pass STDs to their unborn baby during pregnancy or to the baby during delivery. In infants, STDs can cause complications. In some cases, they can be life-threatening.
To help prevent STDs in babies, doctors often encourage pregnant women to get tested and treat for STDs if they have one. Your doctor may recommend testing for STDs even if you have no symptoms. In some cases, it may be advisable to give birth by cesarean section to reduce the risk of transmission during delivery.
6. Diagnosis of STDs
In most cases, doctors can diagnose STDs based on symptoms alone.
Depending on your sexual history, your doctor may recommend testing for STDs even if you have no symptoms. This is because STDs do not cause noticeable symptoms in many cases. But even an STD with no symptoms can be harmful to your health and pass it on to others.
Diagnose most STDs using urine or blood tests. At the same time, a sample can be taken by wiping a cotton ball on the genitals. If ulcers are present, the ulcer site may be examined.
Home testing kits are also used for some STDs, but the results are not always reliable. Use them with caution.
The Pap smear is a test for STDs. The Pap smear checks for the presence of precancerous cells on the cervix. It can be combined with an HPV test. A negative Pap smear doesn't mean you don't have an STD.
7. Treatment of STDs
Recommended treatments for STDs vary, depending on the STD you have. It is important that you and your partner are successfully treated for an STD before resuming sexual activity. Otherwise, it is possible to pass the infection back and forth between the two.
7.1 Treating bacterial STDs Usually, antibiotics can easily treat bacterial infections. It is important to take all antibiotics as prescribed. Keep taking them even if you feel better until the end of the course of treatment. Tell your doctor if your symptoms do not go away or return after you have taken all of your prescribed medicines.
7.2 Treating viral STDs Antibiotics cannot treat viral STDs. Most viral infections don't have a cure, only some can go away on their own. And in many cases, the treatment options available can help relieve symptoms and reduce the risk of transmission.
For example, medications are available that help reduce the frequency and severity of herpes outbreaks. Antiretroviral drugs can reduce the risk of transmitting HIV to others.
7.3 Treating Other STDs Some STDs are not caused by both viruses and bacteria. Instead, they are caused by other small organisms. Examples include: pubic lice, trichomoniasis, scabies. These STDs are usually treatable with oral or topical medications. You should ask your doctor for more information about your condition and to choose the right treatment option.
8. Prevention of STDs

When used correctly, condoms provide effective protection against many STDs. For optimal protection, it is important to use a condom during vaginal, anal, and oral sex. Mouth guards can also be protective during oral sex.
Condoms are usually effective in preventing STDs from being spread through fluids, such as semen or blood. It can also provide complete protection against STDs that are spread by skin contact. If the condom doesn't cover the infected skin, you can still get an STD or pass it on to a sexual partner. Condoms can help protect against not only STDs, but unwanted pregnancies as well.
In contrast, many other types of birth control reduce the risk of unwanted pregnancy but do not reduce the risk of STDs. Examples: oral contraceptives, contraceptive implants, intrauterine devices (IUDs).
Regular STDs screening is a good idea for anyone who is sexually active. It is especially important for people with new or multiple sex partners. Early diagnosis and treatment can help stop the spread of the infection.
Before having sex with a new partner, it's important to talk to each other about your sexual history and get tested for STDs. Because STDs often have no symptoms, testing is the only way to know for sure if the disease is present. If your partner tests positive for an STD, you should ask about how to protect yourself. If your sex partner has HIV, your doctor will likely encourage you to take pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP). You and your partner should also get vaccinated against HPV and hepatitis B.
9. Living with STDs
If you test positive for an STD, it's important to get treatment as soon as possible. If left untreated, an STD can lead to serious consequences. In rare cases, STDs can even be fatal.Most STDs are highly treatable. In some cases, they can be completely cured. In other cases, early and effective treatment can help relieve symptoms, reduce the risk of complications, and protect sexual partners.
Vinmec International General Hospital offers a screening package for social diseases for all ages, for both men and women. Examination and testing performed tests such as: HIV Ab rapid test, Chlamydia rapid test, Treponema pallidium rapid test, qualitative and quantitative Treponema pallidum TPHA test, bacteriological staining and laboratory testing. testing fungal staining ... to detect disease early to have effective treatment, avoid complications.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Article referenced source: Healthline.com.