This is an automatically translated article.
Polyps are a fairly common condition, found in many organs of the body. Polyps can progress with many dangerous complications, threatening the patient's health.
1. What are polyps?
A polyp is a cluster of small cells that develop inside the body. There are two types of polyps: pedunculated and flat, which grow directly from the surrounding tissue (sessile). Some benign polyps cannot turn cancerous, but others can turn malignant into cancer (precancerous polyps). The rate of malignant progression depends on the location, cause, and time of polyp formation.
2. Common types of polyps
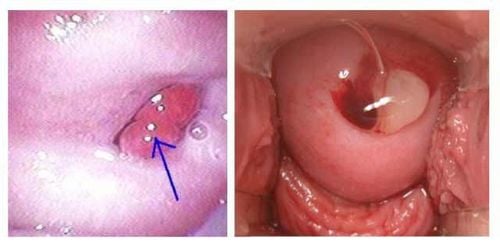
2.1 Colon polyps Colon polyps are more common than you think. Nearly 50% of people worldwide have colon polyps. There are 2 main types:
Hyperplastic polyps: Small in size, growing near the end of the colon and not turning into cancer; Adrenal polyps: Affect more people. When polyps are large, they are more likely to develop into cancer (but often takes years). Most polyps are still not cancerous. To make a diagnosis, the doctor will use an endoscope to insert a small camera into the patient's anus to view the colon. If polyps are found, the doctor will remove them. At the same time, the doctor also sent a sample of polyp tissue for a biopsy to determine if it was cancerous or not. The odds of polyps progressing to cancer are lower if polyps are detected and removed early. Your doctor will give you advice on when to diagnose and remove polyps, usually when you are in your 50s.

Hầu hết các khối polyp đại tràng thường không phải là dấu hiệu ung thư
2.2 Epidural Polyps These clusters of grape-like polyps develop in the middle ear or ear canal. They are usually red and bleed easily if touched. Sometimes these polyps are also a sign of cancer. At first, it will be difficult for the doctor to determine if these polyps are self-growing or caused by an infection or some other condition.
If your doctor thinks the polyp is caused by an infection, he or she may prescribe antibiotics to remove the polyp. If that doesn't work, your doctor may biopsy the polyp to determine if it's cancerous. If polyps don't go away, you may need surgery to remove them.
2.3 Nasal polyps Most nasal polyps are not cancerous. They form inside your nasal passages or sinuses when the lining becomes inflamed and swollen for a long time. Nasal polyps can interfere with taste or smell, and cause a runny nose, headaches, and snoring. Usually, when they grow to a large size, they cause infection or difficulty breathing.
Based on the symptoms you share, your doctor may suspect you have nasal polyps. They will use a nasal endoscope to look at the nose and confirm the diagnosis. To get rid of nasal polyps, you can take oral medications or nasal sprays. Antibiotics may also be effective if an infection is the cause of nasal polyps. If the above treatments don't work, your doctor can remove the polyps with laparoscopic surgery.
2.4 Uterine Polyps This condition is also known as endometrial polyps. Polyps grow inside the lining of your uterus. Some polyps have stalks and some are sessile. They have a slightly rounded shape, which can be as small as a sesame seed or as large as a golf ball. They are not usually cancerous but can alter your menstrual cycle, making it difficult for you to get pregnant.
Along with checking, sharing information about monthly menstrual cycle, blood volume, ... the doctor can preliminary diagnose whether you have uterine polyps or not. In addition, the doctor may also examine the uterus or take a sample of polyp tissue for examination. If there are no symptoms, the patient may not need treatment. However, if polyps are causing heavy bleeding, affecting your ability to get pregnant, or after menopause, you may want to have the polyp removed. Medication will ease the symptoms of uterine polyps, but surgery will remove the polyps completely.
2.5 Vocal polyp This is a noncancerous growth or lesion on the vocal cord sheath. It usually only grows on one side of the vocal cords. When you have vocal cord polyps, your voice may become hoarse, lower than usual, or break in between sentences, take more strength to speak or sing, etc.
To make a diagnosis, your doctor may ask about problems voice related topics. Additionally, they will pass an endoscope through the patient's mouth to view the vocal cords. At the same time, your doctor will check for acid reflux, allergies, or hormone problems. These are the possible causes of your voice becoming deeper and hoarse. You can rest, practice vocal exercises to make your voice clearer. Even if you want to keep your voice, you may need surgery.

Polyp dây thanh không phải là dấu hiệu ung thư
2.6 Stomach polyps Stomach polyps form on the lining of the stomach. Most stomach polyps do not develop into cancer, but having multiple polyps increases your risk of cancer. Stomach polyps usually don't have any symptoms. Most patients only discover it by chance during another medical examination.
If your doctor suspects you have stomach polyps, they will examine your stomach with an endoscope. If stomach polyps are adenomas that could progress to cancer, your doctor may remove the tumor or take a tissue sample for testing. Besides, your doctor will also check for Helicobacter Pylori bacteria in your stomach, prescribe antibiotics if you have it. With small polyps that are not adenomas, patients only need periodic health check-ups. With large polyps, your doctor may choose to remove them.
When detecting polyps in any organ of the body, the patient needs to calm down and follow all instructions of the doctor to have the most appropriate intervention plan.
Vinmec International General Hospital is a high-quality medical care address with a team of experienced doctors and experts and modern machinery and equipment. Therefore, customers can completely trust to visit the doctor when they have any health problems.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.