This is an automatically translated article.
Now scientists have discovered factors that increase the risk of cancer in humans. And there are 4 most studied factors and also the most common factors that can cause cancer in certain groups of people.
1. Does drinking a lot of alcohol cause cancer?
The less alcohol you drink, the lower your risk of cancer. When you drink alcohol, your body breaks down alcohol into a chemical called acetaldehyde. Acetaldehyde damages DNA and prevents your body from repairing the damage. DNA is the genetic material that controls the normal growth and function of cells. When DNA is damaged, cells can start to lose control and create cancerous tumors.
Drinking alcohol increases the risk of six types of cancers of the mouth and throat, larynx, esophagus, colon and rectum, liver and breast (in women).
All alcoholic beverages, including red and white wine, beer, cocktails and liquor, have all been linked to cancer. The more you drink, the higher your cancer risk.
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2015-2020 recommend that, if you drink alcohol, drink in moderation, no more than one drink per day for women and no more than two drinks per day. day for men. If you don't drink alcohol, don't use it even if alcohol can have any health benefits.

Uống rượu nhiều làm tăng nguy cơ mắc một số bệnh ung thư
Alcohol is not allowed in the following cases:
Not yet of drinking age. Are pregnant or may become pregnant. Have health problems and alcohol use can make the condition worse. Working as driver. In addition, you should also not use alcohol when drinking to treat disease, including cancer treatment.
2. Lung cancer risk of smoking
When it comes to cigarettes, you probably think that smoking can increase the risk of lung cancer. That is correct as smoking (including cigarettes and cigars) causes nearly nine out of 10 cases of lung cancer, but smoking can cause cancer in almost every other organ in the body. such as:
Bladder Blood (acute myeloid leukemia ) Cervical colon and rectum Esophagus Kidneys and pelvis Liver Lungs, bronchi and trachea Mouth and throat Pancreas Stomach Laryngeal
Hút thuốc lá có nguy cơ gây ung thư thanh quản và một số tạng khác
Tobacco smoke has at least 70 cancer-causing chemicals, also known as carcinogens. Every time you breathe in cigarette smoke, these chemicals enter your bloodstream, carrying chemicals to all parts of your body. Many of these chemicals can damage DNA, which controls how your body makes new cells and directs each type of cell to perform a variety of functions. If DNA is damaged, it can cause cells to grow differently than they normally do. These abnormal cells can turn into cancer.
However, smokers are not the only ones who can get cancer from secondhand smoke. Everyone around them, children, friends, co-workers who also breathe in the cigarette vapors produced by smokers are also at risk of getting cancer, which is called passive smoking.
Smokeless tobacco products, such as snuff and chewing tobacco, can also cause cancer, including cancers of the esophagus, mouth and throat, and pancreas. Cigar smoking causes lung cancer and increases the risk of cancers of the mouth, throat, larynx, and esophagus.
E-cigarettes create an aerosol by heating a liquid that usually contains nicotine, the addictive substance in cigarettes, cigars and other flavored tobacco products, and other chemicals. help create aerosols. The user inhales this aerosol into the lungs. People around can also inhale this gas when the user breathes out into the air. E-cigarettes are not safe for teens, young adults, pregnant women, or adults who are not currently using tobacco products.

Thuốc lá điện tử không an toàn cho người sử dụng
3. HPV virus
Cancer is a disease in which cells in the body grow out of control. Cancer is often named after the body location where it started, even if it spreads to other body parts later.
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is the most common sexually transmitted infection in the United States. There are more than 40 types of HPV that can infect the genital areas of men and women, including the skin of the penis, the vulva (the area outside the vagina) and the anus, the lining of the vagina, the cervix, and the rectum. colon. These viruses can also infect the lining of the mouth and throat.
The classification of viruses as low risk (causes warts) or high risk (causes cancer) is based on whether these viruses put people at risk for cancer. The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) of WHO has discovered 13 types of HPV that can cause cervical cancer and one of these types can cause cancer of the vulva, vulva, and vulva. vagina, penis, anus, and some head and neck cancers (specifically, cancers of the nasopharynx, back of the throat, base of the tongue, and tonsils). The viruses that can cause genital warts are not the same as those that can cause cancer.
Most people infected with HPV do not know they are infected. Normally, the body's immune system can clear an HPV infection naturally within two years. This is true for both high-risk and low-risk categories. By age 50, at least 4 out of 5 women will be infected with HPV at some point in their lives. HPV is also very common in men and often has no symptoms.
When the body's immune system fails to handle an HPV infection, it can persist over time and turn normal cells into abnormal cells and then cancer. About 10% of women have a persistent HPV infection that puts them at risk for cervical cancer. Likewise, when HPV persists and infects the cells of the vulva, vagina, penis, or anus, it can cause cell changes known as precancerous. They can eventually develop into cancer if they are not detected and removed in time.
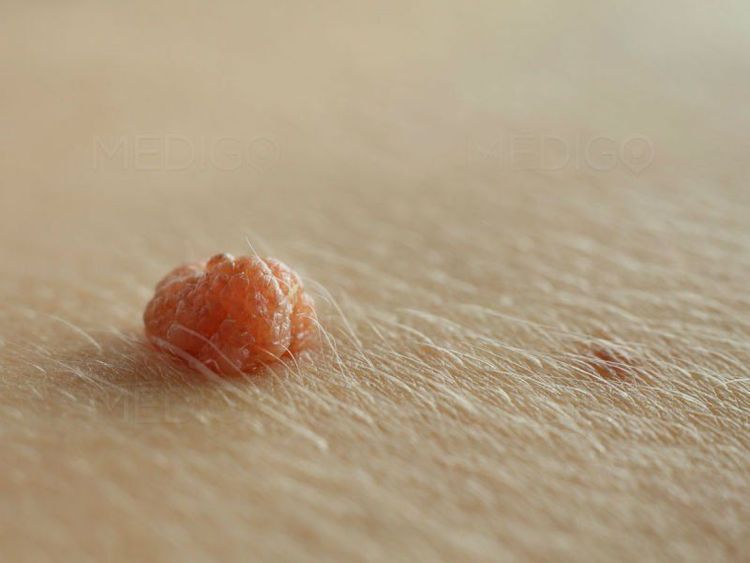
Virus HPV gây ra tình trạng mụn cóc và có khả năng lây truyền cho người khác
4. Family history
Family members may share genes, habits and environment that can affect cancer risk. Therefore, when examining a doctor, the doctor often asks very carefully for information about diseases that are inherited in the family:
The person who comes to the doctor's office Parents and grandparents Siblings Children Aunts, uncles and grandchildren. Information usually includes:
Who has cancer and what type of cancer? At what age was the person diagnosed with cancer? Are they still alive? If not, at what age did he die and what was the cause of death?
If you have a family history of breast, ovarian, uterine or colorectal cancer, you may have a higher risk of developing these cancers than other people. Tell your doctor if:
Immediate relatives (parents, siblings or children) diagnosed before age 50 with ovarian, uterine, breast or colorectal cancer. Two or more other close relatives (grandparents, aunts, uncles, nieces or nephews) on either side of the mother or father have ovarian, uterine, breast, or colorectal cancer. Having a male relative with breast cancer. Talking to your doctor about your family health history is the first step in figuring out if you may have a higher-than-average risk of cancer. This is useful to help your doctor decide what types of tests you need to have, when to start and how often. Knowing your family health history also helps you and your doctor decide if genetic counseling or genetic testing might be right for you.

Một số loại bệnh lý có thể mang tính chất gia đình, di truyền cho các thế hệ sau
What is genetic counseling and testing? If your family health history suggests you may carry the gene mutation, your doctor may refer you to genetic counseling.
A genetic counselor will ask you about your family's health history and help you decide if genetic testing is right for you. Genetic testing uses saliva or blood to look at your DNA, and the results of this test will tell you if you have a genetic mutation that can increase your risk of cancer.
What should I do if I have a genetic mutation? Having a gene mutation does not mean you will definitely get cancer. There are several steps you can take to reduce or manage your risk of cancer such as:
Tests. You may need to start testing earlier and get tested more often than others. Medicines or surgery can reduce the risk of cancer. Follow healthy lifestyles like quitting smoking, not drinking alcohol, exercising regularly, and keeping a healthy weight.
Which genetic disease increases the risk of cancer Some genetic conditions can increase the chance of getting cancer. The two most common conditions are Hereditary Breast-Ovarian cancer syndrome (HBOC) and Lynch syndrome:
People with HBOC syndrome have an increased risk of breast, ovarian, and ovarian cancers. prostate and pancreatic cancer. Having these syndromes means you have a mutation in the BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene. People with Lynch syndrome have an increased risk of colorectal, uterine, and ovarian cancers. Early cancer screening is considered the perfect measure in timely detection and treatment of cancers. Reduce the cost of treatment and especially reduce the mortality rate in patients. Vinmec International General Hospital always deploys and introduces to customers a HIGH-TECH CANCER CHECKLIST PACKAGE to help with gene testing, imaging, and biomarkers for early tumor detection. Vinmec International General Hospital has many packages of early cancer screening. A single gene test can assess the risk of 16 common cancers in both men and women (lung cancer, colorectal cancer, breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, cervical cancer) Bowel cancer , stomach cancer , prostate cancer ,....)
Early detection of early signs of cancer through imaging, endoscopy and ultrasound. The examination is simple, careful and precise. A team of well-trained experts, especially in oncology, is capable of handling cancer cases. With facilities, advanced and modern medical equipment and a team of doctors with deep expertise and experience. At Vinmec, the examination process becomes quick with accurate results, saving costs and time for patients.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
Reference to the article: cdc.gov
Recommended video:
Cancer screening: Early detection method, reducing treatment costs and cancer mortality
MORE:
Cancer treatment notes Proper understanding of cancer risks How does cancer arise?