This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Doctor Vo Ha Bang Suong - Doctor of Medicine - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital. The doctor has more than 15 years of experience in the treatment of internal diseases.Hand, foot and mouth disease is a common infectious disease in young children, the virus that causes hand, foot and mouth disease is capable of spreading from person to person, through direct contact with nasopharyngeal secretions, saliva, secretions from blisters or stools of the patient. Therefore, when taking care of sick children, it is necessary to take good preventive measures to avoid spreading the disease from young children.
1. Overview of hand, foot and mouth disease in children
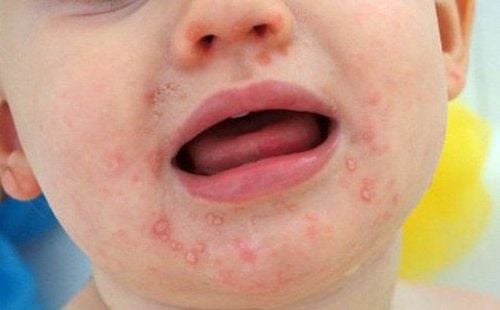
During the incubation period of about 3-7 days, hand, foot and mouth disease in young children does not have any signs to recognize. When the onset stage is 1-2 days, the child will have symptoms such as low-grade fever, fatigue, sore throat, loss of appetite, diarrhea several times a day. In the full-blown stage, which can last from 3 to 10 days, children begin to have typical symptoms of the disease as follows:Mouth ulcers: Red sores or blisters with a diameter of 2-3mm in the oral mucosa , gums, tongue will cause mouth pain, causing children to stop eating, stop sucking, increase salivation. Blister rash: Burns that appear on the palms, soles, knees, and buttocks and are short-lived (less than 7 days) may leave a bruise, but very rarely ulcer or superinfection. Mild fever and vomiting: If the child has a high fever and vomits a lot, there is a risk of neurological, cardiovascular, and respiratory complications and usually appears early from day 2 to day 5 of the illness. Basically, if you can make sure your child gets the right treatment then complications of hand, foot and mouth disease in young children will be rare, because the health complications of hand, foot, and mouth disease unpopular. If it occurs, it is very dangerous with a number of complications such as:
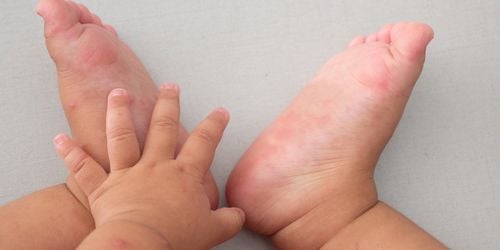
Neurological complications: the child may have encephalitis, brain stem inflammation, encephalitis, meningitis. Myoclonic tremor, startle: Myoclonic tremors are short 1 to 2 seconds, mainly in the arms and legs, easy to appear when the baby starts to go to sleep or when the baby is lying on his back. Drowsiness, dozing, restlessness, wobbling, stumbling, trembling, eyes looking backwards. Weakness, limb paralysis (acute flaccid paralysis), cranial nerve palsy. Nystagmus, convulsions, coma – These are usually very severe signs, often accompanied by respiratory and circulatory failure. Increased muscle tone (manifestations of cerebral extensor, cortical rigidity) Cardiovascular and respiratory complications: Myocarditis, acute pulmonary edema, hypertension, heart failure, vascular collapse. Water burns will appear on the palms, soles, knees, buttocks and are short-lived
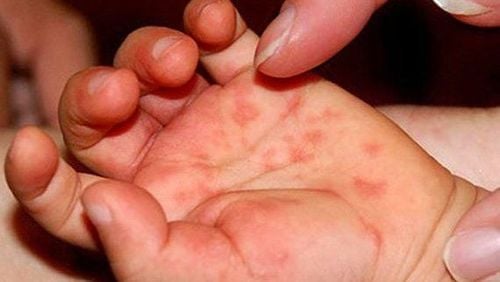
Phỏng nước sẽ xuất hiện ở lòng bàn tay, lòng bàn chân, gối, mông và tồn tại trong thời gian ngắn
2. Can adults transmit HFMD in children?
Hand, foot and mouth disease is an infection mainly caused by the coxsackie virus A16 with few complications and usually resolves on its own. However, this disease can also be caused by enterovirus 71 (EV71) with many dangerous complications and can lead to death. Each infection only produces antibodies to a certain virus, so it is possible to get sick again if infected with another virus of the enterovirus group.The virus that causes hand, foot and mouth disease is capable of being transmitted from person to person through direct contact with nasopharyngeal secretions, saliva, fluid from blisters or feces of an infected person; through sharing utensils. As doctors note, the risk of transmission is strongest in the first week after infection, but the infectious period still lasts several weeks (because the virus is localized in feces).
With the above characteristics, the answer is that hand, foot and mouth disease can be transmitted to adults, because when adults take care of sick children, if they do not maintain good hygiene for children, the caregivers themselves and not If you take preventive measures, hand, foot and mouth disease will spread to adults. The disease is also very contagious in crowded environments such as schools and public places.
The virus that causes hand, foot and mouth disease in children will often have the above symptoms, but in adults, the symptoms often do not show any outward signs, so it is difficult to control.
Therefore, in order to control the spread of hand, foot and mouth disease in children, it is necessary to prevent the disease in adults who directly care for patients, like how to prevent cholera, typhoid... It's not just about taking care of patients.
If you do not maintain good hygiene for children and do not take preventive measures, hand, foot and mouth disease will spread to adults.
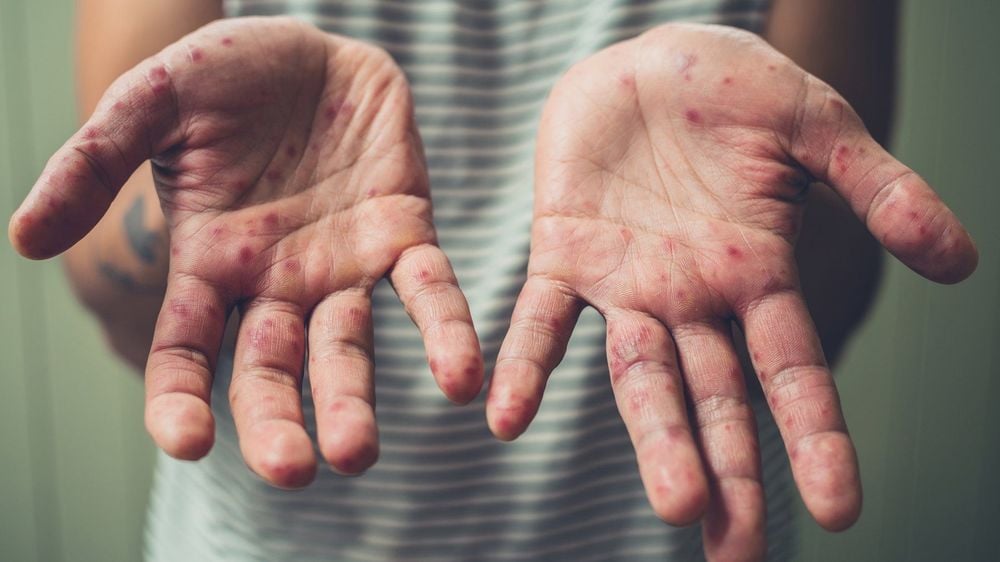

Nếu như không giữ gìn vệ sinh tốt cho trẻ và không có biện pháp phòng tránh thì bệnh tay chân miệng sẽ lây sang cho cả người lớn
3. Measures to prevent infection when taking care of sick children
There is currently no vaccine for hand, foot and mouth disease, young children and adults taking care of infected children can only prevent infection by:When adults take care of sick children, they need to wash their hands often with soap and water , especially after contact with blisters or sores, before cooking, or before eating, before feeding a child, after using the toilet and changing diapers; Regularly clean children's everyday surfaces and objects such as toys, school supplies, doorknobs, stair handrails, table or chair surfaces, and floors with soap or common detergents. normally, then disinfected with diluted chlorine bleach. In addition, avoiding direct contact (hugging, kissing, sharing utensils,...) with infected children also helps reduce the risk of infection. Cover your nose and mouth when sneezing or coughing; dispose of used tissues and diapers in a covered trash can; Maintain hygiene at home, kindergarten, school... Practice good eating and drinking hygiene such as eating well, drinking well; ensure the use of clean water in daily activities; do not give food to children; absolutely do not let children eat, suck, suck or suck on toys; Do not let children share napkins, handkerchiefs, eating utensils such as cups, bowls, plates, spoons, toys that have not been disinfected. If the child has not had hand, foot and mouth disease, it is best not to let the child come into contact with people who are sick or suspected of having the disease to avoid spreading the disease to the child. When detecting that a child shows signs of suspected hand, foot and mouth disease, parents need to take the child to a doctor or immediately notify the nearest medical agency for treatment and care for the child.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space. You can rest assured when taking care of your health here.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.