This is an automatically translated article.
Article written by Dr. Hoang Minh Duc - Team Leader of Experimental Production Project, Vinmec
Research Institute of Stem Cells and Gene Technology
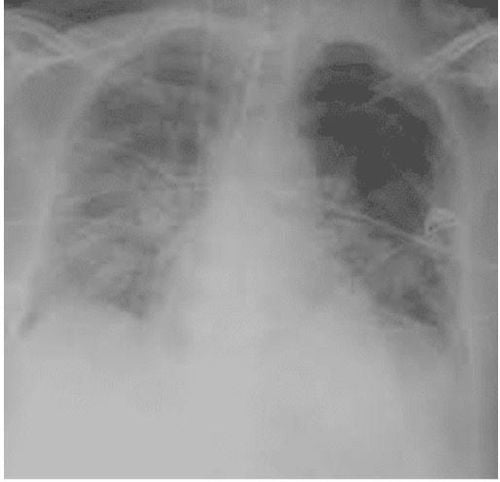
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) is a clinical syndrome characterized by acute hypoxia, which appears suddenly and rapidly progresses after a pulmonary or organ disease On the other hand, on the chest X-ray film, there are bilateral diffuse lesions.
1. Acute respiratory distress syndrome
ARDS is always a matter of concern in the intensive care units because of its burdensome nature, difficulty in treatment and high mortality rate. There have been many studies that have brought a fairly thorough understanding of the pathogenesis as well as many advanced solutions that have been applied, the mortality rate of ARDS is still very high, up to 40 - 70% depending on the mechanism. resuscitation facility.
According to the Berlin 2012 definition of ARDS, a new diagnostic and classification standard for ARDS has been published. Accordingly, cases with PaO2/FiO2 ≤ 300 on mechanical ventilation or CPAP with PEEP ≥ 5 cmH2O were diagnosed as ARDS. Depending on the degree of hypoxemia, ARDS is divided into 3 severity levels: mild, moderate and severe, corresponding to the degree of hypoxemia.

From December 2019 to present, the COVID-19 pandemic is an infectious pandemic caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, which is currently affecting mainland China, with multiple cases in more than 201/204 countries and territories around the world and it is easy to progress to ARDS. As of March 29, 2020, the number of confirmed COVID-19 infections globally has surpassed 600,000 across 200 countries and territories, with more than 20,000 deaths. In which, more than 130,000 cases have recovered.
The new strain of virus causing confirmed cases is SARS-CoV-2 (temporary name new coronavirus (2019-nCoV)), which is the seventh strain in the family of coronaviruses known to infect humans. Humans, with genomic sequences reported to be up to 79.5% similar to those of SARS-CoV and 96% similar to the coronavirus strains infecting horseshoe bats.
SARS-CoV-2 has no specific treatment or vaccine, although efforts to develop them are underway. ARDS, pulmonary failure, and pneumonia are the major pulmonary diseases in COVID-19 patients that induce extrapulmonary diseases through in vivo cytokine storms.
2. Pathogenesis
The basic lesion in ARDS is diffuse, heterogeneous alveolar-capillary membrane damage. This lesion may originate from the alveolar side or from the capillary side.
Injury from the alveoli: causes of lung injury directly destroy the surfactant membrane and alveolar epithelial cells (type I and type II cells) thereby reducing alveolar fluid reabsorption, reducing alveolar fluid reabsorption. surfactant production. The inflammatory response is initiated by phagocytosis, release of inflammatory cytokines, and neutrophil chemotaxis. These neutrophils are activated and migrate in large numbers on endothelial and alveolar epithelial surfaces, releasing proteases, cytokines, and reactive oxygen species. These mediators further damage alveolar epithelial cells and alveolar-capillary membranes, creating a pathological spiral, and exacerbating the lesions in ARDS.
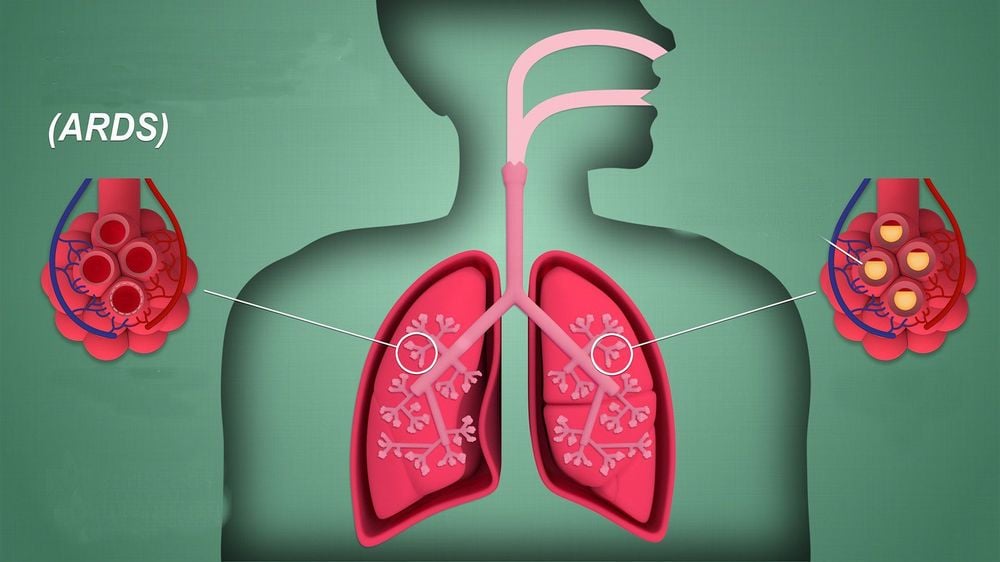
Injury from the capillary side due to causes of indirect lung injury such as septic shock, severe infection, acute pancreatitis or severe trauma... damages the endothelial cells of the pulmonary capillaries, causing hyperactivity permeability of the pulmonary capillaries. Thereby, red blood cells and substances with high molecular weight such as albumin, globulin and fluid from the capillaries escape out of the interstitium and into the alveoli, leading to the infiltration of inflammatory cells into this area, filling the interstitial space. inflammatory exudates, alveolar-capillary membrane edema, and lungs become less elastic.
No matter which side the injury originates, it leads to the same result: interstitial edema, edema and collapse of the alveoli, and decreased lung elasticity. The reduction in the number of alveoli involved in gas exchange and damage to the alveolar-capillary membrane causes the actual volume of the lung to narrow and create shunts in the lungs, the blood flow through the lungs is not oxygenated. cause severe hypoxia in ARDS.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.