This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Doctor Vo Thi Thuy Trang - Gastrointestinal Endoscopy - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Da Nang International Hospital.Acute pancreatitis is one of the most common gastrointestinal toxicity in clinical practice, occurring after meals containing a lot of fat and protein, especially after drinking alcohol. So is acute pancreatitis dangerous? What are the clinical manifestations of acute pancreatitis?
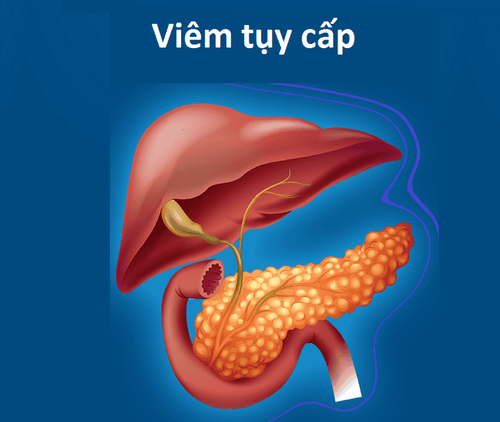
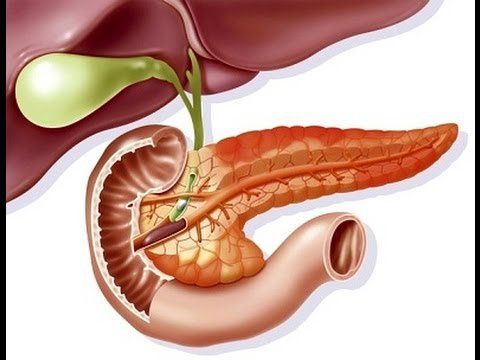
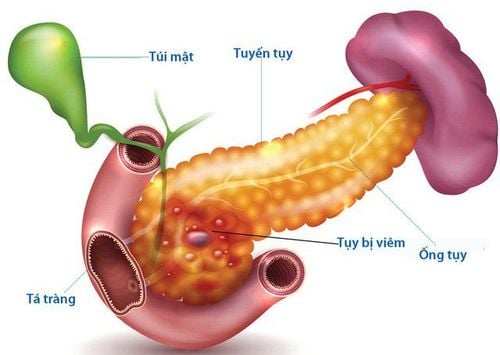
1. What is acute pancreatitis?
Acute pancreatitis is an acute inflammation of the pancreatic parenchyma, which may include damage to adjacent organs. The disease is potentially fatal.There are 3 main groups of causes of acute pancreatitis:
Alcohol: is the main cause of acute pancreatitis; Due to increased blood fat; Due to gallstone obstruction leading to obstruction of the common duct or sphincter of Oddi blocking the pancreatic duct flow. Retained pancreatic enzymes cause destruction of pancreatic structures; In addition, acute pancreatitis can also occur due to blunt trauma to the pancreas, metabolic disorders, autoimmune diseases...; In about 10-15% of cases of acute pancreatitis, no cause can be found. Acute pancreatitis is an autoimmune process of tissue destruction caused by pancreatic enzymes themselves. According to normal physiological function, the pancreas will secrete pancreatic enzymes amylase, lipase, trypsin... to contribute to the digestion of food. These enzymes are secreted in an inactive form and they become active only in the duodenum. But due to some reason increasing the sensitivity of the pancreatic follicular cells to acid, cholecystokinin, acetylcholine, these enzymes are activated in the lumen of the pancreatic duct itself and converted to an active form that causes destruction of pancreatic tissues, leading to the destruction of pancreatic tissues. to acute pancreatitis.
Clinically, acute pancreatitis manifests through 3 main diseases:
Acute pancreatitis with edema; Hemorrhagic acute pancreatitis; Hemorrhagic necrotizing pancreatitis: This case has up to 80-90% death.
Trắc nghiệm: Làm thế nào để bảo vệ lá gan khỏe mạnh?
Làm test trắc nghiệm kiểm tra hiểu biết về gan có thể giúp bạn nhận thức rõ vai trò quan trọng của gan, từ đó có các biện pháp bảo vệ gan để phòng ngừa bệnh tật.2. Symptoms of acute pancreatitis
Clinical symptoms of acute pancreatitis are atypical but common signs are as follows:Acute abdominal pain: Mainly epigastric pain, severe pain, occurring suddenly after a large meal of protein, fatty or after drinking alcohol. Pain persists continuously or intermittently, pain spreads to the back or spreads to the lower ribs on both sides. Acute pancreatitis is easily confused with stomach pain;

3. Is acute pancreatitis dangerous?
Acute pancreatitis if not treated will progress very quickly, complicated to severe complications, can easily affect other organs, even cause death. For severe cases, the resuscitation treatment does not respond, the patient should be indicated for immediate surgery to remove the necrotic tissue. Here are the dangerous developments of acute pancreatitis:Shock: Is one of the early complications occurring in the early days of the disease. Shock can be caused by severe infection or by bleeding. Cases of shock due to severe pancreatic parenchymal infection usually occur later in the 3rd week from the onset of signs of inflammation; Bleeding: Hemorrhagic complications can appear in the pancreas, in the abdominal cavity, in the digestive tract or other organs, leading to damage to the blood vessels. This complication occurs during the first week of illness. All cases with hemorrhagic complications have a severe prognosis; Infection in the pancreas: Occurs at the end of the first week or the beginning of the second week of illness. This is the main cause leading to the formation of abscesses in the pancreas causing generalized peritonitis, tissue necrosis. In this case, the prognosis is severe; Acute respiratory failure: Severe prognosis; Pancreatic pseudocyst: Appears in the 2nd or 3rd week of the disease due to the process of encapsulation to localize the lesions in the pancreatic parenchyma. Pancreatic pseudocysts contain pancreatic enzymes, fluids, and fragments of pancreatic parenchyma. This cyst may be cleared or self-drained into the pancreatic duct and disappear after 4 to 6 weeks. Cysts if left for a long time can progress to abscess or cause superinfection. Acute pancreatitis is one of the serious medical emergencies, with many complications with severe prognosis including hypovolemia, necrosis of the pancreatic parenchyma, acute respiratory failure, sepsis or functional bowel paralysis. .. The disease, if not treated, can cause systemic complications affecting the functioning of other functional organs such as cardiovascular collapse, impaired kidney function,... especially bleeding in the pancreas. can lead to death within the first few days of illness.
With nearly 20 years of working at Da Nang General Hospital in the field of gastrointestinal endoscopy - hepatobiliary disease, every year, Doctor Vo Thi Thuy Trang participates in endoscopy more than 1500 cases including: endoscopic diagnosis of diseases stomach, colon such as: detecting inflammation, ulcers, polyps, cancer, finding HP bacteria, detecting cancer early in the digestive tract...; Endoscopic treatment such as: Hemostasis in gastrointestinal bleeding, esophageal varices ligation in cirrhosis, endoscopic gastrointestinal polypectomy...
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.