This is an automatically translated article.
Acute myeloid leukemia is common in people over 65 years of age, and acute myeloid leukemia is rare in children. Similar to other diseases, acute myeloid leukemia also has risk factors that increase the likelihood of disease.1. An overview of acute myeloid leukemia
Leukemia is a malignancy of the hematopoietic system. Disease occurs when healthy cells mutate and grow out of control. Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a disorder in the production of white blood cells, red blood cells, and/or platelets. AML is also known as acute non-lymphocytic leukemia next to acute myeloid leukemia. Unlike chronic myeloid leukemia, AML progresses rapidly and requires early treatment. AML occurs in all age groups but is most common in adults over the age of 65. Acute myeloid leukemia in children has rarely been reported.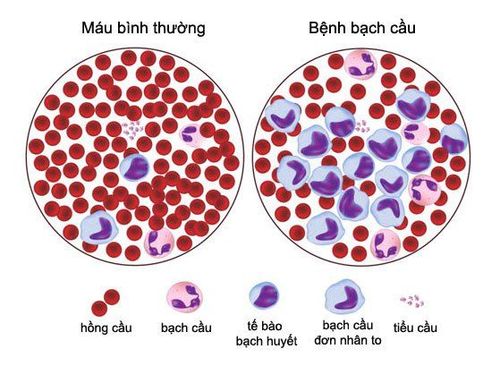
Bệnh bạch cầu là bệnh lý ác tính của hệ tạo máu
2. Risk factors for acute myeloid leukemia
Risk factors for AML do not directly cause the disease but do influence the rate of disease progression. Risk factors increase the likelihood of disease. However, some people with multiple risk factors do not get the disease, while others without any risk factors unfortunately become ill. Recognizing the existence of risk factors to inform your doctor gives you more advice on how to take care of your health and improve your lifestyle.Although the cause of acute myeloid leukemia is unknown, many factors have been identified that increase the risk of developing the disease, including:
Age: Acute myeloid leukemia is common in people age and can occur at any age. More than half of the patients diagnosed with the disease are over the age of 65. Smoking: The risk of acute myeloid leukemia is increased with exposure to secondhand smoke, even through passive inhalation of secondhand smoke. Gene Mutations: Many studies have shown that leukemia occurs in members of the same family due to inherited genetic mutations. AML is more common in the presence of the following genetic abnormalities: Down syndrome Li-Fraumeni syndrome Ataxia - vasodilation Fanconi anemia Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome Familial platelet disorder (Family Platelet Disorder (FPD).

Nhiều nghiên cứu chỉ ra rằng bệnh bạch cầu xuất hiện ở các thành viên trong cùng một gia đình do các đột biến gen có tính di truyền
Radiation: People exposed to high doses of radiation have a higher chance of developing acute myeloid leukemia. Cell phones are not an obvious risk factor for the disease. Previous cancer treatment: Chemotherapy and radiation treatments for other malignancies such as breast cancer, ovarian cancer, and lymphoma increase the risk for many years after treatment. Chemicals: Prolonged exposure to chemicals containing benzene also increases the likelihood of AML. Other bone marrow disorders: People with bone marrow-related abnormalities including myeloproliferative disorders have a higher incidence.
If you have unusual symptoms, you should be examined and consulted with a specialist.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: cancer.net
MORE:
What is leukemia? Common Types of Leukemia What is the number of white blood cells in the body?