This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Do Xuan Chien - Head of Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital.Acute heart failure and acute pulmonary edema due to heart disease is a common disease or also a consequence of diseases that damage the cardiovascular system, a dangerous disease that threatens the life of the patient.
1. Learn about acute heart failure and acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema
Heart Failure is when the weak contractility of the heart muscle reduces the heart's ability to eject blood, reducing the blood supply needed by the body, not enough to meet the body's metabolic needs. There are many ways to classify heart failure in diagnosis so that appropriate treatment can be given. In which, according to pathophysiology, it is divided into 2 types: acute heart failure and chronic heart failure. What is acute heart failure? Heart failure is defined as the rapid onset of symptoms of impaired cardiac function, which is life-threatening and requires emergency management. In which, acute heart failure is classified as follows: chronic decompensated heart failure, acute pulmonary edema, acute hypertensive heart failure, cardiogenic shock, isolated right heart failure, heart failure and acute coronary syndrome. Acute pulmonary edema occurs when pulmonary capillary pressure rises above the threshold, causing fluid to escape from the lumen into the interstitial and alveolar spaces. Thereby causing serious disturbances of gas exchange manifested by severe dyspnea, sudden or clinically present at night.2. Causes of acute heart failure and acute pulmonary edema
Causes of acute heart failure:
Myocardial ischemia : acute coronary syndrome due to blockage or excessive constriction of coronary arteries. Heart valve disease: open, narrow heart valves Cardiomyopathy: Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, myocarditis Other cardiovascular disease: Hypertension, cardiac arrhythmias, infective endocarditis, arterial dissection aneurysm host ,... Sepsis , thyrotoxicosis , anemia , pulmonary embolism ... Chronic heart failure non-adherence to treatment , fluid overload , infection , cerebrovascular disease , renal dysfunction , asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, drug poisoning, alcohol poisoning...
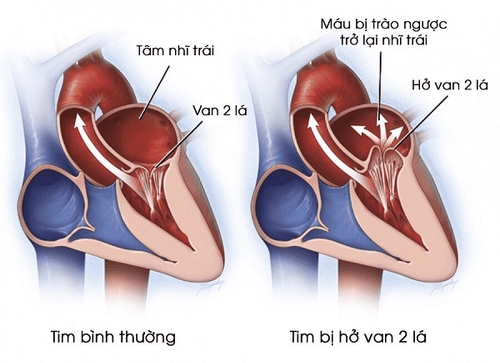
Hở van tim là nguyên nhân gây suy tim cấp
3. Manifestations of acute heart failure and acute pulmonary edema
Acute heart failure has acute clinical manifestations including:
Shortness of breath, sometimes severe and sudden, developing rapidly. Accompanied by patients with anxiety, struggle, cyanosis... Some cough up blood or even spit pink foam into their mouths. Chest pain, tightness in the chest, feeling short of breath Fainting or having a bout of fatigue Feeling of palpitations, rapid or irregular heartbeat Examining the patient has difficulty breathing fast, shallow. Auscultation of the lungs can be seen with hissing rales, snoring rales and especially small and large moist rales on both sides of the lung (may develop in a tidal pattern from the two bottoms of the lungs). Paraclinical symptoms:
Electrocardiogram: In order to determine the heart rate and common causes, especially with acute myocardial infarction X-ray of the heart and lungs: The image of the heart is enlarged, the pulmonary veins are thickened. Blurred butterfly wings spread from two hilars, showing Kerley B line. Arterial blood gases: Helps to assess hypoxia, metabolic disorders in heart failure Echocardiography plays an extremely important role in recognition. manifest heart failure and ejection fraction less than 55% Other tests include: renal function, electrolytes, blood count
4. Treatment of acute heart failure and acute cardiac pulmonary edema
Treatment purpose
Anti-respiratory failure Prevent the progression of the disease. Improve quality of life, reduce hospitalization time. Prolong the life of the patient. Control water and salt stagnation. Increase myocardial contractility. Reduce heart work. Reduces pulmonary and systemic venous congestion. Initial supportive measures:
Provide oxygen to ensure ventilation. Intubation and artificial ventilation if indicated Leaving the patient in a semi-sitting position to reduce dyspnea due to stagnation Administering the intravenous drug Morphine sulphate is very important because it reduces anxiety for the patient. In patients with pulmonary and systemic venous vasodilation, intravenous furosemide diuretics reduce circulatory burden and have an immediate effect on rapid pulmonary artery dilation when administered intravenously. Nitroglycerin is a major venous dilator that reduces preload and has a synergistic effect with furosemide. Inotropic agents are indicated after the above initial measures and in patients with low blood pressure or cardiogenic shock. Find the cause and solve the causes of acute heart failure and acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema
Dùng thuốc để điều trị bệnh suy tim cấp và phù phổi cấp do tim
5. Prevention of acute heart failure and acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema
To prevent acute heart failure or acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema is to minimize risk factors. Many risk factors can be controlled and eliminated, such as hypertension and coronary heart disease, by lifestyle changes combined with medication.
Lifestyle changes that can help reduce rates of cardiovascular disease include:
Stop smoking Control underlying conditions, such as high blood pressure and diabetes Stay physically active Eat healthy Maintain a healthy weight Reduce stress Acute heart failure and acute pulmonary edema should be treated early to avoid serious consequences, so when you find yourself showing signs of illness, you should see your doctor for a diagnosis. early diagnosis and treatment.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical professionals, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Master. Doctor Do Xuan Chien is former Deputy Head of Cardiology Department of Phu Tho Provincial General Hospital with more than 11 years of experience working in Cardiology and Metabolic Pathology. Currently, he is the Head of the Department of Medical Examination and Internal Medicine, Vinmec Ha Long International General Hospital.
Associate Professor. Dr. Hoang Dang Mich has over 42 years of medical career, has strengths in the specialized fields of Liver - Kidney - Immune pathology... Currently, he is a Specialist Consultant of General Internal Medicine Department of Examination. Medicine & Internal Medicine, Vinmec Ha Long International General Hospital.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.