This is an automatically translated article.
Article written by BSCK II Pham Thi Van Hanh, Children's Center, Vinmec Times City International Hospital
Acute diarrhea in children caused by some viruses or infections in the intestines, food allergies, side effects of drugs... The disease is dangerous for children if it is not diagnosed early and treated promptly. due to severe dehydration of the body.
1. Outline
1.1. Definition Diarrhea is a sudden increase in the amount of fluid in the stool, manifested by the passage of loose stools ≥ 3 times in 24 hours.
Acute diarrhea is diarrhea that has an acute onset and lasts no more than 14 days.
Diarrhea can be a disease or it can be a symptom of a disorder in the gastrointestinal tract or outside the digestive tract. The two main mechanisms of diarrhea are osmotic (usually due to malabsorption) and secretory (usually due to toxins).
1.2. Causes In young children, acute diarrhea is mostly caused by viruses (Rotavirus, Adenovirus, Norwalkvirus). In addition, it can be caused by intestinal infections (E.coli, bacillus dysentery, typhoid, Campylobacter Jejuni, Giardia..), extra-intestinal infections (respiratory tract, urinary tract, otitis media, meningitis ..). ), food allergies (cow's milk protein, peanuts, eggs, shrimp, marine fish) side effects of drugs (antibiotics, antiviral drugs, laxatives) and some other causes (absorption disorders, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, immunosuppression, vitamin deficiency, acute appendicitis).
1.3. Predisposing factors for diarrhea Children < 2 years old, especially children aged 6-18 months. Immunocompromised children (malnourished, after measles, HIV infection...). Feeding habits (not breastfeeding in the first 4-6 months, weaning too early, contaminated food and water). Weather: In summer, diarrhea is often caused by bacterial infections, and in winter, diarrhea is often caused by Rotavirus.

Hệ miễn dịch suy giảm khiến trẻ dễ mắc bệnh tiêu chảy cấp
2. Patient assessment
2.1 Ask the illness of the mother and caregiver When did the child begin to have loose stools, the number of bowel movements a day, the amount of water, the color, and whether there is blood in the stools; Ask the number of times of vomiting, vomit, vomit when the child eats or when changing positions; Other symptoms: fever, irritability, thirst, abdominal pain, fatigue, cough, rash, ear discharge, runny nose. Developmental history and acquired diseases; Nutrition before and during illness, milk, fruit... how to prepare; Used drugs, antidiarrheal drugs, laxatives..; Epidemiology: number of people with diarrhea, same diet. Ask for vaccinated vaccines. 2.2. Medical examination Detecting critical signs: lethargy, lethargy, convulsions, coma, high fever, vomiting a lot.
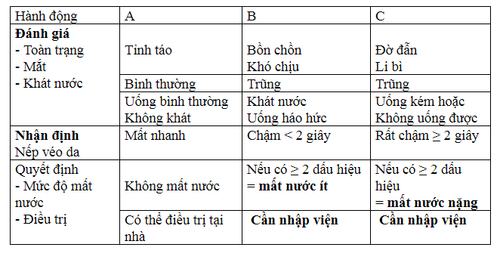
Check for signs of dehydration :
General condition: alertness, irritability, fussiness, poor feeding, abort, lethargy, coma; Thirst: Drink normally, drink eagerly, drink poorly or not drink at all..; Are the eyes sunken? Ask if the eyes are different from normal? Skin elasticity: fast loss, slow loss less than 2 seconds, very slow loss; Signs: pulse, heart rate, breathing rate, urine output, capillary filling time.

Khi trẻ có dấu hiệu khát nướccần đưa trẻ đến bệnh viện sớm
Other symptoms
Limbs: Skin on the lower legs, hands are normally warm and dry, fingernails are pink. When severe dehydration, signs of shock, the skin is cold and moist, purple veins appear...; Pulse: When dehydrated, the pulse and thighs rotate faster, if severe, it can be small and weak; Breathing: Frequency increases with severe dehydration due to metabolic acidosis; Weight loss: Less than 5%: No clinical signs of dehydration. Loss of 5-10%: There is moderate to mild dehydration. Loss of more than 10%: Severe dehydration is present. The anterior fontanelle is more sunken than usual and is very sunken in the presence of severe dehydration. Urinating less; Is there a state of malnutrition; Fever and infection: look for signs of infection (otitis media, pneumonia...); Convulsions: find the cause of convulsions in diarrhea such as high fever, hypoglycemia, hyper or hyponatremia... Gastrointestinal examination: Abdominal condition, stool, vomit, liver, spleen enlargement, abdominal fluid. There are signs of complications such as: acute renal failure, electrolyte disturbances, abdominal distention due to hypokalemia or inappropriate antidiarrheal drugs, acid-base disturbances.
2.3 Testing Routine testing is not required.
Electrolyte test when the child has dehydration, severe dehydration or disease progression disproportionate to the degree of diarrhea; CTM, CRP when the child has fever, suspected infection or dehydration;

Cần xét nghiệm điện giải đồ khi bé mất nước
Screening, stool culture when infectious diarrhea is suspected (bloody stools, severe and prolonged diarrhea, severe watery diarrhea suspected of cholera, diarrhea in immunocompromised children; Fresh screening for parasites when clinical Suspected parasitic infection; Look for fat particles, muscle fibers when malabsorption is suspected; Abdominal ultrasound when children have abdominal pain, distention, bloody stools, vomiting a lot...; Abdominal X-ray when there is abdominal distention, X-ray -Pneumonia when pneumonia is suspected.
3. Diagnosis
General principle:
Distinguish between symptomatic diarrhea and diarrhea; Assess the degree of dehydration, dehydration according to the World Health Organization; Diagnosis of complications; Diagnose the cause of diarrhea. 3.1 Classification and treatment of dehydration
Diarrhea with isotonic dehydration The equivalent amount of salt and water loss:
+ Na+ concentration: 130-150 mmol/L.
+ Plasma osmolality: 275-295 mOsmol/l. Severe loss of extracellular fluid causing volume depletion
Acute diarrhea with hypotonic dehydration Loss of salt more than water. Na+ concentration < 130 mmol/l. Plasma osmolality <275 mosmol/l. The patient is lethargic, possibly convulsing. Or occurs when the patient vomits a lot, malnourished.

Tiêu chảy cấp mất nước nhược trương khiến trẻ li bì
Hypertonic dehydration acute diarrhea Loss of more water than Na+ . Na+ concentration > 150 mmol/l. Plasma osmolality >295 mosmol/l. The patient is agitated, very thirsty, convulsing. Occurs when drinking hypertonic solutions.
3.2 Diagnosis of complications - Other disorders Blood potassium: Hypokalemia: Potassium < 3.5 mmol/l. Clinical: muscle weakness, muscle weakness, abdominal distension, decreased reflexes, arrhythmia. Electrocardiogram: ST collapse, low T wave, appearance of U wave, if too severe decrease PR prolonged, QT dilated. Hyperkalemia: Potassium > 5.5 mmol/l. Clinical: muscle weakness, arrhythmia. Electrocardiogram: high T-point, short QT, A-V block, ventricular fibrillation (potassium ≥ 9mmol/l) Metabolic acidosis: pH < 7.2, HCO3ˉ < 15 mEq/l, rapid, deep breathing, red lips. Acute renal failure: oliguria or anuria, BUN, blood creatinine increased. 3.3 Diagnosing the cause of diarrhea Diarrhea caused by viruses, bacteria or other agents
Children < 2 years old: acute diarrhea, watery stools, no blood, vomiting a lot, dehydration due to damage to the absorptive cells In the small intestine, it is usually caused by Rotavirus causing severe diarrhea, or by irritating toxins that cause increased secretion of fluids and electrolytes (Cholera, ETEC...). Diarrhea caused by intestinal bacteria: E.coli includes types of ETEC (E.coli toxin), EPEC (E.coli causing disease), EHEC (E.coli causing bleeding), EIEC (E.coli invading bacteria). ), EAEC (E.coli adhesion). Shigella: bacillus dysentery, cholera: often causes outbreaks. Other bacteria: Campylobacter Jejuni, Salmonella ... Often cause dysentery diarrhea due to lesions in the ileum and colon, presenting with fever, abdominal cramps, frequent bowel movements, small quantity of stools, bloody mucus. Intestinal parasitic infections: Giardia, Cryptosporodia, amoebae Extraintestinal infections: respiratory infections, urinary tract infections, meningitis... Find other causes: due to drugs, food allergies, digestive disorders assimilation, absorption. Inflammation of the bowel caused by chemotherapy or radiation. Surgical diseases...
4. Hospitalization and follow-up criteria
4.1 Indication for hospitalization The child needs to be monitored at a medical facility and re-evaluated during follow-up when the following signs appear:
Dehydration: the child is dehydrated or at risk of oral failure; Recurrent vomiting or vomiting of bile;

Khi trẻ tiêu chảy kèm nôn nhiều cần đưa trẻ nhập viện
Instruct caregivers to detect early signs of dehydration to take them to a medical facility promptly when:
Children have frequent bowel movements, more watery stools; Thirst a lot; Fever or higher fever; Nasal bloody mucus stools; Vomiting everything; Refused to eat. As a key area of Vinmec Medical system, Pediatrics Department always brings satisfaction to customers and is highly appreciated by industry experts with:
Gathering a team of leading pediatricians: including leading experts with high professional qualifications (professors, associate professors, doctorates, masters), experienced, worked at major hospitals such as Bach Mai, 108.. Doctors All are well-trained, professional, with a mind - range, understanding young psychology. In addition to domestic pediatric specialists, the Department of Pediatrics also has the participation of foreign experts (Japan, Singapore, Australia, USA) who are always pioneers in applying the latest and most effective treatment regimens. . Comprehensive services: In the field of Pediatrics, Vinmec provides a series of continuous medical examination and treatment services from Newborn to Pediatric and Vaccine,... according to international standards to help parents take care of their baby's health from birth to childhood. from birth to adulthood Specialized techniques: Vinmec has successfully deployed many specialized techniques to make the treatment of difficult diseases in Pediatrics more effective: neurosurgery - skull surgery, stem cell transplantation. blood in cancer treatment. Professional care: In addition to understanding children's psychology, Vinmec also pays special attention to the children's play space, helping them to have fun and get used to the hospital's environment, cooperate in treatment, improve the efficiency of medical treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.