This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by the Doctor in charge of the Dental - Jaw - Facial Unit - Interdisciplinary Department - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.
When a tooth constantly ache and keeps you awake at night with pain it can be more of a concern than a simple toothache. An abscessed tooth is when the infection has spread around the apex or root of the tooth.
1. What is a periapical abscess?
This periapical abscess originates in the inner cavity of the tooth, known as the "pulp chamber". Contained in the pulp chamber are the blood vessels and nerves, collectively known as "the pulp". Prior to the formation of an abscess, the tooth has essentially lost its ability to fight infection and bacteria can enter the pulp chamber and multiply. As bacteria multiply, the infection usually spreads from the pulp chamber and exits from the apex of the root into the bone. An abscess is a collection of pus made up of dead white blood cells, tissue debris, and bacteria.
A periapical abscess is different from a gingival or periodontal abscess due to the primary source of infection. A periapical abscess originates in the pulp and exits the tooth at the root apex. Gum abscess or periodontal abscess begins in the extra-gingival pocket next to the root due to gum and periodontal disease. Treatment will depend on where the infection originates.
2. What are the signs and symptoms of a periapical abscessed tooth?
Teeth turn darker than surrounding teeth. Necrotic pulp by-products seep into the spongy tooth layer causing this discoloration.
There is pain when eating or pressing on the teeth and in many cases there is no pain. The abscess has spread to the apex (peduncle) causing the supporting structures (gingiva and bone) to be affected. Sometimes the throbbing or pounding pain is so intense that it can't be relieved with pain medication. This is often associated with extensive infection that puts more pressure on the surrounding structures of the gums and bone.
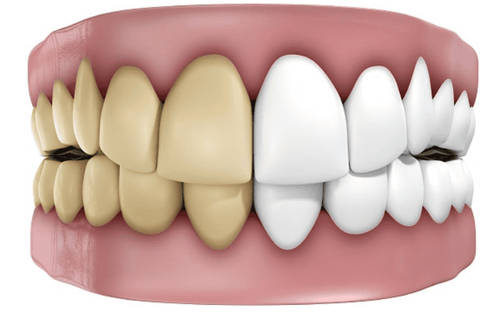
Răng chuyển màu tối hơn so với răng xung quanh có thể là triệu chứng của răng bị áp xe quanh chóp
Swollen gum tissue and filled with pus. Swollen gums look like a pimple near a diseased tooth. Perforated acne can create a "fissure" and rupture to release pus. This is a clear sign of an infection. Another sign of a tooth abscess is a bad smell in the mouth.
Swelling of the face, jaw or local lymph nodes is often a sign of an increasing infection. There may be jaw pain due to swelling.
It is also important to note that a tooth with an abscess around the apex may not have any symptoms at all. Because the tooth is dead (unresponsive to stimulation) however, an abscess is present and can spread. Occasionally, an abscessed tooth is discovered during a routine radiographic examination in which the patient is completely free of any symptoms of an abscessed tooth.
3. How to diagnose a tooth abscess?
The diagnosis of dental abscess is generally confirmed by (1) signs and symptoms reported by the patient, (2) physical examination and tests performed by the dentist, and (3) imaging studies. by dental X-ray.
4. Are home remedies effective for a tooth abscess?
In general, home oral health remedies are not recommended for an abscessed tooth. Home remedies that can be used for temporary relief of symptoms include applying warm salt water or warm tea bags pressed on the affected area and taking over-the-counter pain relievers such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. (NSAIDs). However, the infection will still progress if not treated properly. Furthermore, avoiding treatment can lead to more serious complications. Seeking care and advice from a dental professional is advisable as soon as possible.

Các biện pháp chăm sóc răng tại nhà không được khuyên dùng cho răng bị áp xe
5. How to treat abscess around the apex?
In adult teeth, the usual treatment for an abscessed tooth begins with proper removal of the infection. Treatment depends on how far the tooth infection has spread. The course of action usually involves oral antibiotics such as penicillin. The tooth is opened to remove the infected tissue in the pulp chamber. If necessary, make an incision and drain the soft tissue to continue draining the pus and relieve the pressure of a developing infection.
In some situations, infections can spread quickly and require immediate intervention. If a dentist cannot be seen immediately, a person with a fever, swelling in the face, or swelling in the jaw should go to the emergency room. Emergency medical care is required if breathing or swallowing is difficult.
Once the infection is cleared up and the tooth can be restored, a root canal treatment will be performed. "Root or endodontic treatment" is to clean the entire internal space of a tooth (pulp chamber and canals) and replace that space with a filling with an inert rubber material called gutta percha. Cleaning and filling the internal space will protect the tooth from further invasive infection. The tooth may need to be extracted if too much of the tooth structure or bone surrounding the tooth is lost due to decay and infection.
For children's primary teeth (baby teeth), if there is an abscess, there is less chance that the tooth can be saved. The infection has progressed and there is no way to completely eliminate all infections. If root canal therapy is considered unsuccessful, the primary tooth will have to be extracted. Complete removal of an abscessed baby tooth is also important in avoiding a persistent infection that could potentially harm the developing adult teeth underneath. Oral antibiotics may or may not be needed depending on the extent of the infection.

Răng sữa bị áp xe sẽ khó để cứu răng hơn
During pregnancy, tooth abscess requires immediate attention to minimize the spread of infection. Any risk of infection during pregnancy is a concern because the infection can be more serious in a pregnant woman or could harm the unborn baby.
6. What is the prognosis for a periapical abscessed tooth?
Prognosis depends on how far the infection has spread. Usually, when the infection is localized to the tooth, the prognosis is good if treated as soon as signs and symptoms are noticed. If the infection affects much of the surrounding jawbone of the tooth and causes the tooth to become loose, the chances of saving the tooth are reduced.
To register for examination and treatment of oral health problems at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact the nationwide Vinmec Health System Hotline, or register for an online examination HERE.