This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Dr. Nguyen Dinh Hung - Diagnostic Imaging - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
Abdominal magnetic resonance imaging is widely used in the diagnosis and prognosis of many diseases of the digestive system, endocrine system, blood vessels and other organs in the abdomen. Contrast enhances contrast and further assesses organ perfusion and injury. So what is the procedure of abdominal magnetic resonance imaging with injection of magnetic contrast?
1. Outline
In humans, most of the digestive system is located in the abdominal cavity including the stomach, duodenum, small intestine, colon, and anus. In addition, there are exocrine organs such as the liver, bile and pancreas. The kidneys and urinary system are also located in the abdomen. In addition, some other important organs such as spleen and adrenal gland are all parts that magnetic resonance can survey well about anatomical structure if there is a suspected lesion.
Magnetic resonance imaging is based on the principle of magnetic resonance of atoms. The magnetic resonance machine will generate a magnetic field and send waves to the hydrogen atoms in the organ tissue, from which these atoms absorb and emit the signals to the receiver of the machine. Depending on the density of atoms present in the tissue, the signal density will be received, the information processing unit will convert these signals into an image form to help reconstruct the image of the organ to be examined.
Suspected intra-abdominal lesions are the main indications for abdominal magnetic resonance imaging. Depending on the clinical situation, the pathology needs further investigation on the perfusion capacity and blood supply of the injured organ. Therefore, contrast agents may be used in certain situations.
Chụp MRI ổ bụng giúp chẩn đoán các tổn thương vùng ổ bụng
2. Indications for abdominal magnetic resonance imaging with injection of magnetic contrast agent
● Investigate suspected pancreatic lesions such as pancreatic cancer, evaluate pancreatic duct obstruction or dilation, fluid collection, peripancreatic or pancreatic fluid leakage, chronic pancreatitis, complicated acute pancreatitis, follow-up after treatment treatment;
● In the spleen, detect suspected tumor lesions, evaluate the spleen;
● Detection of kidney tumors, preoperative assessment, renal vasculature, renal function, urinary excretion, urinary tract abnormalities, post-treatment follow-up;
● Investigation of damage to the adrenal gland;
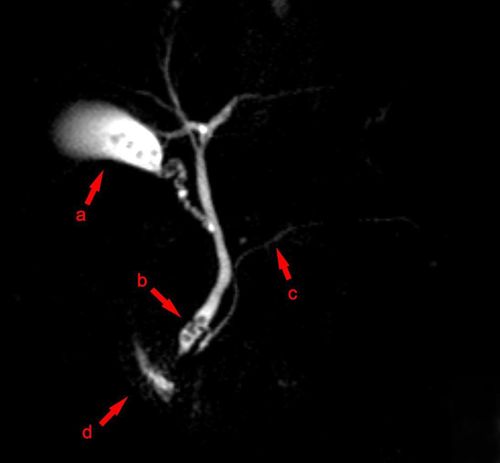
● Detect and evaluate lesions in the biliary tract and gallbladder such as: cholangiocarcinoma, choledocholithiasis, gallbladder, congenital biliary malformation, stage assessment and follow-up after treatment;
● Evaluation and investigation of lesions in the gastrointestinal tract such as gastric tumors, rectal cancer, inflammatory disorders in the gastrointestinal tract, acute abdominal pain in the fetus, peritoneal or mesenteric tumors, fluid accumulation.
Ung thư tuyến tụy nên được chụp cộng hưởng từ ổ bụng có tiêm thuốc đối quang từ
3. Contraindications to magnetic resonance imaging with injection of magnetic contrast agents
● Absolutely contraindicated in patients who wear metal-based electromagnetic devices such as pacemakers, anti-vibration machines, cochlear implantation, automatic subcutaneous injection devices. Surgical implantation of intracranial means, blood vessels, eye sockets < 6 months, the patient is in critical condition.
● Relative contraindications for those carrying metal surgical instruments > 6 months, phobia of loneliness, fear of the dark, glomerular filtration rate < 30 mL/min, pregnant or lactating women suck.
4. Preparation steps before abdominal magnetic resonance imaging with injection of magnetic contrast agent
● Medical staff: doctors and radiology technicians.
● Equipment: 1.5 Tesla or more resonator, film and storage system.
● Medicines: sedatives, contrast agents, skin and mucosal antiseptics.
● Medical supplies: needles, syringes, distilled water or 0.9% NaCl, cotton, gauze, shockproof box
● Patient: no fasting, explained and advised on what to do , remove contraindicated items and place an intravenous line.
Máy chụp cộng hưởng từ mới 3.0 Tesla công nghệ Silent tại Bệnh viện Đa khoa Quốc tế Vinmec
5. Steps to conduct an abdominal magnetic resonance imaging with injection of magnetic contrast agent
● Select the field of view (FOV) with the highest resolution and high signal ratio, possibly the entire area or just the organ to be assessed. Most organs examined in the abdomen use sequence of T1W and T2W images.
● Carry out multi-section imaging to determine the anatomical relationship, the thickness of the cut should not exceed 1 cm with the distance between the two slices not exceeding 3mm.
● The T1W pulse sequence has a choice of routine echo routine spin echo, echo train spin echo (TSE) or fast spin echo (FSE) or gradient (echo).
Selectable T2W series such as fast spin echo or hybrid gradient and spin echo (GRASE) technique
Fat removal can select techniques such as inversion recovery (STIR), selective liposuction, or spectral presaturation inversion recovery (SPIR) or Dixon techniques and water stimulation.
● Note that when taking fast gradient echo T1W images while holding your breath, routine and fast echo T2W images are often noisy for movement. Use breathing techniques to create T2W images.
● 3D rendering algorithms for both T1W and T2W images have many advantages over 2D because of increased sharpness, reduced noise ratio, increased in-plane and trans-plane resolution, uniform fat removal.
● Contrast is used to detect and characterize intra-abdominal tumors, vascular abnormalities, and foci of advanced inflammation. However, some contraindications should be noted such as no intravenous access, history of allergy to contrast agents, severe or acute renal failure, systemic fibrosis due to renal disease.
● Based on drug pharmacokinetics (pre-injection, arterial, venous, equilibrium) is useful for evaluation of blood vessels and solid tumors. Using background erasure technique helps to increase the ability to detect the increase of contrast agent of the tumor.
Bệnh nhân suy thận nặng chống chỉ định tiêm thuốc đối quang từ
● Delayed post-injection images help detect urinary tract diseases and cancers of the biliary system.
● Diseases in the gastrointestinal tract, using oral contrast agents to increase the ability to detect lesions.
● In-phase and out-phase pulse sequences help detect intracellular lipids in cases of adrenal adenoma, renal clear cell carcinoma and assess pancreatic infiltrates.
● T2W series in cholangiography (MRCP) helps to examine the pancreatic duct and biliary tract.
6. Read and return results
● The results are printed to a movie or to a CD.
● The specialist reads and describes the lesion, prints the results.
● Can provide professional advice and suggest further testing in case of need.
Vinmec International General Hospital is currently one of the major hospitals with modern machinery and equipment for general medical examination and treatment procedures and accurate and modern MRI for brain and vascular diseases. brain blood in particular.
Especially, Vinmec International General Hospital is the first unit in Southeast Asia to put into use the new 3.0 Tesla Silent Resonance Imaging machine from the US manufacturer GE Healthcare.
The machine currently applies the safest and most accurate magnetic resonance imaging technology available today, without using X-rays, non-invasive. Silent technology is very beneficial for patients who are young children, the elderly, patients with weak health or have just had surgery.
Doctor Nguyen Dinh Hung has over 10 years of experience in the field of diagnostic imaging (Ultrasound, CT, MRI). Trained and practiced on hepatobiliary interventional radiology at Bach Mai Hospital (Intervention under ultrasound guidance, DSA, CT...) and deployed at the Diagnostic Imaging Department of Viet Tiep Hospital Hai Phong. Currently, he is a doctor at the Diagnostic Imaging Department of Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
To register for an examination at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact the nationwide Vinmec Health System Hotline, or register online HERE.