This is an automatically translated article.
Celiac disease is a common digestive disorder, especially in Western countries. So what is celiac disease? How do I know I'm sick? We invite you to read this article together!
1. What is celiac disease?
Celiac disease is a digestive disorder that occurs as a result of a reaction to gluten, a protein found in rye, barley, wheat, and foods prepared with these grains. The body's immune system reacts to gluten and damages the intestines.
Celiac disease is also known as gluten sensitive intestine. This is a fairly common syndrome, with an estimated 1.8 million Americans suffering, they need to follow a gluten-free diet.
2. Celiac disease symptoms
2.1 Gastrointestinal symptoms Symptoms can vary from mild to severe. Even when the intestines are damaged, the person still has no symptoms. Celiac disease can be misdiagnosed as irritable bowel syndrome, Crohn's disease, or a stomach ulcer. Gastrointestinal symptoms of celiac disease can include:
Pain, bloating; Diarrhea ; Vomiting; Constipation ; Passing pale colored stools. 2.2 Symptoms of Weight Loss & Malnutrition Gluten in food will activate the immune system of people with celiac disease. The antibodies attack the lining of the intestines, damaging, flattening, or destroying small tissues such as hairs (villi) in the small intestine. When this layer of villi is damaged, the intestinal wall cannot absorb nutrients effectively, causing all proteins, vitamins and fats to pass into the stool. This condition can lead to malnutrition in the long run.
Many adults with celiac disease do not have digestive symptoms, but they fail to absorb nutrients leading to other problems such as weight loss and malnutrition. Symptoms related to weight loss and malnutrition in people with celiac disease include:
Anemia; Tired; Osteoporosis ; Infertility or miscarriage Mouth ulcers; Numbness and tingling in the hands and feet.
Nhiều người lớn mắc bệnh celiac không có các triệu chứng tiêu hóa
2.3. Skin symptoms For some people, celiac disease causes an itchy, blistering rash called dermatitis herpetiformis. The patient has an intense burning sensation around the elbows, knees, scalp, buttocks, and back. Clusters of red, itchy bumps that form and then scab over.
Celiac disease usually first appears during adolescence and is more common in men than in women. The rash usually resolves with a gluten-free diet but can also be treated with medication.
2.4. Memory and emotional symptoms Some people with celiac disease are depressed, irritable, have poor memory, and have trouble concentrating. Having a chronic illness can contribute to memory problems, especially when there is chronic pain or fatigue associated with anemia.
2.5. Warning Signs of Celiac Disease in Children Celiac disease symptoms can begin as early as when children are introduced to foods containing gluten. Common signs are yellowing enamel, brown spots, pits on the teeth. Children whose parents or siblings have celiac disease should be tested.
3. Foods that Trigger Celiac Disease
Wheat is the staple food in Western countries. Many foods containing gluten from wheat can trigger celiac disease such as breads, cookies, muffins, pasta, pizza, cakes, and pies. Fried chicken can also be a food to limit for people with celiac disease because it is breaded.
In addition, Japanese udon noodles are also made from wheat, rye and barley also contain gluten. Pumpkin bread, barley soup, and beer are all gluten-containing foods, which can trigger celiac disease.

Một số người mắc bệnh celiac bị trầm cảm
4. Distinguishing celiac disease allergy from wheat allergy and lactose intolerance
Celiac disease and wheat allergy both involve the immune system but the body's internal response is different. Celiac is an autoimmune disease that damages the lining of the intestines and is a lifelong disorder. Meanwhile, symptoms of a wheat allergy can include a skin rash, wheezing, abdominal pain, or diarrhea. Wheat allergy usually gets worse.
Celiac disease damages the inner lining of the small intestine and can lead to intolerance to lactose, a sugar found in milk and dairy products. The gluten-free diet helps the intestines recover and people with celiac disease can digest lactose again.
5. Subjects at risk of celiac disease
Although no one knows exactly why, the following factors put you at greater risk of celiac disease:
Family history of celiac disease ; Children under 3 months of age who have been exposed to foods containing gluten; People who have experienced major events in life, emotional stress; pregnant women or after surgery in people with a genetic predisposition; Have type 1 diabetes, thyroid disease or other autoimmune disease; Have another genetic disorder such as Down or Turner syndrome.
6. Celiac disease can have a late onset
Celiac disease can occur at any age, even in the elderly. Although the disease tends to be inherited, science doesn't explain why some people develop an immune response after years of being intolerant to gluten. It can take up to 4 years for gluten intolerance to develop symptoms.7. Diagnosing Celiac Disease
7.1. Blood tests The symptoms of celiac disease are so varied that it's usually not difficult to detect or misdiagnose. Blood tests may allow high levels of certain disease antibodies to be detected. If the results are negative, your doctor may order additional testing, including DNA analysis, for an accurate diagnosis.
7.2. Genetic testing Genetic testing provides another important piece of information. About one-third of Americans have the DQ2 or DQ8 gene, which is considered common to cause celiac disease. If you don't have those genes, your doctor can rule out celiac disease as one cause of your symptoms. However, studies also show that many people have the gene and still do not develop celiac disease.
7.3. Diagnosing Celiac Disease Bowel Biopsies Small bowel biopsies are the definitive method of confirming celiac disease results. An endoscope is inserted through the mouth and stomach into the small intestine to remove a small amount of tissue. Small intestine tissue is taken for diagnosis because celiac disease damages or destroys the lining of the intestines.
Note, people who are sensitive to gluten have symptoms similar to celiac disease, like abdominal pain, fatigue, or headaches, but they don't have the intestinal damage or more serious consequences that celiac disease causes. If they follow a gluten-free diet, these symptoms will be eliminated.
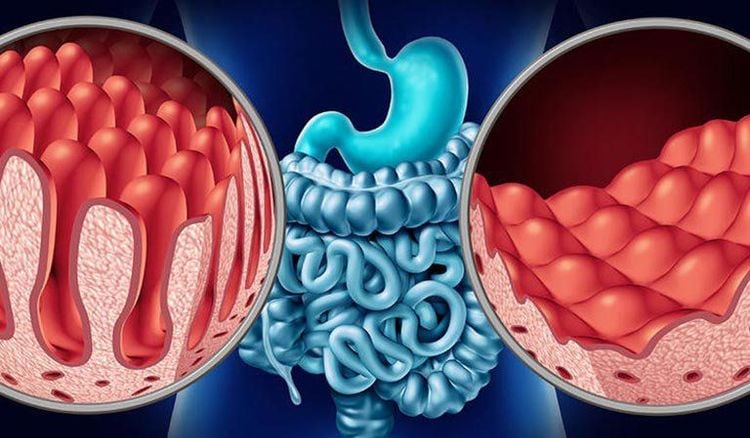
Bệnh celiac gây tổn thương trong ruột non
8. What are the risks of untreated celiac disease?
More than 60% of children and 40% of adults have celiac disease but do not have any symptoms. When the intestinal lining is damaged, the patient does not absorb nutrients well, leading to the risk of malnutrition. People with celiac disease are at increased risk for osteoporosis, infertility, and other neurological problems.
Diabetes: People with type 1 diabetes may be prone to celiac disease. Untreated celiac disease can lead to low blood sugar or unstable blood sugar levels. In addition, the patient may have other autoimmune diseases including rheumatoid arthritis, thyroid disease; Osteoporosis: When the small intestine is damaged by celiac disease, the body doesn't absorb nutrients well. People with celiac disease are at risk for osteoporosis, and many of them will need aggressive treatment to compensate for low bone density. At that time, the patient needs to be supplemented with calcium and vitamin D, and have regular bone density checks.
9. Caring for someone with celiac disease at home
People with celiac disease need a reasonable diet. Specifically:
Follow a Gluten-Free Diet: There is no cure for celiac disease, but completely avoiding gluten will stop symptoms and allow the intestines to repair itself. In fact, people may feel better within a few days of eliminating gluten from their diet. The most common foods to avoid include pasta and cereals. Even small amounts of gluten that can be found in other foods should be limited; People with celiac disease need to be careful with potentially gluten-containing foods such as processed meats, potatoes and deep-fried foods, and sauces and soups that contain wheat. Gluten can also be found in lipsticks or medications. Patients should also be cautious with oats as they may also have added wheat. Consult your doctor before including oats in your diet. Wine and distilled spirits are generally safe, but most beer isn't safe for people with celiac disease. Beer is made from grain and has not undergone distillation. Therefore, people with celiac disease should not drink beer; Use foods that are naturally gluten-free: Many other starches that can be added to a gluten-free diet include rice, buckwheat, flaxseed, potatoes, soybeans, and corn. Buckwheat is not a wheat but a relative of rhubarb and is gluten-free. The Japanese use buckwheat to make soba noodles, kasha, porridge, pancakes. Processed foods such as chips should be carefully checked to make sure they are not made with foods that contain gluten, such as flour; Other micronutrient supplements: People with celiac disease should take vitamin and mineral supplements if they have deficiencies such as iron, calcium, vitamin D, zinc, copper, folic acid, and other B vitamins.

Người bị bệnh celiac không được dùng bia
10. Other treatments and living with celiac disease
Among people with celiac disease, there are some patients who do not respond to the gluten-free diet. These people may be prescribed steroids to be taken by mouth or injected into a vein for short periods of time.
Meat, fish, rice, beans, fruits and vegetables are all good for people with celiac disease if prepared with gluten-free ingredients. Many stores sell gluten-free pasta, pizza, and cookies. Following a strict diet can help prevent health problems from celiac disease. If there is no improvement, the patient should seek out potential sources of gluten in the foods used.
Studies are underway for new drugs that help people with celiac disease eat gluten safely, such as using enzymes in the form of oral tablets that break down gluten. Immunotherapy can counteract the underlying immune response to gluten. Scientists even tested hookworms, an intestinal parasite, to see if they could help people with celiac disease, but no recommendations have been made since the study.
Celiac is known to be an autoimmune disease, the body's immune system reacts to gluten - the main component of wheat. If the disease is not treated, it can lead to weight loss, malnutrition, osteoporosis.... Therefore, recognizing the early signs and symptoms will help patients to examine and treat early, limiting complications. more dangerous.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: webmd.com












