This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Thi Hong On - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital.Fetal malformations are defects in the body of a baby that are acquired while in the mother's womb that may not be recognized until birth. Today, thanks to the development of modern medicine, parents can detect fetal abnormalities right in the womb thanks to prenatal screening tests.
1. Purpose of prenatal diagnosis
Prenatal diagnosis helps early detection of pregnancies with severe birth defects, genetic diseases or children with intellectual disabilities: Down syndrome, Trisomy 13 (3 chromosomes 13), Trisomy 18 (3 infections). Chromosome 18), Thalassemia... then advise pregnant women and their families on how to end pregnancy in order to reduce the burden on the family and society. Early diagnosis of fetal malformations that can be repaired after birth such as cleft lip, cleft palate, clubfoot... will help to prepare better psychologically for the couple.2. 7 measures of prenatal diagnosis
Pre-implantation diagnostic measures include:Preimplantation genetic diagnosis. Supersonic. Vegetable spine biopsies. Amniocentesis. Umbilical cord blood aspiration. Maternal blood test (triple test, quadtro test). Free DNA test in maternal blood.
2.1 Preimplantation genetic testing
Preimplantation genetic testing is used to identify genetic abnormalities in IVF (in vitro fertilization) embryos prior to embryo transfer to the mother's uterus. Preimplantation genetic testing helps diagnose X-linked genetic diseases and determine sex.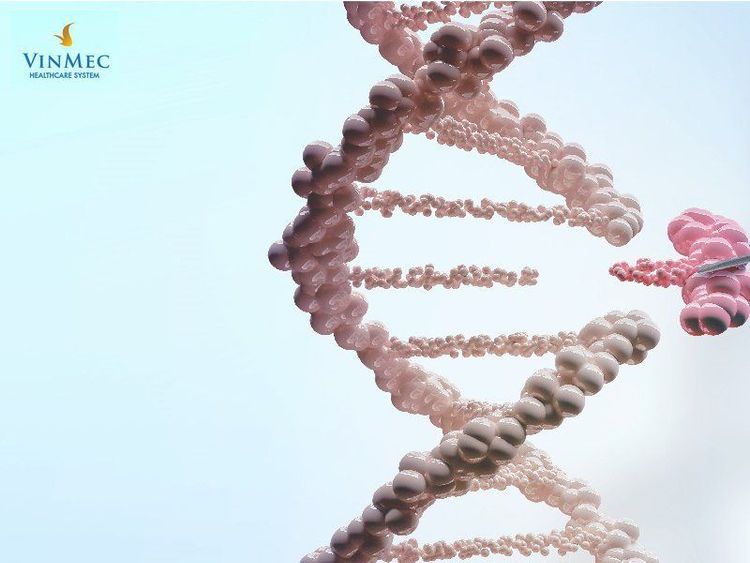
Xét nghiệm di truyền tiền làm tổ giúp chẩn đoán bệnh di truyền liên kết
2.2 Ultrasound
Diagnostic ultrasound helps to detect:Head malformations: ventricular dilatation, hydrocephalus, neural tube defects (cerebral hernia, meninges), anencephaly Heart defects: left ventricular hypoplasia, vertebral inversion vasculitis, septal hypoplasia, Ebstein's syndrome, tetralogy of Fallot, equestrian aorta. Thoracic malformations: diaphragmatic hernia, lung cysts Digestive system atrophy: esophageal atrophy, umbilical hernia, abdominal wall clefts Renal - urinary anomalies: hydronephrosis, polycystic kidney, ovarian tumor Anomalies Other defects: Cartilaginous dysplasia, osteochondrosis, vertebral cleft Ultrasound measurement of nuchal translucency and nasal bone gain accurate results when the time of measurement is from 11 weeks to 13 weeks and 6 days. whether the fetus has any chromosomal abnormalities or has Down syndrome.
Siêu âm giúp chẩn đoán một số dị tật bẩm sinh
2.3 Biopsy of vegetable spines
This is a procedure performed in the early stages of pregnancy, from 12-14 weeks of age, to help check for fetal abnormalities. This prenatal diagnostic test is performed when one parent has a family history of the disease, the mother is over 35 years old.A placental abruption is performed by removing a sample of the placenta from the uterus using a catheter (a long tube) or a needle inserted through the woman's abdomen or vagina under ultrasound guidance.
2.4 Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis is usually done at 16 weeks of pregnancy or more. Amniocentesis and placental biopsy are performed only in pregnant women who are at high risk of giving birth to babies with genetic disorders, genetic disorders of the father and/or mother, a history of birth defects, or a pregnancy women over 35 years old.Amniocentesis is performed using a very fine needle, injected through the abdominal wall into the uterus under ultrasound guidance and aspiration of the small amount of amniotic fluid needed for diagnosis. The pregnant woman's body will regenerate the amount of amniotic fluid that is sucked out. For the most part, the baby will be unaffected during and after the procedure. Some pregnant women will experience mild abdominal pain during or after the procedure.
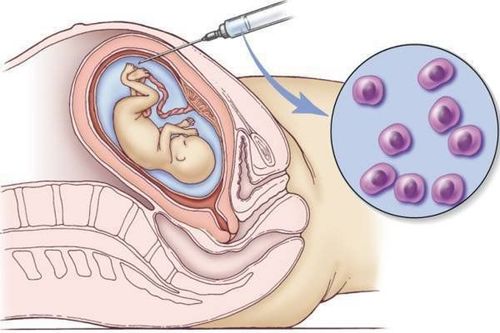
Chọc hút ối thường được thực hiện từ tuần thứ 16 của thai kỳ trở đi
2.5 Umbilical cord blood aspiration
The method of umbilical cord blood collection to diagnose genetic abnormalities of the fetus as indicated by the antenatal clinician. This technique is performed at 11-13 weeks gestation.Under the guidance of ultrasound, a needle is inserted through the abdominal wall of the pregnant woman into the uterus, then into the blood vessels in the umbilical cord, about 1cm from the placenta. A small amount of blood is taken for testing and diagnostic results in cases of suspected anemia, measles infection, toxoplasmosis, herpes or fetal growth retardation. The risk of fetal harm when performing this method is quite high, from 1-2%.
2.6 Maternal blood test Double test Triple test, Quadtro test
Double test: PAPP-A + free β-hCG Triple test: AFP + hCG + Estriol Quadtro test: AFP + hCG + Estriol + Inhibin A In which:PAPP-A (Pregnancy Associated Plasma Protein A) is a glycoprotein produced by placental secretion in maternal serum AFP: Alpha-fetoprotein is a protein secreted by the baby's liver. Hormone hCG: born from the placenta Estriol: a hormone of the placenta and the baby's liver. Inhibin A: hormone produced by the placenta and ovaries. Double test combines nuchal translucency measurement by ultrasound, maternal age, gestational age, ... to assess the risk of chromosomal abnormalities such as Down syndrome, Edwards (Trisomy 18) and Patau (Trisomy 13) syndromes. . Double test screening is usually done in the first trimester, which is around the first 3 months of pregnancy. Double can be best done between 11 - 13 weeks of pregnancy, preferably during 12 - 13 weeks of pregnancy. Based on the ultrasound results to determine the gestational age, pregnant women can perform the test. after ultrasound examination to measure nuchal translucency.
Triple test is done when the fetus is 15 - 20 weeks old to find out the risk of neural tube defects. However, for the most accurate results, the test should be performed at 16 - 18 weeks of pregnancy. Triple test uses the mother's blood to check for fetal malformations thanks to the increase or decrease of 3 indicators. The above points help doctors predict the risk of abnormalities. All pregnant women should have this test, especially those with high risk: Family history of birth defects, pregnant women over 35 years old, use of drugs or substances that can cause birth defects. harmful to the fetus, diabetes and insulin use, viral infection during pregnancy, working or living in an environment exposed to chemicals, high doses of radiation,...
Quadtro test ( Quad test) is performed between 15 and 20 weeks of pregnancy by drawing blood from a woman's arm vein. The results of the quad test show an increased risk of fetal abnormalities or chromosomal abnormalities, such as spina bifida or Down syndrome (3 chromosomes 21), Edwards Syndrome (3 chromosomes 18). Subjects needing Quad test are similar to Triple test mentioned above.
2.7 DNA test in maternal blood
A maternal blood DNA test is also known as a noninvasive genetic test (NIPT). NIPT is a fetal DNA test in maternal blood to screen for fetal chromosomal abnormalities: 3 chromosomes 21, 3 chromosomes 13, 3 chromosomes 18,...Non-invasive genetic testing NIPT is considered "the key" key" to "decode" fetal malformations from a very young gestational age, only 9-10 weeks old. NIPT is recommended to be indicated for high-risk subjects and performed routinely at Vinmec. Analytical results will be available in about 1-2 weeks and will be assessed by genetic pathologists at the Institute of Stem Cells and Gene Technology and will be paid through various methods such as direct payment, pay at home, by email or phone number. Customers will be consulted specifically about possible risks, especially for false positive / negative cases to have appropriate intervention direction.
Screening for fetal malformations during pregnancy can detect and intervene early in the fetus or treat early after birth, helping the child develop normally. In some cases, the fetus has severe defects that are difficult to survive, which will help the pregnant woman make the decision to keep or abort the fetus. Therefore, the results of screening for fetal malformations play a very important role, so when choosing an antenatal clinic, pregnant women should choose safe reputable medical facilities for an accurate diagnosis.
Vinmec International General Hospital is proud to be a high-quality medical facility that is highly appreciated by customers for its quality of examination and treatment as well as professional services. Vinmec has the most modern equipment system, with the most advanced ultrasound and testing machines in the world and a team of experienced obstetricians in prenatal diagnosis and intervention to help monitor obstetrics well. and early detection of fetal abnormalities.
For specific information about fertility and maternity packages at Vinmec, please contact the hospitals and clinics of Vinmec health system nationwide.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.