This is an automatically translated article.
Cervical cancer is one of the most common cancers in women. Cancer can be difficult to detect through normal observation, because the disease often does not show specific symptoms in the early stages. The best way to detect cancer early is to perform diagnostic tests to prevent and treat cancer early.1. What is cervical cancer?
Cervical cancer is the growth of abnormal cells in the lining of the cervix. Normally, the cervix is an important organ in the female reproductive system, which includes the fallopian tubes, uterus (womb), ovaries, vagina (birth canal) and vulva (genital tract). external genitalia).
Women's cervix usually has an outer surface that opens into the vagina and an inner surface that is the cervical canal. These two surfaces are covered by two different types of cells, including:
Squamous cells: These are thin and flat cells that cover the outer surface of the cervix (ectocervix). Cancer in this area is called squamous cell carcinoma.
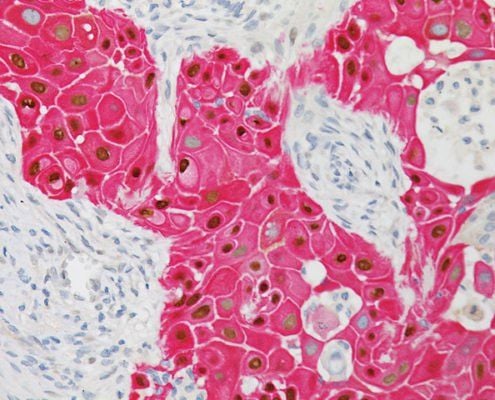
Hình ảnh ung thư biểu mô tế bào vảy
Glandular cells: These are column-shaped cells that cover the inner surface of the cervix (cervical canal or cervical canal). Cancer in this area is called adenocarcinoma. Overall, the most common type of cervical cancer in women is squamous cell carcinoma, which accounts for 80-85% of cases. In addition, adenocarcinoma is often less common and more difficult to diagnose.
2. Is cervical cancer hereditary?
Most cases of cervical cancer are caused by HPV infection. Although you can't inherit cervical cancer, you can still get the disease because of your genes.
For example: Women who have a mother or sister with the disease have a higher risk of developing the disease on their own. However, researchers have not yet determined exactly whether genetics is what makes some women more susceptible to HPV infection than others.
3. The main stages of cervical cancer
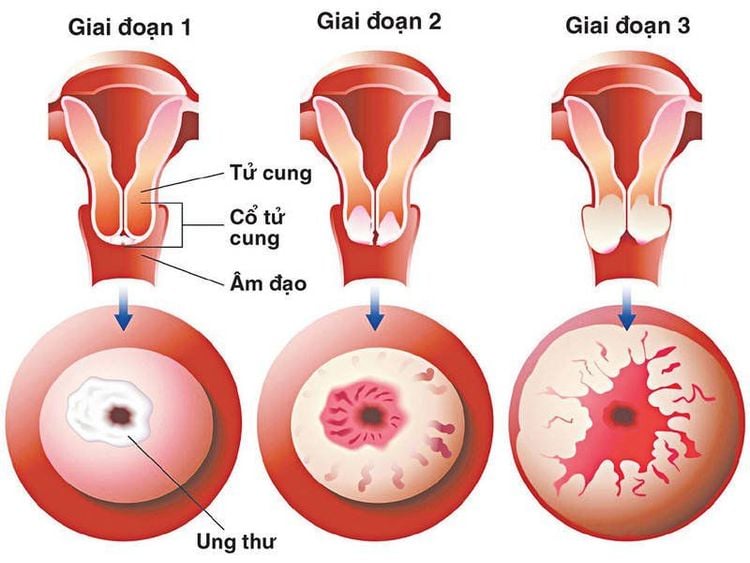
Giai đoạn ung thư cổ tử cung
Health professionals divide cervical cancer into 4 stages, each of which corresponds to how advanced the cancer is: Within each stage there are sub-stages, listed from a - d to describe the extent of the tumor.
Stage I: Cancer is found only in the tissue of the cervix. Stage II: Cancer has spread outside the cervix to the upper two-thirds of the vagina or to another part of the cervix. Stage III: Cancer has spread to the lower third of the vagina or to the tissue on the side of the pelvis (pelvic wall). Cancer has also spread to lymph nodes in the pelvis or abdomen, causing the kidneys to stop working. Stage IVa: Cancer has spread to the bladder or rectum (lower large intestine). Stage IVb: Cancer has spread beyond the pelvis to the lungs, liver, or bones.
4. Symptoms of cervical cancer
Cervical cancer often has no specific symptoms in its early stages. The only way to detect abnormal cells in the cervix is to do a cervical screening test.
If symptoms do occur, they usually include:

Chảy máu âm đạo ở giữa các kỳ kinh có thể là triệu chứng của ung thư cổ tử cung
Vaginal bleeding between periods, after menopause, during or after sex. Pelvic pain Pain during sex Unusual vaginal discharge A prolonged or heavier menstrual cycle.
5. Risk factors for cervical cancer
In fact, cervical cancer is not contagious. On the other hand, it is also not caused by a faulty genetic makeup, so family members are usually not at risk for the disease.
Some of the main risk factors for cervical cancer include:
Smoking and secondhand smoke: The harmful chemicals in tobacco can damage the cells of the cervix, make cancer more likely to develop in women with HPV.

Nếu sủ dụng thuốc tránh thai từ 5 năm trở lên sẽ có nguy cơ cao bị ung thư cổ tử cung
6. How to prevent cervical cancer?

Tiêm phòng HPV giúp phòng ngừa ung thư cổ tử cung
To prevent the development of cervical cancer, you can do the following:
Get vaccinated against HPV : The HPV vaccine can protect against the high-risk strains of HPV that commonly cause cancer. cervical mail. It is most effective when taken before first sexual intercourse and is generally recommended for women aged 9-26, or on the advice of a doctor if over this age. Cervical cancer screening: Women 25 years of age and older should have cervical cancer screening. Depending on age, each person may receive different types of tests, such as: Pap tests, HPV tests help detect abnormal changes in the cervix and the presence of different types of HPV high risk. The recommended frequency for cervical cancer screening is every 3 years for the Pap test and every 5 years for the HPV test. Vinmec International General Hospital now has a package for early detection of gynecological cancer, helping to detect gynecological diseases early such as: cervical cancer, uterine cancer, ovarian cancer even before they have it. symptom. This is one of the medical facilities that apply the automated system HPV genotype PCR test and transvaginal ultrasound of the uterus and ovaries. For prevention and early detection and treatment of diseases.
For detailed information, please contact the hospitals and clinics of Vinmec health system nationwide.
Reference source: iconcancercentre.sg
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
MORE
What causes cervical cancer? Types of cervical cancer 6 things to know about cervical cancer