This is an automatically translated article.
Emergency technique of circulatory arrest is a basic technique, everyone should know to save the life of patients with circulatory arrest. Because the cause of circulatory arrest is not only due to cardiovascular and respiratory diseases, ... but also can be encountered due to drowning accidents, electric shock...
1. What is circulatory arrest?
Circulatory arrest is a phenomenon in which the heart stops supplying blood to the whole body, especially important organs such as the brain, coronary circulation, lungs... There are 3 basic states of circulatory arrest that are fatal systole, ventricular fibrillation, and electromechanical dissociation.
Circulatory arrest can occur suddenly with a previously perfectly healthy heart, as in accidents caused by anaphylaxis, multiple trauma, electric shock, drowning,...
Song Circulatory arrest can also be the result of a chronic end-stage disease such as heart failure, kidney failure, cancer, cirrhosis...
Normally, cerebral blood flow will always be maintained stable in 50ml/100g brain tissue in 1 minute even though blood pressure ranges from 50-150 mmHg. The reason for this is because of the self-regulation of the cerebral vascular system, when the arterial blood pressure is low, the cerebral blood vessels will dilate to receive more blood and vice versa when the blood pressure increases, the Cerebral blood vessels constrict to reduce blood flow to the brain.
Brain cells can live when the cerebral blood flow is as low as 20ml/100gr/min, below this threshold, the brain vessels will dilate to the maximum but still not provide enough blood for the brain and the survival of the cells. Brain cells are directly dependent on the duration of cerebral ischemia. Once brain cells have been damaged, they are not able to regenerate and repair like other cells.
Under normal conditions, brain cells can tolerate hypoxia for a maximum of 5 minutes. This is the stage of clinical death and the emergency to re-supply blood and oxygen to the brain must be carried out quickly during this period to save the patient's life.
When the circulatory arrest lasts for more than 5 minutes, the brain cells will be irreversibly damaged and then the patient will enter the brain death stage.
In certain special cases, brain cells' ability to tolerate hypoxia may be longer, such as:
Under hypothermia conditions; The patient had previously used drugs that reduce brain oxygen consumption such as Barbituric; Infant...
There are different causes of circulatory arrest. Specifically:
Cardiac causes: ischemic heart disease, acute coronary occlusion, cardiomyopathies, myocarditis, acute cardiac tamponade, direct stimulation to the heart. Circulatory causes: Acute circulatory volume deficiency, which is shock; pulmonary embolism due to gas or embolism; vagus reflex mechanism. Respiratory causes: Severe pneumothorax; acute hypoxia due to foreign body obstruction of the airway; superiority. Causes of metabolic disorders: potassium metabolism disorders, acute hypercalcemia, acute elevation of catecholamines, hypothermia. Cause of drugs, poisoning: Drugs cause cardiac arrest, due to side effects of drugs. Other causes: Electric shock, drowning.
Có một số nguyên nhân khác nhau ảnh hưởng tới thời gian cấp cứu ngừng tuần hoàn
2. How to recognize circulatory arrest?
Circulatory arrest is diagnosed based on the following 3 basic symptoms:
Loss of consciousness: When the patient is called to ask questions, there is no response, no awakening reflex. Apnea or yawn: When the patient's chest and abdomen are completely absent, there is no breathing movement. Cardiac arrest: When the carotid or inguinal pulses are examined, there is no pulse. In addition, patients may also have other symptoms such as:
Pale or cyanotic skin. The pupils are dilated and the pupils are unresponsive to light. If the patient is in the process of surgery, the blood will appear purple and black in the incision and stop bleeding. If the patient is in a coma, on a ventilator, the heart monitor will alarm, the SpO2 will drop suddenly.
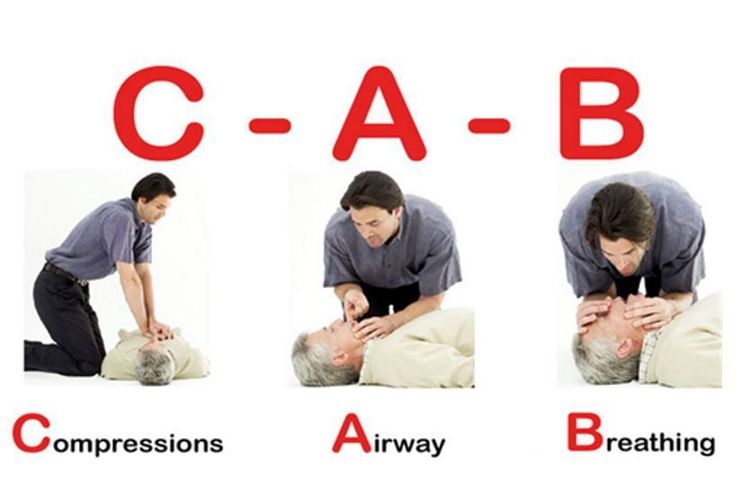
3. What is CAB in CPR?
CAB in cardiac arrest means:
A (Airway): Release the airway. B (Breathing): Give CPR or CPR. C (Chest compressions): Compression. In 2010, the American Heart Association (AHA) released new guidelines in basic CPR, in which the sequence of steps is changed from airway clearance, breathing, to chest compressions. chest compressions, airway clearance, rescue breaths. If you have enough medical equipment, you should give medicine and electric shock immediately.
3.1. Chest compressions (C) You should choose an appropriate position on one side of the patient, place one hand on the center of the lower half of the patient's sternum, then place the other hand on top, to fingers alternate and in the same direction.
Next, use the force from your hands, shoulders and torso to press down perpendicularly to the patient's ribcage so that the sternum sinks 4-5 cm. Then lift your arm and continue with a second compression, at a rate of at least 100 beats/min.
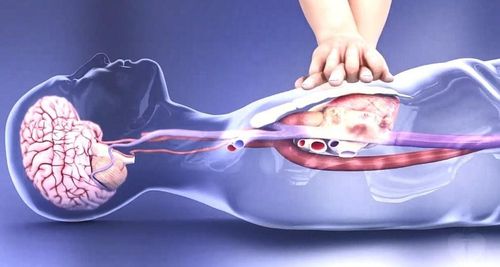
With each correct chest compression you will have to capture a pulse in the carotid or inguinal arteries. Thus, the effect of bringing blood into the circulation is achieved thanks to the direct pressure on the heart combined with the change in pressure in the thoracic cavity.
Cardiac compression will push blood from the right ventricle to the lungs for gas exchange and bring blood from the left ventricle into the coronary circulation and cerebral circulation, then the blood will return to the atrium passively when the compression stops, because The heart then relaxes and the pressure in the chest decreases.
It is necessary to combine alternating chest compressions and rescue breaths in a rhythmic, cyclical manner. This cycle consists of 30 chest compressions followed by 2 rescue breaths, regardless of whether one or more rescuers are present.
3.2. Open the airway
To open the patient's airway, you need to first place the patient on their back on a firm platform, with the head and neck in maximum extension, with their face turned to one side. This is necessary because during cardiac arrest, the muscles lose their tone, causing the mandible and base of the patient's tongue to drop low, blocking the patient's airway and obstructing CPR.
You open the patient's mouth, and then use your fingers to remove sputum and foreign objects in the mouth if possible. With foreign objects located deep in the throat and difficult to get, you should not try to remove them because it will take time and may even push the foreign object deeper or completely block the patient's airway.
In that case you should use the Heimlich maneuver to dislodge the foreign body from the airway. The Heimlich maneuver is performed as follows:
You stand behind the patient, one hand is clenched just below the patient's nose, the other hand is on top of the other. Then hug the patient up so that the fist strongly pushes the epigastrium toward the patient's chest. If the patient is larger than you, making it impossible for you to lift, place the victim on his or her back on a hard floor, sit on top of the patient, place your hands on the patient's epigastrium and push strongly towards the chest. The mechanism of the Heimlich maneuver is a sudden increase in intrathoracic pressure. It should be noted that this test should not be performed when the stomach is full because it can cause gastroesophageal reflux, and should not be repeated many times without being able to remove the foreign body because it will take time.
For young children, you can hold your feet and turn the child upside down and then use your hand to pat the area between the shoulder blades to be able to dislodge the foreign body.
Ép tim ngoài lồng ngực là một động tác trong CAB trong cấp cứu ngừng tuần hoàn
3.3. Blow the patient You can choose mouth-to-mouth or mouth-to-nose technique. Usually mouth-to-mouth blowing is more effective.
You put one hand on the forehead, then push the patient's head back, and use the index finger and thumb of that hand to pinch the patient's nose. Using the fingers of the second hand, lift the patient's lower jaw forward and open the patient's mouth. Then you take a deep breath and press your mouth to the patient's mouth and blow all the stored air through the mouth into the patient's lungs.
You can apply mouth-nose blowing if the patient is too big, you use one hand to lift the patient's lower jawbone up and forward while closing the patient's mouth, the second hand will be placed on the patient's forehead push your head back. Next, you take a deep breath and press your mouth to the patient's nose and then blow all the stored air through the nose into the patient's lungs.
Should perform breaths with a frequency of 10-12 times/minute, on average for adults, each blow should reach about 500ml - 750ml (10-15ml/kg of patient's body weight). If you do the right technique, then with each blow, you will see the patient's chest move up and down.
When you do not perform the technique correctly, you will not see the patient's ribcage expand with the breathing rhythm, and at the same time, you will see the patient's abdomen getting bigger with each blow (air goes down to the stomach) or the air expands. directly on the patient's face.
Blow is to bring oxygenated air into the patient's lungs, passive exhalation after stopping blowing helps the air in the lungs escape to bring CO2.
In the case of equipment, it is possible to endotracheal intubation for the patient or face up with a balloon squeezing masque, then you need to use the masque to fit snugly over the patient's nose and mouth, this masque is connected to the balloon. You need to squeeze the patient's balloon at a rate of about 20 beats/min. It is best to squeeze the balloon connected to an oxygen supply with a flow rate of 6 to 8 liters per minute.
4. How long is the emergency period for circulatory arrest?
The time of emergency circulatory arrest is from the time the patient is detected until the goal of blood and oxygen supply to the cerebral circulation, coronary circulation and other cellular organizations is achieved. Manifestations are the patient's lip mucosa is pink again, the pupil constricts if the brain lacks oxygen for a long time and has the ability to recover.
Even better if the patient has signs of life such as:
The patient is breathing again. The patient's heart beats again. Consciousness returns... It should be noted that if the patient has only signs of oxygenated tissues (pink lips) but no signs of cerebral circulation recovery (pupils constriction), it is still must persevere. At the same time, call an ambulance immediately or carry out emergency treatment and transport the patient to the nearest medical facility.
If you have taken the above measures correctly and fully and do not have the conditions to transport or call the hospital, then after 60 minutes, if the patient's pupils do not constrict and the heart does not beat again, it is allowed to stop. emergency treatment and identification of dead patients. In the case of a patient with circulatory arrest in special conditions, it is necessary to perform emergency care more persistently because it can still save the patient's life.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.